What is a 301 Status Code?
A 301 redirect is an HTTP status code indicating that a specific URL has permanently moved to another address, and it automatically redirects visitors and search engines from the old URL to the new one.
A 301 status code is among various HTTP responses, including the familiar 404 (Not Found), 403 (Forbidden), and 500 (Server Error).
Typically, when you access a webpage that loads successfully, it carries the 200 – OK status. Consider the 301 status code as a change of address for content. If content moves from its original URL, visiting that URL would usually lead to a 404 error message. But, to enhance user experience, you can configure the server to reroute visitors from the outdated URL to its new location using a 301 code. This process is nearly instantaneous, so users typically won’t notice the switch.
They might, however, observe a change in the URL or be informed by browser tools like Ayima Redirect Path.
A 301 status code serves as a vital tool in various digital scenarios, signaling a permanent shift from one URL to another for both users and search engines. One common use is during website relocation or rebranding, ensuring that visitors to an old domain are seamlessly routed to the new one.
Typical use cases for a 300 response
If a website undergoes structural modifications, such as transitioning from HTTP to HTTPS, reorganizing its content, or even changing file extensions, the 301 code comes to the rescue and prevents disruptions.
They’re also indispensable when merging websites, archiving outdated pages, or addressing duplicate content, ensuring the preservation of search engine rankings and link equity. Regardless of the specific scenario, the overarching aim is to provide a frictionless user experience while safeguarding a site’s SEO value.
For search engines, a 301 response serves a vital function. It signals search platforms like Google and Bing that a specific content piece has shifted. In essence, it tells search engines, “The popular content you indexed from search results? It’s relocated here.
Please transfer its online prominence to this fresh URL.” This function underscores the significance of 301 responses in SEO.
Let’s now explore how a 301 status code impacts SEO.
How Does 301 Redirect Impact SEO
A 301 response, indicating that a URL has permanently moved to a new location, plays a significant role in SEO for various reasons:
| Link Equity Transfer | One of the most important aspects of a 301 status code in SEO is the transfer of link equity, also known as “link juice“. When you move content from one URL to another, the 301 status helps pass on a majority of the ranking power of the original URL to the new URL. Generally, it’s believed that a well-implemented 301 redirect can transfer up to 90-99% of the original page’s link equity. |
| User Experience | Broken links or pages that return 404 errors can result in a poor user experience. By using 301, you ensure that users find the content they’re looking for, thus improving user satisfaction. Better user experience can indirectly influence SEO, as satisfied users are more likely to share, link to, or engage with the content. |
| Avoiding Duplicate Content | Sometimes, websites might have content accessible via multiple URLs. This can confuse search engines and potentially lead to duplicate content issues. A 301 status code can be used to consolidate these URLs, directing all traffic and link equity to one primary version and signaling to search engines which version of the content should be indexed. |
| Maintaining Organic Traffic | If you’re rebranding, redesigning, or restructuring your website, a 301 redirect strategy ensures that you don’t lose your existing organic traffic. Users clicking on old URLs from search results or external sites will be seamlessly redirected to the relevant new page. |
| Search Engine Indexing | Search engines will update their index based on the 301 status codes. When a search engine encounters a 301, it understands that the old URL is obsolete and should be replaced with the new one in its index. This ensures that search results show the most current and relevant URL to users. |
| Domain Migrations | If you’re changing your domain name, 301 responses are necessary to maintain the SEO value of the old domain. They help in transferring the authority and trust of the old domain to the new one. |
| HTTPS Migration | Moving from HTTP to HTTPS (a more secure version) can be beneficial for SEO. A 301 code ensures that users and search engines are directed to the secure version of your site. |
However, while 301 status codes are beneficial, they should be used judiciously:
- Avoid redirect chains (i.e., when one redirected URL leads to another URL, which then links to another, and so on).
- Ensure that redirects are set up to the most relevant page.
- Periodically audit redirect rules to make sure they are still necessary and accurate.
In total, the 301s are essential tools in an SEO’s arsenal, aiding in the preservation of link equity, enhancing user experience, and maintaining website authority during changes or migrations.
Google About 301 Redirect
Over the years, Google representatives have shed light on the role and impact of the 301 status code on search rankings. Matt Cutts, the former head of Google’s Webspam team, mentioned in 2012 that while Google could follow a sequence of redirects, it might stop after four to five consecutive ones.
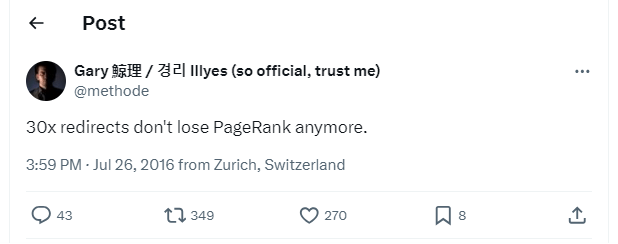
By 2013, he acknowledged a minor loss in PageRank with 301, though without pinpointing a specific percentage. Contrasting this, Gary Illyes tweeted in 2016 that “30x redirects don’t lose PageRank anymore.”
John Mueller, in 2018, emphasized that consolidating 100 domains into a single one might not bolster SEO, but using distinct domains for promotional purposes, even if they lead to a primary domain, can be effective.
In 2020, Mueller elaborated on the significance of updating internal links, sitemaps, and other references when leveraging the 301 status code. He highlighted that Google typically navigates up to five chained redirects.
For additional insights, watch the complete video provided below:
By mid-2021, he suggested that even without a redirect, Google might give preference to a new URL based on different signals, like internal links. That same year, Illyes advised keeping the 301 active for at least a year to guarantee a smooth transition of ranking signals:
Google’s official Advanced SEO guide consistently advocates for server-side redirects, particularly when updating a URL’s appearance in search results.
Redirect Loops
A redirect loop happens when URL A leads to URL B, which then links back to URL A, creating an infinite loop that browsers cannot resolve, resulting in an error message.
Multiple Hops
When one redirected URL points to another redirected URL, causing multiple “hops” before reaching the final destination, it can slow down the page load time and may not be followed entirely by search engines.
Inconsistent Redirects
Sometimes, redirects are set up inconsistently across a website, leading to confusion both for users and search engines. For instance, some pages might be redirected to the HTTPS version while others remain on HTTP.
Non-Canonical Redirects
If a 301 response points to a URL that’s not the canonical version, it can create confusion for search engines about which version of the page should be indexed.
Expired Redirects
Sometimes, temporary redirects (like 302) are used instead of 301, or old 301 remains even after they are no longer relevant. These can confuse search engines and lead to indexing issues.
URL Redirect Checker Tool for Identifying HTTP 301 Status Codes
The URL Redirect CheckerTool analyzes URL redirections, including HTTP 301 status codes, to maintain website health and user experience. It helps webmasters verify correct and permanent redirection of URLs, ensuring seamless navigation for users and search engines, thus preserving site integrity and SEO value. Additionally, it detects redirect chains, loops, or inconsistencies, aiding in troubleshooting issues that could impact site performance or search rankings.
Conclusion
A 301 status code is a permanent digital change of address for online content, ensuring a seamless user experience and accurate search engine indexing. It’s essential for managing transitions like moving from HTTP to HTTPS or during domain migrations, safeguarding a site’s SEO value. Google has emphasized the importance of 301 responses in various contexts. However, it’s vital to avoid issues like redirect chains or loops.
Tools like the URL Redirect CheckerTool can help monitor and optimize redirects for the best website performance.