What are Meta Tags?
Meta tags are snippets of text that describe a page’s content, but they don’t appear on the page itself; instead, they exist in the page’s source code. These tags are read by search engines and help them understand what the content of the page is about. Essentially, meta tags provide information about the data on your website, hence the name “meta” which means “information about.”
Key Characteristics of Meta Tags:
- Invisible to Visitors: While meta tags play a crucial role behind the scenes, they’re not visible on the website itself when a user browses through it. They work in the background, providing vital information to search engines and browsers.
- Located in the <head> Section: Meta tags are typically placed in the <head> section of an HTML document. This section contains information about the page’s title, character set, styles, scripts, and other meta data.
- Variety of Functions: Not all meta tags are about SEO. Some meta tags are used to control the behavior of web browsers. For instance, the “viewport” meta tag helps control how a page scales on different devices, while the “charset” meta tag defines the character set used on the page.
Why are Meta Tags Important? Meta tags are essential for several reasons:
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): They give search engines information about your page, which can affect how it’s indexed and ranked.
- User Experience: Meta tags, like the meta description, can influence click-through rates from search engine results pages (SERPs). A compelling meta description might entice users to click on your link over a competitor’s.
- Social Media Sharing: Some meta tags determine how information from your site is displayed on social platforms. For instance, Open Graph tags, used by Facebook, allow you to specify the title, image, and description that you want to be shown when your content is shared.
What are Meta Tags and Why Are They Important?
Meta tags are small pieces of code embedded in the HTML of a webpage. They provide metadata about the content of the page, which means they offer information about other data. While they’re not directly visible to website visitors, they play a pivotal role in how a page interacts with search engines and browsers.
Understanding Meta Tags:
- In the Code, Not on the Page: If you’ve ever right-clicked on a webpage and selected “View Page Source,” you’ve seen the raw HTML of that page. Within that code, particularly in the <head> section, you’ll find various meta tags providing information about the page.
- Diverse in Purpose: Meta tags aren’t solely about search engine optimization. Some, like the “viewport” tag, influence how a page appears on different devices. Others, like the “charset” tag, determine text encoding, ensuring characters display correctly across various platforms.
The Significance of Meta Tags:
- SEO and Search Engine Visibility: Search engines use meta tags as one of the many factors to determine what a page is about. While they’re not the sole determinant of search rankings, they can influence how search engines index and present a page in search results.
- Enhancing User Engagement: Some meta tags, especially the meta description, appear in search engine results. A well-crafted description can motivate users to click on your page when it appears in search results.
- Control Over Content Presentation: Meta tags can influence how content from your website is displayed on other platforms, especially social media. For instance, with the right meta tags, you can dictate the image, title, and description displayed when someone shares your content on platforms like Facebook or Twitter.
In Summary: Meta tags serve as a bridge between your website’s content and the external platforms interacting with it, be it search engines, browsers, or social media platforms. Using them effectively ensures that your content is understood, displayed correctly, and optimized for both search engines and users.
Google About Meta Tags
John Mueller, a Google Search Advocate, has spoken about meta tags on Twitter on several occasions. Here is a summary of his key points:
Meta tags are still important for SEO. Mueller has said that meta tags are one of the many ranking factors that Google uses to rank websites in search results.
However, meta tags are not as important as they used to be. In the past, Google relied heavily on meta tags to understand the content of a website. However, Google’s algorithms have become more sophisticated over time, and now Google can understand the content of a website without relying as much on meta tags.
It is important to use meta tags accurately and honestly. Google will penalize websites that use meta tags to mislead users or to try to manipulate search results.
Here are some specific examples of what Mueller has said about meta tags on Twitter:
Overall, Mueller’s advice on meta tags is to use them accurately and honestly, and to include relevant keywords but not to keyword-stuff.
Here is a short video about importance of the meta tags:
Meta Title
The meta title, often simply referred to as the title tag, is a fundamental meta tag that specifies the title of a particular web page. This title is displayed on search engine results pages (SERPs) as the clickable headline for a given search result and is crucial for both SEO and social sharing.
Why it’s important for SEO
The meta title is one of the first things a search engine looks at to determine the subject of a page. Its significance for SEO includes:
- Relevance: Search engines use the title tag to assess the relevance of a page to a search query. A well-matched title can help the page rank higher for specific keywords.
- User Experience: When users see relevant titles in search results, they’re more likely to click on them. This can lead to higher click-through rates (CTR), which search engines can interpret as a sign of a quality page.
- First Impressions: The title tag is often the first piece of information a potential visitor encounters. An accurate and compelling title can make a strong first impression.
Optimizing Your Title Tags for SEO
Optimization of title tags is essential for improved search visibility and user experience:
- Keyword Placement: Place important keywords closer to the beginning of the title. This ensures they’re seen by users and given more weight by search engines.
- Be Concise: Aim for titles that are 50-60 characters long. Longer titles might be truncated in SERPs.
- Unique Titles: Every page on your website should have a unique title. This helps search engines understand that the content on each page is distinct.
- Branding: Consider including your brand or site name at the end of the title, separated by a dash or pipe, especially if your brand has strong recognition.
How to add a title tag to your page
To add a title tag to your page:
- Access the HTML: Open the HTML of the page you wish to edit.
- Locate the <head> section: Within this section, look for the <title> tag. If it doesn’t exist, you’ll need to add it.
- Insert the Title: Between the opening <title> and closing </title> tags, type the desired title for the page.
- Save and Test: Save your changes and view the page in a browser to ensure the title displays correctly.
How to find and fix common title tag mistakes
Regular audits can help you catch and rectify title tag errors:
- Duplicate Titles: Use SEO tools like Screaming Frog or SEMrush to identify pages with duplicate title tags. Ensure each page has a unique title that accurately reflects its content.
- Too Long or Too Short: Titles that are too long may be truncated in SERPs, while very short titles may not provide enough context. Aim for the 50-60 character range.
- Irrelevant Titles: Ensure that your title accurately reflects the content of the page. Misleading titles can harm user experience and bounce rates.
- Missing Keywords: If a page is targeting specific keywords, ensure they’re present in the title in a natural and readable manner.
Meta Description
The meta description is a brief summary of a webpage’s content, typically ranging from 50 to 160 characters. While it doesn’t directly influence rankings, it plays a crucial role in user experience, particularly in how your page is perceived in search results.
Why it’s important for SEO
The significance of the meta description for SEO encompasses:
- User Engagement: A compelling meta description can entice users to click on your link when it appears in search results, leading to higher click-through rates (CTR). A higher CTR can be an indirect signal to search engines of the page’s relevance and quality.
- Relevance Preview: It provides users with a brief preview of what they can expect on the page, helping them decide if the content is relevant to their search query.
- Keyword Highlighting: If a user’s search query matches part of the meta description, search engines often highlight the matched words in the SERPs, making the link more eye-catching.
Optimizing Your Meta Descriptions for SEO
Effective meta description optimization can enhance visibility and user engagement:
- Be Concise: Aim for a description that’s between 50-160 characters. This ensures that the entire description is visible in most search engines without truncation.
- Incorporate Keywords: While meta descriptions aren’t directly used for rankings, including targeted keywords can make the description more relevant to users.
- Write for Users: Ensure the description is compelling and offers value. It should provide a brief overview and entice users to click through.
- Unique Descriptions: Every page should have a distinct meta description that accurately summarizes its content.
How to add a meta description to your page
To integrate a meta description to your webpage:
- Access the HTML: Navigate to the HTML of the page you’re modifying.
- Search for the <head> section: Within this segment, look for the <meta name=”description”> tag. If absent, you’ll have to add it.
- Insert the Description: In the content attribute, like this: <meta name=”description” content=”Your meta description here.”>, type in your desired meta description.
- Save and Review: After saving your changes, preview the page in a browser or use SEO tools to ensure the meta description is set correctly.
How to find and fix common meta description mistakes
Periodic checks can help you identify and correct meta description errors:
- Duplicate Descriptions: Tools like Moz or Ahrefs can help spot pages with identical meta descriptions. Each page should have its unique descriptor.
- Length Issues: Descriptions that surpass the recommended character count might be cut off in SERPs, while extremely short ones might not provide sufficient information.
- Irrelevant Descriptions: Ensure every meta description offers an accurate summary of its page. Inaccurate descriptions can lead to poor user experience and increased bounce rates.
- Omission of Keywords: While not a ranking factor, incorporating relevant keywords can enhance the meta description’s relevance to potential visitors.
Meta Robots
The meta robots tag provides search engines with directives about how to index and display a webpage in search results. It’s a powerful tool that can control which pages of your website are accessible to search engines and how they should treat them.
Syntax
The meta robots tag is placed in the <head> section of a webpage’s HTML and follows this basic structure:
<meta name="robots" content="directive1,directive2">Common directives include:
- noindex: Tells search engines not to index the page, meaning it won’t appear in search results.
- nofollow: Instructs search engines not to follow the links on the page.
- noarchive: Prevents search engines from storing a cached version of the page.
- nosnippet: Stops search engines from showing a snippet of the page (like a description or preview) in the search results.
Why it’s important for SEO
The meta robots tag plays a pivotal role in SEO for several reasons:
- Control Over Indexing: You can prevent specific pages, like internal or private ones, from being indexed and displayed in search results.
- Link Crawling: Direct the behavior of search engine crawlers regarding which links on a page should be followed.
- Avoiding Duplicate Content: By directing search engines not to index certain pages, you can avoid potential penalties associated with duplicate content.
Best practices for Meta Robots Optimization
To harness the full potential of the meta robots tag, consider these best practices:
- Use With Caution: A misplaced directive can result in essential pages not being indexed. Always double-check before implementing.
- Specify Default Behavior: If you want most of your pages indexed and followed, specify this default behavior in a site-wide header or robots.txt file.
- Combine Directives: You can use multiple directives in a single tag, separating each with a comma.
- Remember Other Search Engines: While Google is dominant, remember that other search engines might interpret or handle directives slightly differently.
How to add a meta robots tag to your page
To integrate a meta robots tag:
- Access the HTML: Open the HTML of the desired page.
- Locate the <head> Section: Within this section, you can insert the meta robots tag.
- Insert the Tag: Depending on your directive, it might look something like this: <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex,nofollow”>.
- Save and Verify: After saving your edits, use tools like Google’s Search Console to ensure that the tag is recognized and followed by search engines.
How to diagnose and fix common meta robots mistakes
Regular audits can help spot and rectify meta robots tag issues:
- Unintended Blocking: Check to ensure crucial pages aren’t accidentally set to “noindex” or “nofollow”.
- Conflicting Directives: Ensure that directives in the meta robots tag don’t conflict with those in the robots.txt file.
- Misplaced Tags: The meta robots tag should always be in the <head> section of the HTML. Ensure it hasn’t been mistakenly placed elsewhere.
- Overuse: While it’s powerful, don’t over-rely on the meta robots tag. Not every page needs it, and default behavior can often be set site-wide.
Common directives include:
- noindex: Tells search engines not to index the page, meaning it won’t appear in search results.
- nofollow: Instructs search engines not to follow the links on the page.
- noarchive: Prevents search engines from storing a cached version of the page.
- nosnippet: Stops search engines from showing a snippet of the page (like a description or preview) in the search results.
Why it’s important for SEO
The meta robots tag plays a pivotal role in SEO for several reasons:
- Control Over Indexing: You can prevent specific pages, like internal or private ones, from being indexed and displayed in search results.
- Link Crawling: Direct the behavior of search engine crawlers regarding which links on a page should be followed.
- Avoiding Duplicate Content: By directing search engines not to index certain pages, you can avoid potential penalties associated with duplicate content.
Best practices for Meta Robots Optimization
To harness the full potential of the meta robots tag, consider these best practices:
- Use With Caution: A misplaced directive can result in essential pages not being indexed. Always double-check before implementing.
- Specify Default Behavior: If you want most of your pages indexed and followed, specify this default behavior in a site-wide header or robots.txt file.
- Combine Directives: You can use multiple directives in a single tag, separating each with a comma.
- Remember Other Search Engines: While Google is dominant, remember that other search engines might interpret or handle directives slightly differently.
How to add a meta robots tag to your page
To integrate a meta robots tag:
- Access the HTML: Open the HTML of the desired page.
- Locate the <head> Section: Within this section, you can insert the meta robots tag.
- Insert the Tag: Depending on your directive, it might look something like this: <meta name=”robots” content=”noindex,nofollow”>.
- Save and Verify: After saving your edits, use tools like Google’s Search Console to ensure that the tag is recognized and followed by search engines.
How to diagnose and fix common meta robots mistakes
Regular audits can help spot and rectify meta robots tag issues:
- Unintended Blocking: Check to ensure crucial pages aren’t accidentally set to “noindex” or “nofollow”.
- Conflicting Directives: Ensure that directives in the meta robots tag don’t conflict with those in the robots.txt file.
- Misplaced Tags: The meta robots tag should always be in the <head> section of the HTML. Ensure it hasn’t been mistakenly placed elsewhere.
Overuse: While it’s powerful, don’t over-rely on the meta robots tag. Not every page needs it, and default behavior can often be set site-wide.
Meta Viewport
The meta viewport tag is essential for controlling how a webpage is displayed on mobile devices. It provides instructions on scaling and dimensions, ensuring that the content fits appropriately on various screen sizes.
Why it’s important for SEO
The significance of the meta viewport tag for SEO includes:
- Mobile Friendliness: As mobile searches have surpassed desktop, search engines prioritize mobile-friendly sites. The meta viewport tag is instrumental in achieving this by ensuring content scales and renders correctly on mobile devices.
- User Experience: A page that doesn’t adapt to the user’s device can lead to zooming, side-scrolling, or other disruptions. This can frustrate users, leading to higher bounce rates, which search engines might interpret as a sign of a less valuable page.
- Ranking Factor: Search engines, especially Google, consider mobile-friendliness as a ranking factor. Having a properly configured viewport is a key component of this.
Best practices for Meta Viewport Optimization
To make the most of the meta viewport tag, consider the following best practices:
- Responsive Design: Ensure that your website design is responsive, meaning it adjusts based on the device’s screen size.
- Avoid Fixed Width: Instead of setting a fixed width, use “width=device-width” to match the screen’s width in device-independent pixels.
- Initial Scale: Set the initial zoom level when the page is first loaded by the browser. A common best practice is “initial-scale=1”.
- User Scalability: While some designers disable user zooming with “user-scalable=no”, it’s generally a good practice to allow users to zoom if they wish.
How to add a meta viewport tag to your page
To incorporate a meta viewport tag:
- Access the HTML: Navigate to the HTML of the page you want to edit.
- Find the <head> Section: This is where the meta viewport tag should be placed.
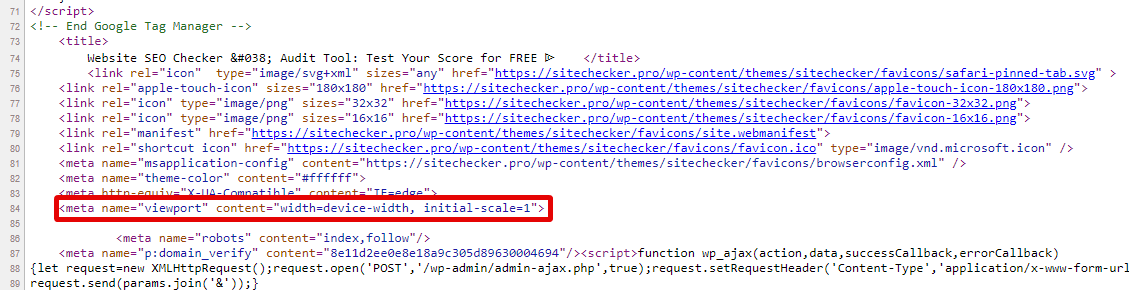
- Insert the Tag: A common viewport tag looks like this: <meta name=”viewport” content=”width=device-width, initial-scale=1″>.
- Save and Test: After making changes, save them. Test the page on various devices or use responsive design testing tools to ensure it displays correctly.
How to diagnose and fix common meta viewport mistakes
Regularly reviewing your site can help identify and correct issues related to the meta viewport:
- Missing Tag: Ensure all pages, especially mobile-optimized ones, include the meta viewport tag.
- Incorrect Values: Double-check the content attribute of the tag to ensure values like “width=device-width” or “initial-scale=1” are correctly set.
- Over-complication: While there are many properties you can set within the viewport tag, it’s often best to stick with the basics unless you have a specific need.
- Testing on Various Devices: Use emulators or actual devices to test how your site appears on different screens. Make adjustments as needed to ensure consistent display across devices.
Meta Charset
The meta charset tag specifies the character encoding for the HTML document. It ensures that the content, including text and special characters, is displayed correctly across different browsers and platforms.
Why it’s important for SEO
The relevance of the meta charset tag for SEO includes:
- Content Integrity: Ensuring that content is displayed as intended is crucial for user experience. Misinterpreted characters can make content unreadable or change its meaning, leading to confusion for visitors.
- Crawling and Indexing: Search engine crawlers rely on correct character encoding to interpret and index content. Incorrect encoding can hinder the crawling process or result in misinterpretation of the content.
- Global Reach: For websites with a global audience, especially those in multiple languages, the correct character set is essential to cater to different languages and alphabets.
Best practices for Meta Charset Optimization
To maximize the effectiveness of the meta charset tag, follow these best practices:
- Use UTF-8: UTF-8 is a universal character encoding that covers almost all characters and symbols in use. It’s widely recommended for its versatility and compatibility.
- Place Early in the Head: The charset declaration should be placed as early as possible within the <head> element, ideally within the first few elements, to ensure it’s detected promptly by browsers.
- Consistent Encoding: Ensure that the declared charset matches the actual encoding of your document. Using tools or text editors, you can verify and save your content in the declared encoding.
How to add a meta charset tag to your web page
To integrate a meta charset tag:
- Access the HTML: Open the HTML of the desired page.
- Locate the <head> Section: Within the early part of this section, you’ll insert the meta charset tag.
- Insert the Tag: A common charset tag for UTF-8 looks like this: <meta charset=”UTF-8″>.
- Save and Verify: After making and saving your adjustments, view the page in different browsers to ensure content displays correctly.
How to diagnose and fix common meta charset mistakes
Regularly reviewing and testing your content can help identify and correct charset-related issues:
- Mismatched Encoding: Ensure that the declared charset in the meta tag matches the actual encoding of the document. Tools like the W3C Validator can help detect mismatches.
- Late Declaration: If the charset tag is placed too late in the <head>, browsers might not detect it in time, leading to potential display issues. Ensure it’s placed early in the <head> section.
- Special Character Errors: If special characters, like accented letters or symbols, appear incorrectly, it’s often a sign of encoding issues. Recheck the meta charset tag and the actual encoding of the document.
Multiple Declarations: Ensure there’s only one charset declaration in the document. Multiple declarations can confuse browsers.
Meta Refresh Redirect
The meta refresh redirect is a method used to automatically refresh a web page after a specified number of seconds or redirect users to a different page. While it can be useful in certain scenarios, it’s typically not the recommended method for redirection, especially from an SEO standpoint.
Why it’s important for SEO
The implications of the meta refresh redirect for SEO encompass:
- User Experience: Unexpected or frequent refreshes can disrupt the user’s experience, leading to confusion or frustration and potentially increasing bounce rates.
- Search Engine Interpretation: Search engines may interpret meta refresh redirects differently from standard 301 or 302 redirects. This can lead to indexing issues or reduced link equity transfer.
- Potential for Misuse: In the past, meta refresh was sometimes used for deceptive practices, like bait-and-switch tactics. As a result, search engines may view frequent use of meta refresh with suspicion.
Best practices for Meta Refresh Redirect Optimization
If you choose to use meta refresh redirects, consider the following best practices:
- Use Sparingly: Only use meta refresh redirects when absolutely necessary. Whenever possible, opt for server-side redirects like 301 or 302.
- Inform Users: If you’re using a meta refresh to give users updated content, inform them that the page will be refreshing and provide a manual refresh option.
- Delay Consideration: If using the refresh for redirection, keep the delay short (typically 0 seconds) to minimize user waiting time. However, if the purpose is to show an interim message (e.g., “You are being redirected…”), ensure the message is visible long enough to be read.
How to add a meta refresh redirect tag to your page (if you really need to)
To incorporate a meta refresh redirect:
- Access the HTML: Open the HTML of the page you wish to add the redirect to.
- Navigate to the <head> Section: This is where the meta refresh tag will be placed.
- Insert the Tag: For a timed refresh, use: <meta http-equiv=”refresh” content=”TIME_IN_SECONDS”>. For a redirect, use: <meta http-equiv=”refresh” content=”TIME_IN_SECONDS;url=DESTINATION_URL”>.
- Save and Test: After implementing and saving, test the page to ensure the refresh or redirect works as intended.
How to find and fix common meta refresh redirect mistakes
Regular audits can help identify and rectify issues related to meta refresh redirects:
- Unintended Redirects: Ensure that all meta refresh redirects are intentional and lead to the correct destination.
- Excessive Delays: If using a redirect, avoid long delays which can frustrate users. If you need to inform users, ensure the message is brief and clear.
- Mobile Considerations: Test the meta refresh on various devices to ensure a consistent experience, especially on mobile where rapid refreshes can be particularly disruptive.
- Alternative Methods: If possible, replace meta refresh redirects with more SEO-friendly methods like 301 redirects.
What About Meta Keywords?
The meta keywords tag is one of the oldest meta tags. It was designed to allow webmasters to provide search engines with a list of keywords that represent the content of their pages. However, its journey through the landscape of SEO has been quite tumultuous.
History and Evolution: In the early days of the web, search engines relied heavily on the meta keywords tag to understand the content of a webpage. Webmasters would fill this tag with keywords related to the page’s content, and search engines would use this information to index the page appropriately.
However, as the web grew and SEO became more competitive, many website owners began “keyword stuffing” this tag, adding irrelevant or excessive keywords in an attempt to manipulate rankings. This misuse led search engines to reduce the importance of the meta keywords tag in their ranking algorithms.
Current State: Today, most major search engines, including Google, have publicly stated that they do not use the meta keywords tag as a ranking factor. The tag has become largely obsolete in terms of SEO value. However, there might be some smaller or specialized search engines that still consider it.
Should You Use It?: Given its lack of importance in modern SEO strategies, it’s generally recommended not to use the meta keywords tag. There’s no real benefit, and its presence can bloat the page’s code. Moreover, it can potentially give competitors insight into your targeted keywords.
Best Practices if Used: If you still choose to use the meta keywords tag for any reason:
- Stay Relevant: Only include keywords that are directly related to the page’s content.
- Avoid Keyword Stuffing: Limit the number of keywords and ensure they are all relevant. Keyword stuffing can be a red flag for search engines, even if they don’t use the tag for ranking purposes.
Keep it Concise: A good rule of thumb is to limit yourself to 5-10 keywords or phrases.
Google Snippet Checker to Check How a Specific Page Snippet Will Look Like
The Google Snippet Checker is key for optimizing website appearance in search results. It previews web page snippets in Google’s SERPs, showing the title, URL, and meta description from a page’s URL or HTML code. This helps understand and optimize the first impression for better click-through rates.
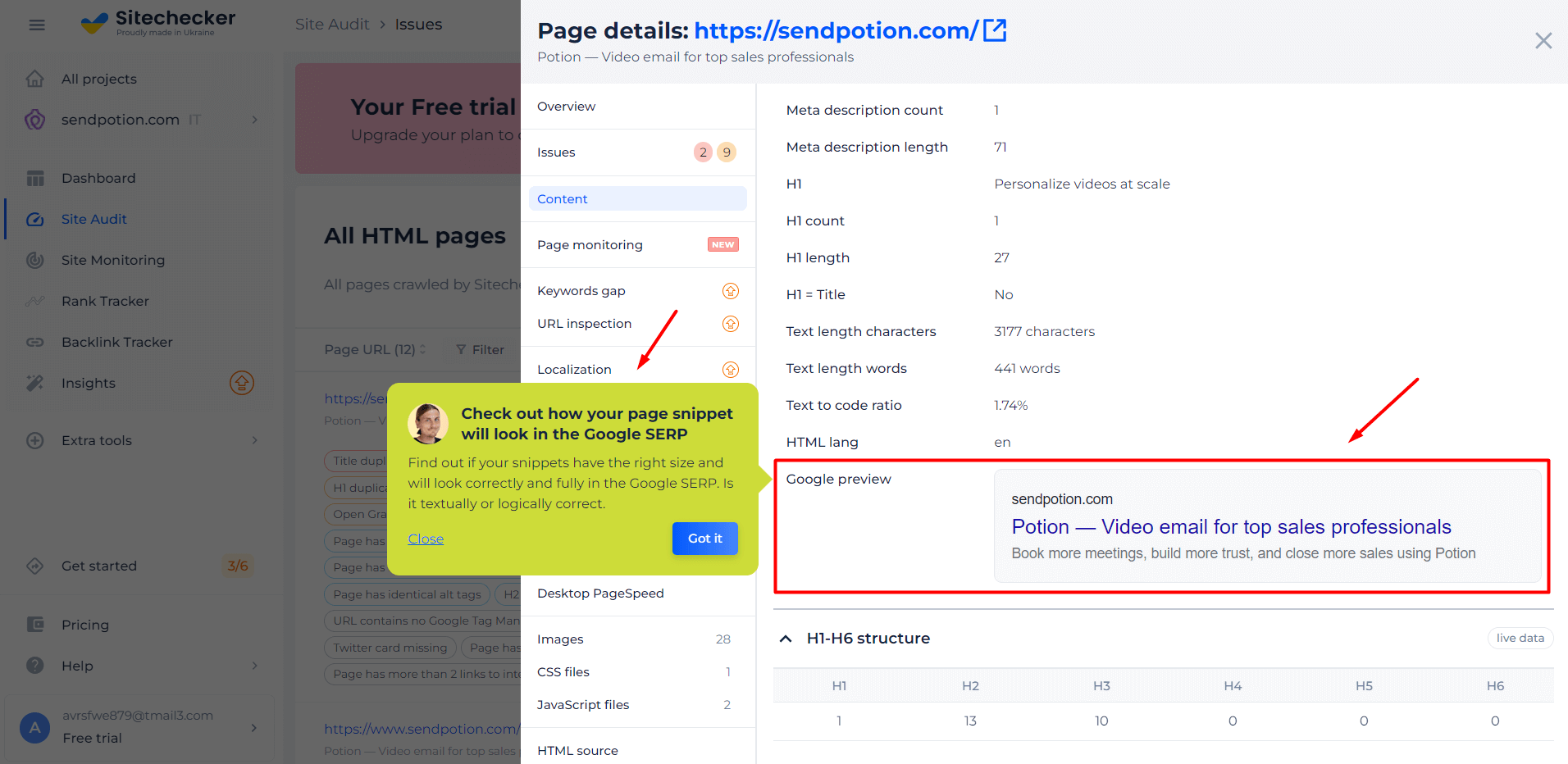
The Google Snippet Checker not only previews but also enables tweaking titles and meta descriptions for more clicks. It offers tips for effective title and description crafting, considering character limits and keywords. This tool is a guide for enhancing SEO and user engagement.
Maximize Clicks with the Best Snippet!
Utilize our Google Snippet Checker to enhance your titles and meta descriptions.
Conclusion
The evolving landscape of SEO has seen various meta tags rise and fall in significance. While some, like meta title and description, remain pivotal in optimizing a website’s search performance, others, like the meta keywords tag, have faded into obsolescence. The key to effective SEO lies in understanding these shifts and adapting accordingly. By focusing on meta tags that genuinely impact search visibility and user experience, webmasters can ensure that their sites remain relevant and competitive in today’s digital age. As always, the goal is to provide value to users, and the right meta tags, used appropriately, can be instrumental in achieving that objective.