What Does the “Canonical Points to Redirect” Issue Mean?
The “canonical points to redirect” issue occurs when a canonical URL, meant to indicate the preferred version of a webpage, points to a URL that forwards to another page.
Canonical shows the search engine robot the priority page to be indexed and listed in the search database. The attribute itself is not a redirect.
A 301 redirect is the best solution to the perceived problems of specifying the canonical tag for a particular URL. Redirect should be used when identical URLs of the same page appear in the search engine database.
Moreover, use forwarding when you know that the problem may occur after a domain change or site migration to another platform.
What Triggers This Issue?
The issue is triggered by the following scenarios:
- URL Changes. When a preferred URL points to a link that has been changed and now redirects to a new location.
- Incorrect Canonical Tags. When canonical tags are incorrectly set to URLs that are not the final destination.
- Site Migrations. During site migrations, canonical tags may still point to old web addresses that now forward to new URLs.
- Temporary Redirects. Using temporary redirects (302 or 307) in the target URL of a canonical tag.
- Redirect Chains. When a canonical URL points to a web address that is part of a chain, leading to multiple forwardings before reaching the final page.
These scenarios can cause search engines to spend extra time following redirects, potentially leading to indexing inefficiencies and reduced SEO effectiveness.
How to Check the Issue?
To check for the “canonical points to redirect” issue, follow these steps:
1. Google Search Console
Check the coverage and enhancement reports for any canonical URL issues.
2. Manual Check
View Page Source: On each page, view the source code (right-click and select ‘View Page Source’) and locate the <link rel=”canonical”> tag.
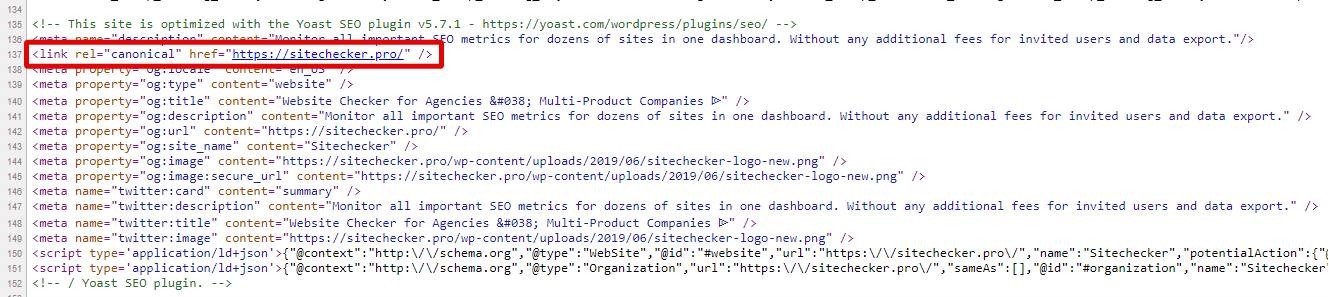
Follow the Canonical URL: Manually visit the URL specified in the canonical tag to see if it forwards to another web page.
3. HTTP Status Code Checkers
Use HTTP Status Code Checker or SEO extensions to input the canonical URL and check if it returns a 3xx status code (indicating a redirect).
4. Review Redirect Chains
Use Sitechecker Site Audit to identify if the canonical URL is part of a longer redirect chain.
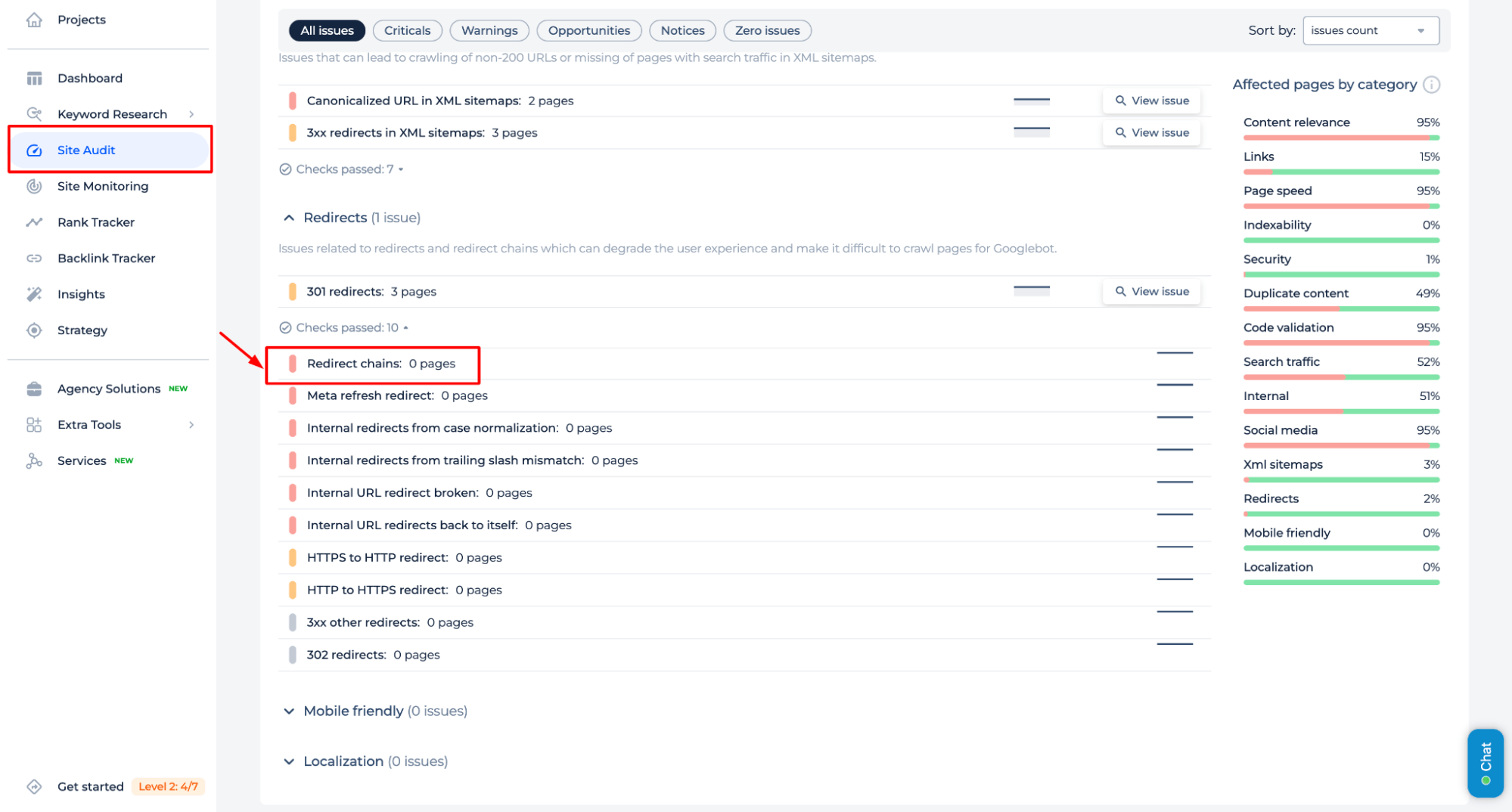
Why is This Important?
Canonical tags exist to solve the problem of duplicate content. If you need multiple pages with the same or similar content, you must choose the highest-priority, so-called canonical version.
If you have the wrong tag, search engines may ignore the instructions and choose a different URL based on other factors.
How to Fix the Issue?
To fix the “canonical points to redirect” issue, follow these steps:
1. Update Canonical Tags
Change the canonical tag to point directly to the final destination URL, avoiding any intermediate redirects.
Ensure that the canonical URL is the correct and preferred version of the page content.
2. Fix Redirect Chains
If a canonical URL is part of a redirect chain, update it to point directly to the final destination URL.
Remove any intermediate or unnecessary forwardings to streamline the path.
3. Check for Broken Links
Ensure that the updated canonical URLs lead to valid, live pages without resulting in 404 errors or further redirects.
4. Implement 301 Redirects for Permanent Changes
Ensure that any redirects involved are 301 (permanent) redirects to pass full SEO value. Make sure all internal links are updated to point directly to the new URL to avoid the need for forwardings.
5. Test and Monitor
Continuously perform site audits to catch any new issues with canonical tags and redirects. Use Google Search Console to monitor the performance of your pages and ensure the changes have a positive impact.
Example Fix Process
1. Change the canonical tag on the original page to point directly to http://example.com/new-page.
<link rel="canonical" href="http://example.com/new-page" />
2. Check Redirects
Ensure that http://example.com/old-page now directly redirects to http://example.com/new-page with a 301 status code.
3. Verify
Use an HTTP status checker to confirm there are no further redirects from the canonical URL.
By ensuring that canonical tags point directly to the preferred final URLs without intermediate redirects, you can improve search engine indexing efficiency and preserve SEO value.