What is a Duplicate Content Checker?
The Website Duplicate Checker by Sitechecker is a free tool that identifies duplicate content on websites. It crawls your site, finds duplicate issues in titles, headings, and descriptions, and provides a detailed audit report. With it, you can categorize duplicate issues and get solutions, like using canonical URLs to address these problems.
How the tool can help you?
- Find duplicate content: The tool effectively scans web pages to identify any cloned data (for instance, repeated titles, headings, and meta descriptions). It is crucial for maintaining the uniqueness and quality of the website’s data.
- Monitor Content Issues on Website: Beyond identical data, it also detects a range of other content issues like missing alt attributes or poor text-to-HTML ratios, aiding in overall data optimization and quality enhancement.
- Assess General SEO Parameters: The tool comprehensively assesses key SEO parameters, such as site speed, mobile responsiveness, and meta tag accuracy. You’ll get a holistic view of the website’s SEO health and actionable insights for improvement.
General features of the Internal Duplicate Content Checker
- Unified Dashboard: The tool provides a centralized dashboard that aggregates all findings and reports, making it easier for users to access and interpret data across their website.
- User-friendly Interface: Designed with usability in mind, the tool offers an intuitive interface, simplifying the process of scanning and making it accessible even to those with limited technical SEO knowledge.
- Complete SEO Toolset: Beyond just identifying identical data, the tool is part of a broader SEO toolkit offered by Sitechecker, which includes various features for optimizing website performance in search engines, encompassing a wide range of SEO aspects.
How to Use SEO Duplicate Content Finder?
Google and other search engines consider unique data to be the main ranking factor. Using a Page Duplicate Content Checker to identify internal duplicates for a whole website is easy.
Step 1: Insert Your URL
Just add your domain and click the button.
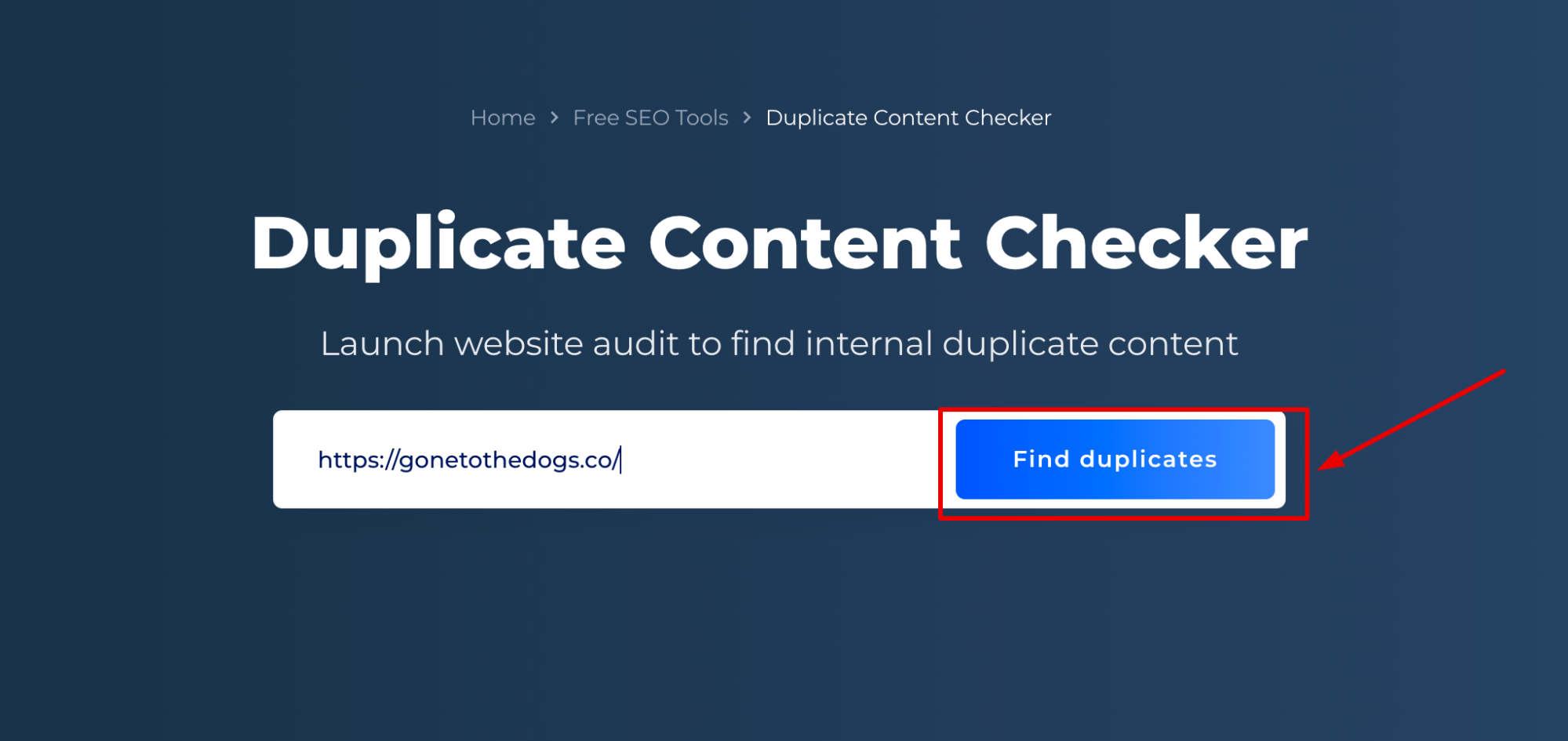
Step 2: Get the Result
We’ll crawl your site and find duplicate content issues: duplicate pages without canonical, title, h1, and description duplicates. All those kinds of problems you will see in the “Duplicate content” category in the on-site audit results.
A dedicated section highlights issues related to identical data, listing specific problems like title duplicates, identical headings, and tags across a number of pages.
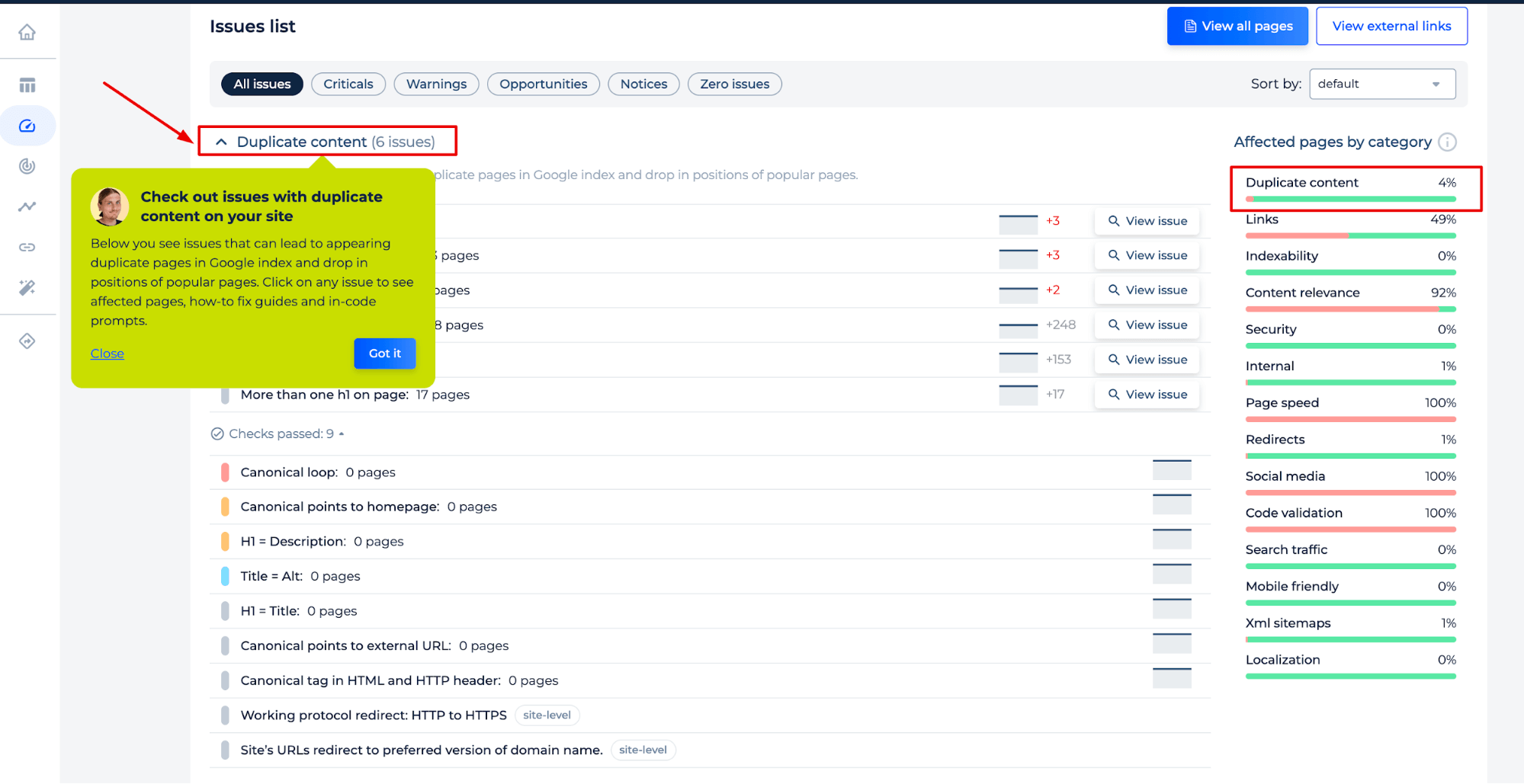
Users can conveniently view details of each issue, indicating an interactive and user-friendly interface. This is part of a complete SEO toolkit designed to diagnose and guide improvements for website optimization.
The Duplicate Content Tester provides a dynamic interface for identifying and resolving SEO issues. It highlights critical areas such as identical headings across a website’s pages and offers actionable solutions. With features like ‘View issue in code,’ the tool directly navigates users to the elements in question within their website’s code.
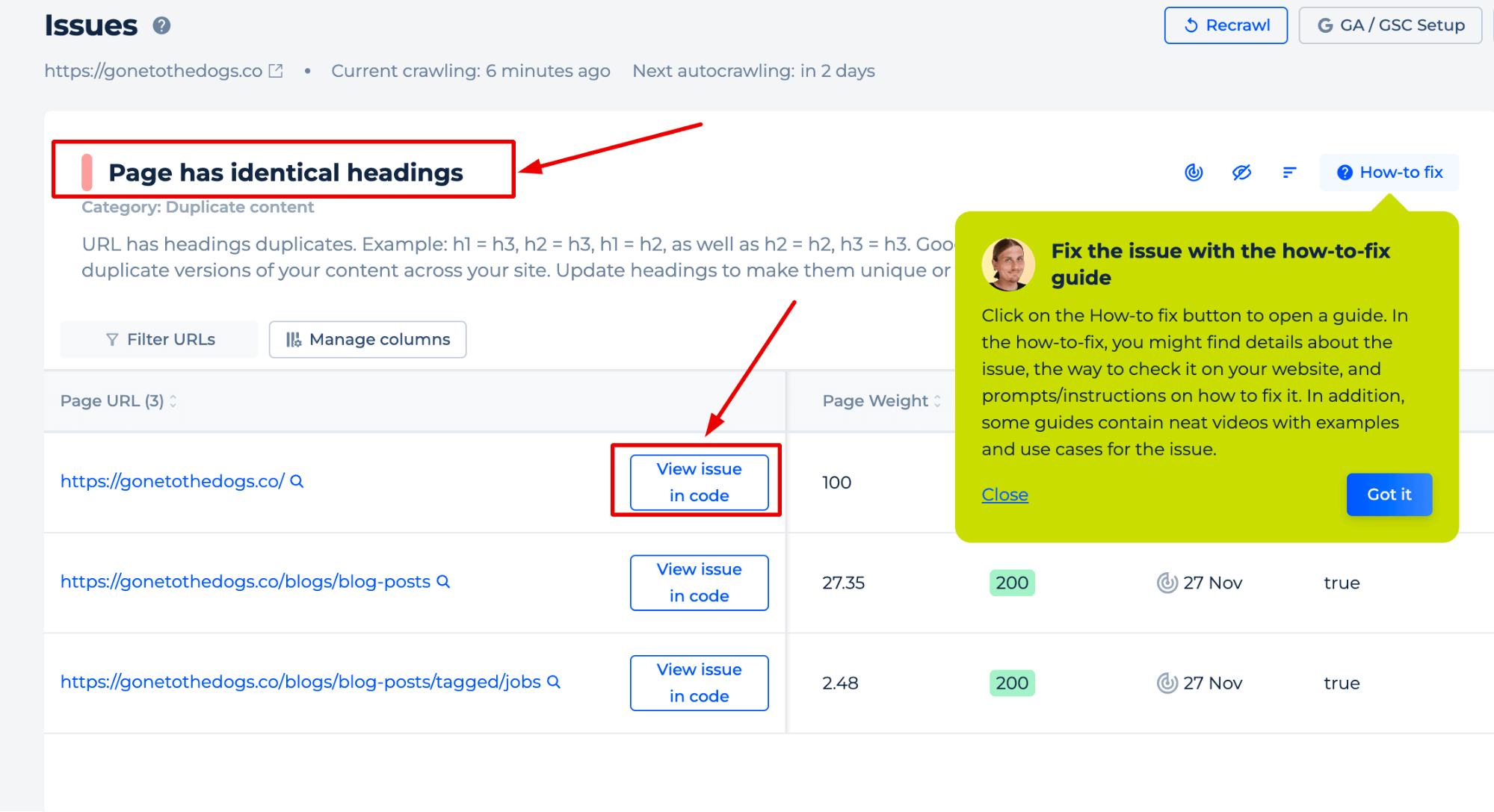
Additionally, the ‘How-to-fix guide’ offers a comprehensive resource, including detailed instructions and visual aids. It assists users in rectifying the identified problems with the content existing on your web page, enhancing the overall SEO health of the site.
Additional Features of Duplicate Content Identifier
Upon revisiting the Site Audit tab, you will gain an overall view of your site’s health indicators and pinpoint any technical issues present on any web page.
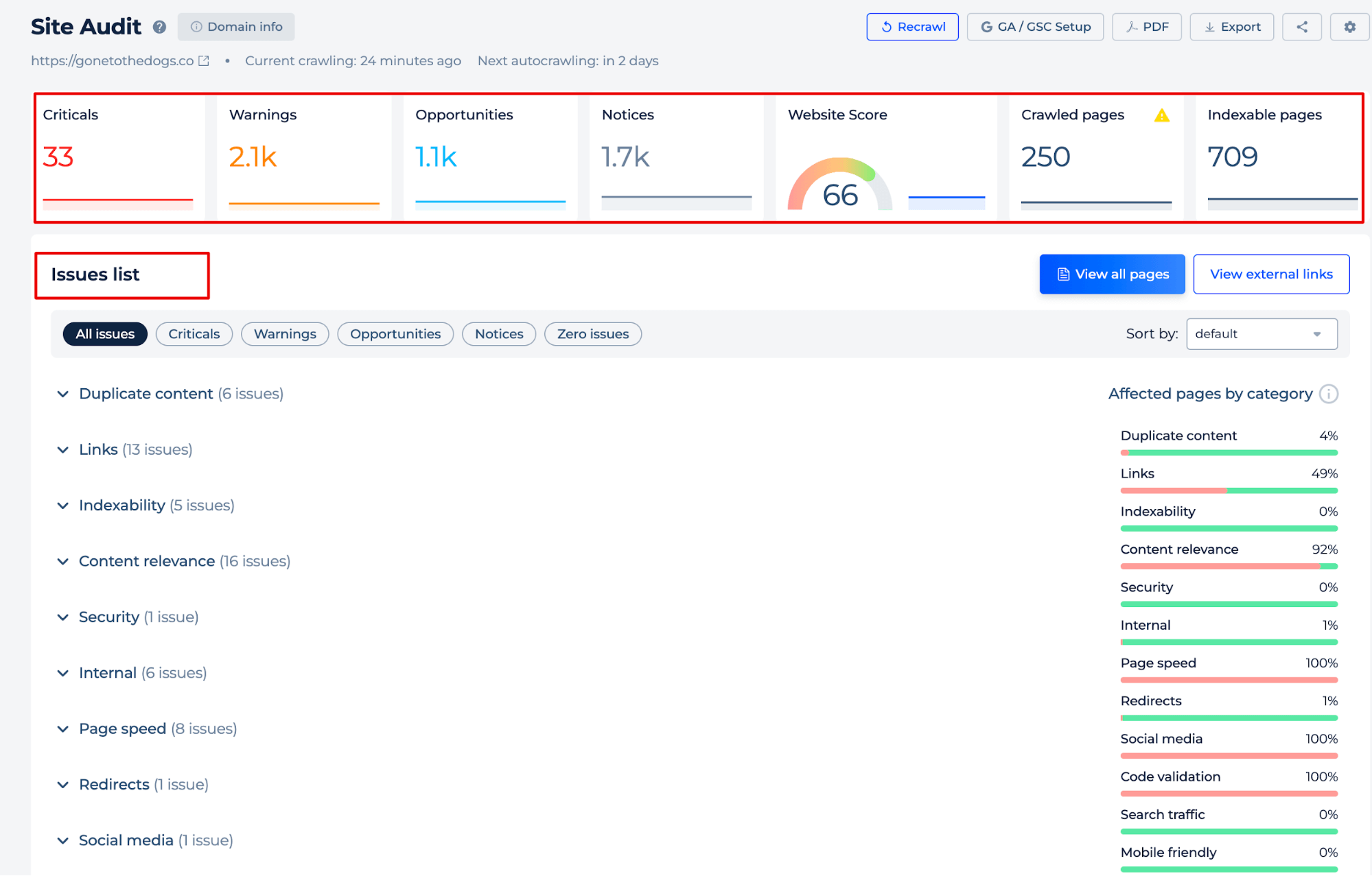
The Duplicate Content Tool offers a comprehensive SEO evaluation, pinpointing issues beyond duplication to include data relevance. It intelligently detects a range of potential improvements, from missing alt attributes to suboptimal heading structures, each quantified and actionable through the interface.
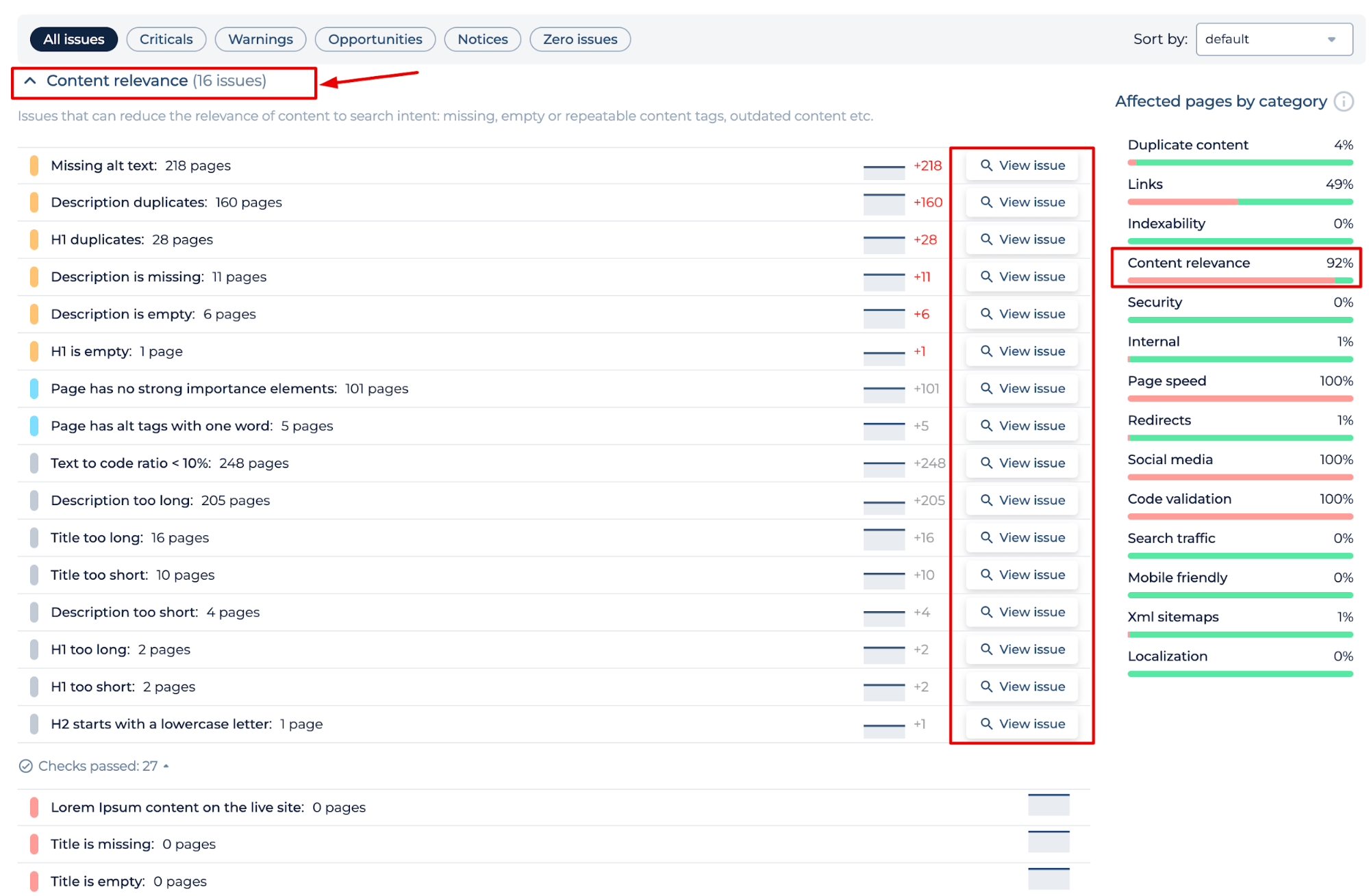
Google Duplicate Content Detector underscores the significance of fine-tuning all aspects of content to align with search intent, directly contributing to the site’s SEO performance.
Conclusion
The Website Content Checker is a comprehensive SEO tool that offers a user-friendly interface and a unified dashboard for webmasters to easily identify and rectify cloned data on their websites. It scans for duplicates in titles, headings, and descriptions and suggests SEO improvements, such as implementing canonical URLs. This free tool, part of Sitechecker’s broader SEO toolkit, also provides detailed audit reports with accurate results, which helps with general SEO parameters. Besides, unlike many other tools, it includes a ‘How-to-fix guide’ for resolving issues. The tool enhances website performance and SEO health by ensuring data uniqueness, a critical factor in search engine rankings.