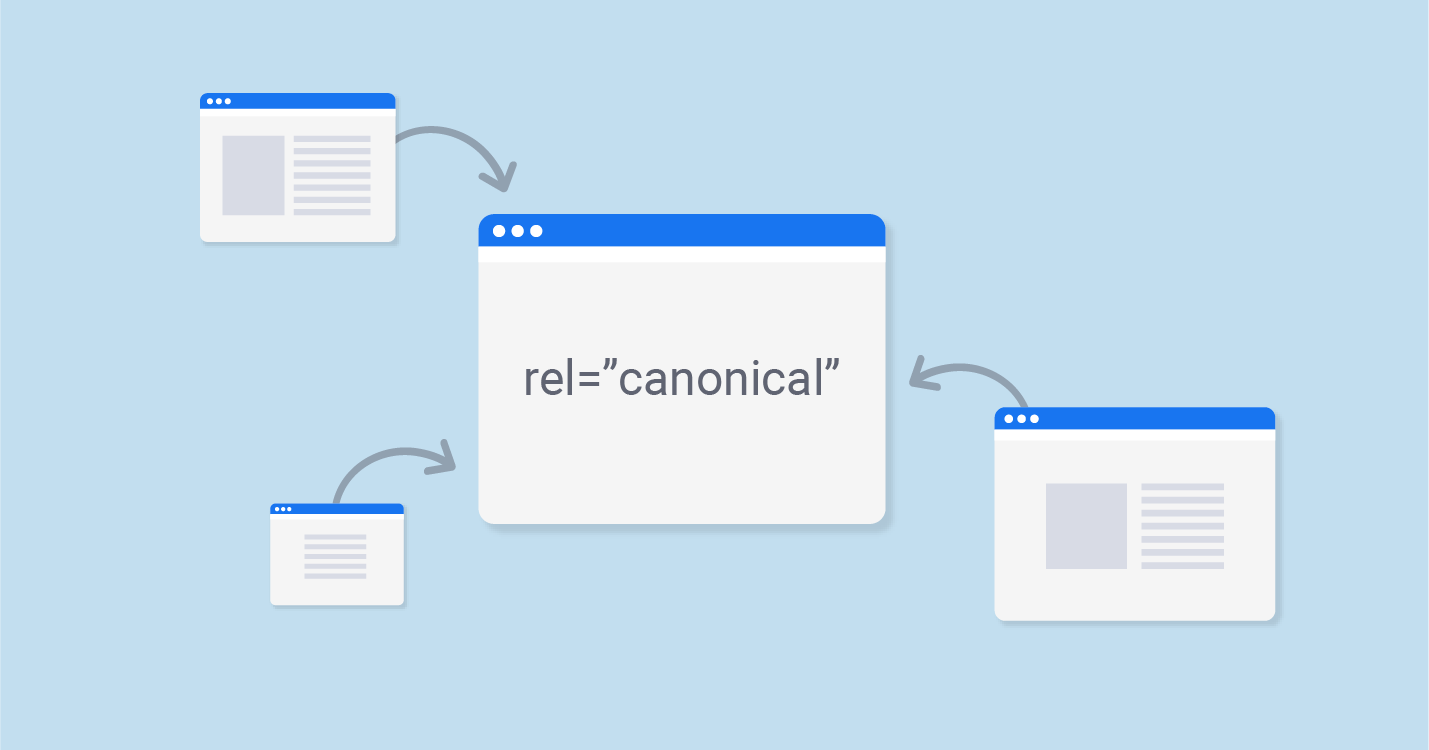
What is a Canonical Tag
At the moment, eliminating the problem of duplicate content for SEO is one of the most important when optimizing the site. In most cases, to solve this problem, it is best to use 301 redirect. But, when we either can not use 301 redirects, or we need pages for viewing by users, then the rel=”canonical” attribute comes to our rescue. But what is canonicalization, where and why it has to be used? The answers to all these questions you will find in this article.
First of all, canonicalization is the process that determines (from several duplicate pages under different links within one resource) the main URL address for subsequent indexing by a search engine. There is one more definition exists, it connects to IP canonicalization. It occurs automatically (according to the specified algorithms), however, to avoid errors, it is necessary to use canonical meta tag in conjunction with 301 redirections to the correct hyperlinks. With this attribute, you can quickly resolve duplicate content problems.
How to Implement rel=”canonical”
1. On the site page (main way)
To specify the canonical link for the current page, in the section, you need to state the following. It is very important to implement in the HEAD section. Since if you accidentally implement this attribute not in this section, this instruction will be ignored by the search engines.
<link rel="canonical" href="http://site.com/canonical-link.html"/>The other way around will be to automate the application of the canonical tags. If you use Adobe eCommerce you can explore the benefits of the Magento 2 SEO Suite Ultimate extension that applies canonical tags to all of your website pages automatically.
2. Via xml-site map
For each page in the xml-sitemap of the site you can implement its canonical link. But, sometimes, search engines can ignore these recommendations.
3. Through the server’s response
This is the best variant for non-html documents. If you need to specify canonical links for non-html documents, for example, for pdf-files, then you can specify a canonical link in the http-header. For this, the server, when requesting a duplicate file, must give the following.
Link: <http://site.com/main-file.pdf>; rel="canonical".But, keep in mind that at the moment Google supports this element of the header only for web search.
When to Use Canonical URLs
1. If you know exactly in which case you have duplicates on your site
If you clearly understand the reason for the appearance of similar or very similar pages on your website and, at the same time, each such page should exist on the site, it is desirable to determine which of these pages of the series is the main one and from all other pages put the canonical links to this one main.
2. When it is difficult or impossible to implement 301 redirects
In general, it is best to use 301 redirects, but if it is quite difficult or long to implement, then you can use the attribute rel=”canonical”. According to Google, link juice through canonical tags absolutely identical to the link juice, which 301 redirects transfer.
3. Multiple pages for one product series
If you have a series of products in the online store, which differs, for example, only in color, then it is better to choose one product as the main (typical) and put on it canonical links from other products.
4. For different sorts of goods in the catalog
If on your website the goods can be sorted in different ways and the sort parameter is specified in the URL:
http://site.com/dresses.html?sort=pricethen, it is necessary, from all different combinations of sortings, to put the canonical links to the catalog with the default sorting. Usually, this is a URL category without parameters, which are responsible for sorting the goods:
<link rel="canonical" href="http://site.com/dresses.html" />5. When creating a catalog page with all products
According to Google’s recommendations, the way in which you make a canonical link from all pages of the catalog to a page with all products / articles is optimal for indexing as site directory pages, and all products / articles on the site. With this method, for each section of the site you need to create a page “View all” and from each page of the pagination put a canonical url to the page “View all”.
6. Print page
If the printing of pages on the site is realized through an additional parameter, for example,
http://site.com/news-1.html?print=yesthen, it is necessary, put the canonical link to the main version of the page
<link rel="canonical" href="http://site.com/news-1.html" />7. When using the affiliate program on your website
If on your site there is an affiliate system or any other referral system, then it is very important to remember to prescribe the canonical urls for all the pages that can be affiliate links.
If you forget to post, then very quickly may appear in the index of search pages dozens, or even hundreds of duplicate pages of the site, because by external links, the Google search robots quickly index the necessary pages.
Therefore, for all pages on which are affiliate links
http://site.com/dresses.html?partner=dkfEi3dj1prescribe the following instruction:
<link rel="canonical" href="http://site.com/dresses.html" />In addition, you can tell Google all the parameters you do not need to be indexed via URL parameters. In this case, you must specify the partner parameter, such that it does not change the contents of the page.
Old version of Google Search Console > Crawl > URL Parameters
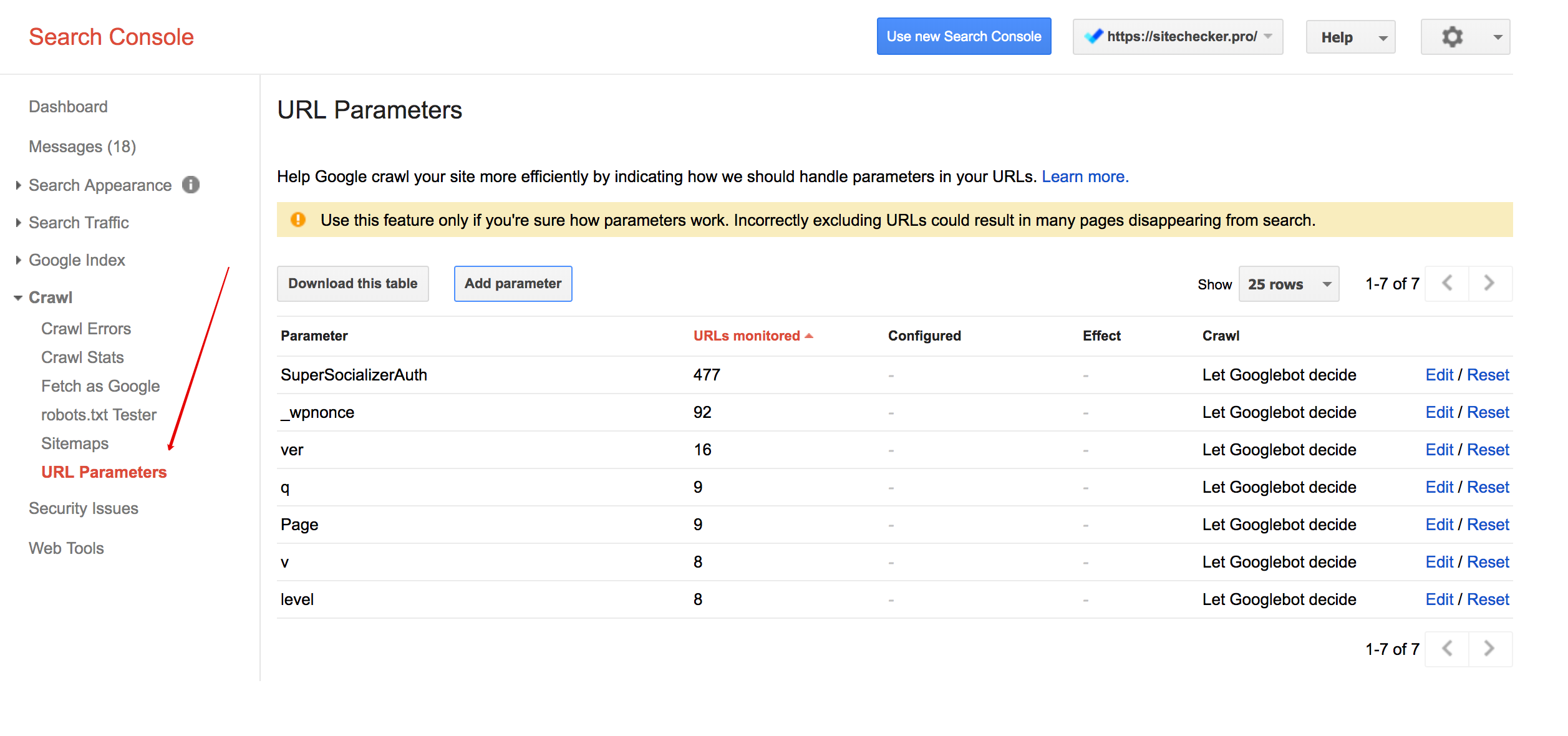
8. To glue the directory index file
It is important to check that the files in the directory type index.html do not lead to duplicates: this can happen when two such addresses are available for indexing http://site.com/dresses/ and http://site.com/dresses/index. html. In such cases, to solve this problem, it is easiest to implement such a canonical url in the http://site.com/dresses/index.html file
<link rel="canonical" href="http://site.com/dresses/" />9. When using the same content on different domains or different language versions
When you create similar sites or make different language versions of your content, but at the same time use the same content on different sites / language versions, then you need to use rel=”canonical” on the main version of the content.
Main Mistakes When Using rel=”canonical”
1. Using on pages of pagination
Very often, with pagination or with some series of pages on the site for all pages of this series, the canonical first page is prescribed. This is incorrect, because it makes it impossible to index all the pages of the series.
2. Сanonical URL is non-indexable
If we put a canonical link to another page, we must make sure that this page is indexable:
- page gives 200 server code;
- on the page there is no prohibition of indexing (through the meta tag of robots and noindex).
It is the mistake that has to be fixed when canonicalized URL is noindex, nofollow.
3. Several rel=”canonical” links from one page
For one page there should be one canonical page. If several pages are specified, then only the first instruction will be taken into account.
It is necessary to fix the problem when pages are with multiple canonical URLs.
4. Different canonical URLs
Be sure to always specify the same canonical pages for different implementations (for example, through the xml-sitemap of the site and through rel=”canonical” on the page itself).
5. Incorrect using of relative links
In the general case, when specifying the canonical URLs, it is always desirable to prescribe absolute links. Fix the issue when canonical is a relative URL.
<link rel="canonical" href="http://site.com/dresses.html" />Since when you specify relative links, there is a very high probability of making an error.
<link rel="canonical" href="site.com/dresses.html" />Then the search engines will simply ignore these instructions.
Check for Canonical URLs on a Specific Page with Canonical Tag Checker
The Canonical Tag Checker by SiteChecker is vital for SEO specialists and webmasters to verify the correct implementation of canonical tags, which are crucial in avoiding duplicate content and maintaining search engine rankings. This tool checks if a webpage’s canonical tag is properly set, ensuring search engines recognize the specified URL as the master copy, especially beneficial for large websites with similar pages.
Tool not only verifies canonical tags but also ensures they point to the correct URLs, preventing misdirection that could confuse search engines. It checks for errors like tags pointing to redirected or non-existent pages. This tool is essential for maintaining a website’s SEO health, ensuring proper indexing and ranking of content by search engines.
Check Your Canonical Tags Now!
Confirm the correctness of your canonical tags with our user-friendly tool.
Conclusion
Canonical tags are essential in SEO for resolving duplicate content issues by identifying the primary URL for search engines among similar pages. They’re crucial when 301 redirects aren’t suitable or when pages must remain user-accessible. These tags guide search engines to index the correct page, thereby safeguarding a site’s SEO standing.
SiteChecker’s Canonical Tag Checker tool ensures the correct implementation of these tags. It verifies whether a page’s canonical tag accurately directs search engines to the intended URL and identifies any implementation errors, such as incorrect URLs. This functionality is vital for large websites, helping to maintain SEO health and prevent content duplication penalties.