What the Issue “Your Site Has no hreflang Tags” Mean?
The message “Your site has no hreflang tags” indicates that your website is missing the hreflang attributes in its HTML code. These tags are used to specify the language and geographical targeting for a web page, which is important for search engines to understand the intended audience for the content on your site. Here’s a more detailed breakdown:
- Hreflang Tags: These are HTML attributes used in the head section of your web pages to specify the language and regional targeting of a URL. They help search engines like Google serve the correct language or regional URL in search results.
- Purpose: Language Targeting: Indicate which language the content is written in.
- Regional Targeting: Specify the geographic region the content is intended for.
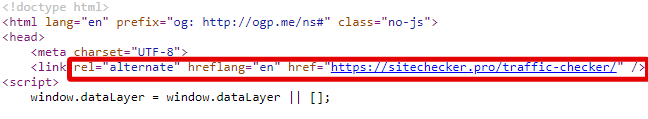
Example:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en" href="https://example.com/en/"/>
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es" href="https://example.com/es/"/>
When are Hreflang Tags Required?
Hreflang tags are essential in several scenarios where a website serves a diverse audience in terms of language and geographic location. Understanding when to use these tags can help you effectively manage your site’s international SEO strategy. Here are the primary situations where hreflang and lang. tags are required:
| Multilingual Websites | If your website offers content in more than one language, hreflang tags are necessary to direct users to the version of the site in their preferred language. This is particularly relevant for global brands and services that cater to audiences speaking different languages. |
| Country-Specific Content | For websites that have different versions of content for users in different countries, even if the language is the same. For example, a site might have separate versions for users in the United States, the United Kingdom, and Australia, each with region-specific information, currency, and cultural references. Hreflang tags help ensure that users are directed to the most relevant content for their location. |
| E-Commerce Sites with Multiple Language and Currency Options | Online stores that offer shopping options in various languages and currencies need to implement hreflang tags to guide users to the appropriate version of the site, enhancing the shopping experience by displaying prices in the user’s local currency and content in their language. |
| Content with Regional Variations | Websites that publish content with slight variations for different regions or languages, such as legal terms, product availability, or cultural nuances, should use hreflang tags. This ensures that the content meets the legal, cultural, and consumer needs of each target audience. |
| Avoiding Duplicate Content Issues | When similar or identical content is accessible through multiple URLs (due to language or regional variations), search engines might flag this as duplicate content, which can negatively affect search rankings. Implementing hreflang tags helps search engines understand that these variations are intended for different audiences, not duplicates, thereby preserving your site’s SEO integrity. |
Implementing hreflang tags is not about whether your website simply exists in multiple languages or versions, but about providing the most relevant content to users based on their linguistic and geographic context. Proper use of hreflang tags is a proactive step in managing your site’s international presence, ensuring content relevance, and optimizing for search engines across diverse markets.
The Trouble with Hreflang Tags
Let’s highlight the capability of Sitechecker tool in resolving hreflang related problems, which are crucial for global SEO strategy and ensuring your content reaches the right audience in different languages and regions. This screenshot shows the Localization section of the Site Audit tool, specifically focusing on hreflang issues. It’s a sophisticated feature that detects and lists any hreflang tags on your site that may be implemented incorrectly, such as missing self-referencing hreflang annotations or missing reciprocal returns, which are essential for signaling to Google the relationship between language and regional URLs.
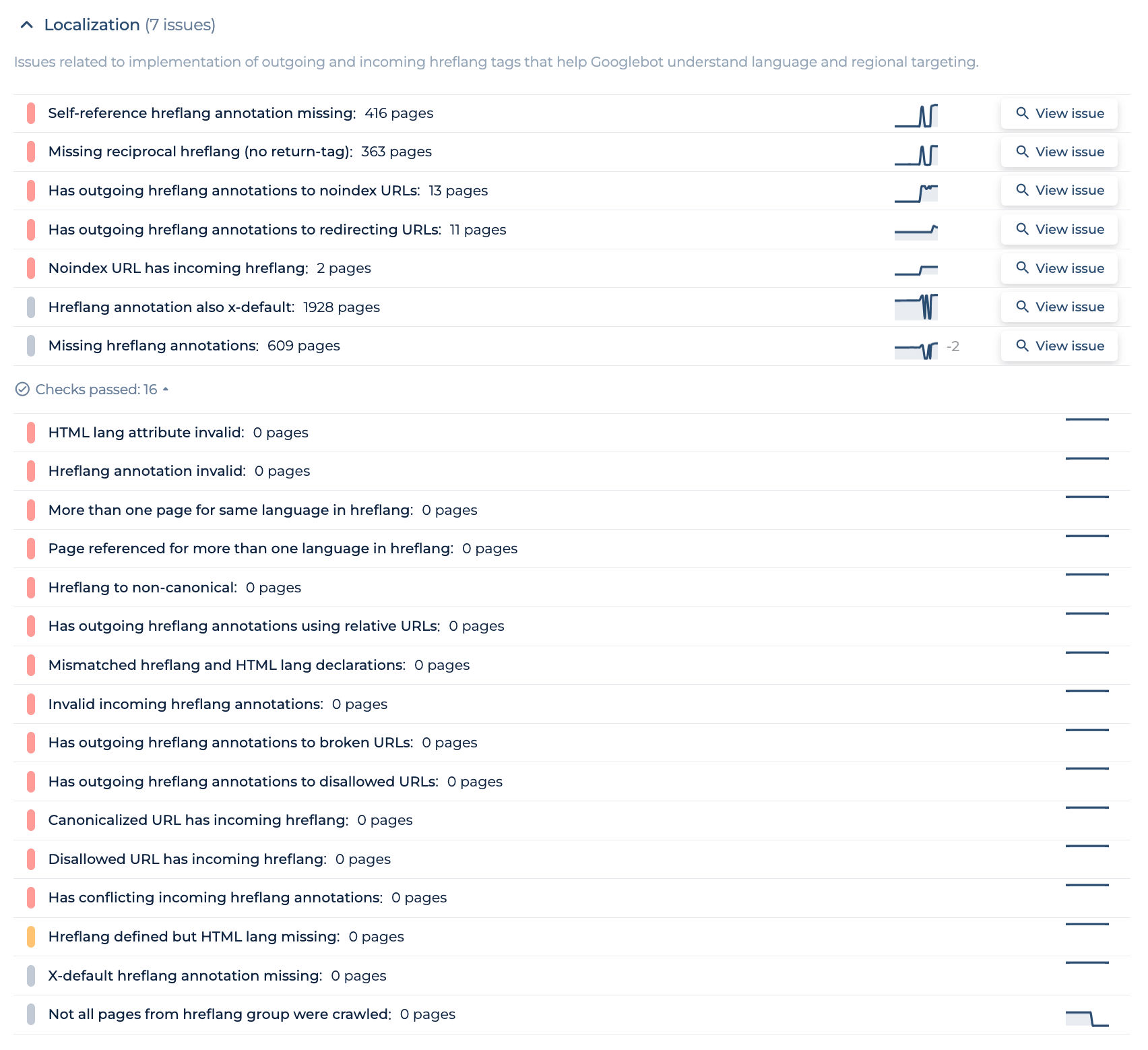
By clicking “View issue,” users can dive into a detailed report that not only quantifies the issue but also presents a dynamic visual representation of the problem and its trend over time. This actionable insight allows you to pinpoint the exact pages that require attention, making it easier to prioritize fixes. Sitechecker simplifies the complex task of managing hreflang attributes by providing a clear, user-friendly breakdown of all hreflang tags, ensuring that they contribute positively to your site’s international SEO efforts.
The implementation of hreflang tags, while crucial for websites with international audiences, can present several challenges that may hinder their effectiveness. Understanding these troubles can help webmasters and SEO professionals navigate potential pitfalls more effectively.
Master Global SEO: Fix hreflang Issues with Ease
Discover and resolve hreflang problems swiftly with Sitechecker's Audit tool.
Complexity in Implementation
Implementing hreflang tags requires careful consideration of various aspects, such as the correct use of language and region codes, the application method (HTML, XML Sitemap, HTTP headers), and the consistency across different versions of the site. The complexity increases with the size of the website and the number of language or regional variations it supports.
Maintenance and Updates
Once hreflang tags are implemented, they require ongoing maintenance to ensure their accuracy over time. Any changes to the site’s content, structure, or the addition of new languages or regions necessitate updates to the hreflang annotations. This ongoing requirement can be resource-intensive for larger sites.
Incorrect or Inconsistent Tags
Common issues include using incorrect language or region codes, failing to provide reciprocal links between localized versions, and inconsistencies between the hreflang tags specified in the HTML of individual pages and those listed in the XML sitemap. These errors can lead to Google and other search engines misunderstanding the intended audience for a page, potentially affecting the visibility of your content in relevant search results.
Overlapping Content Across Regions
For websites targeting multiple regions where the same language is spoken, distinguishing content intended for different audiences can be challenging. Without clear differentiation, search engines might not accurately serve the most relevant regional version to users, impacting user experience and engagement.
Duplicate Content Concerns
While hreflang tags are designed to address duplicate content issues by clarifying the audience for similar content in different languages or regions, improper implementation can inadvertently contribute to the problem. Ensuring that each version is correctly tagged and accessible to search engines is crucial to avoiding penalties associated with duplicate content.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting Errors
Identifying and resolving hreflang tag errors can be complex, requiring tools like Google Search Console to monitor the tags’ status and effectiveness. Troubleshooting issues often involves a detailed review of the site’s implementation to pinpoint and correct the source of the problem.
Methods of Placing Hreflang Tags
Implementing hreflang tags can be done in several ways, depending on your website’s structure and your technical proficiency. Here are the primary methods:
Adding hreflang tags to a website manually
Manual addition of hreflang tags is a hands-on approach that gives you full control over the implementation process. This can be done in two main ways:
Adding hreflang tags manually via HTML headers
This method involves placing hreflang attributes directly on link elements in the <head> section of your HTML documents. Each page that has an alternate version in a different language or for a different region should include a link element with the rel=”alternate” attribute and the hreflang attribute specifying the language (and optionally the region). For example:
<link rel="alternate" href="http://example.com" hreflang="en-us" />
<link rel="alternate" href="http://example.es" hreflang="es-es" />
This approach is ideal for websites with a manageable number of pages, ensuring precise targeting and control.
Adding hreflang tags manually via an XML Sitemap
For websites with a large number of pages, managing hreflang tags through an XML Sitemap can be more efficient. This method involves creating an XML Sitemap that includes hreflang annotations for each URL, providing search engines with the information needed to understand the language and regional targeting of your site’s content. The Sitemap is then submitted through Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools.
Adding hreflang tags to a website with a plugin (and avoiding the “your site has no hreflang tags” issue!)
Many content management systems (CMS) like WordPress offer plugins designed to simplify the process of adding hreflang tags. These plugins can automatically generate the necessary tags based on your site’s structure and content, reducing the potential for errors and saving time.
Page tagging methods through HTML Head
In addition to manually adding tags to individual pages, you can use CMS-specific solutions or development approaches to programmatically insert hreflang tags into the HTML head of each page. This method is particularly useful for dynamic websites where content and language versions might change or expand over time.
Each method of implementing hreflang tags has its advantages and is suited to different types of websites and technical skill levels. Choosing the right approach depends on your site’s complexity, the resources available for implementation, and your specific targeting needs.
What is the Hreflang Error Returned by Google?
When Google crawls a website that uses hreflang tags, it validates the tags to ensure they are correctly implemented. If there are issues, Google Search Console may report hreflang errors, which can affect how your website is displayed in search results across different languages and regions. Common hreflang errors include missing return links, incorrect language codes, and URLs not being reachable. These errors mean that Google might not serve the intended version of a page to users in different locales, potentially impacting your site’s international SEO performance and user experience.
Language Code Errors
Language code errors occur when the language or region codes specified in the hreflang attributes do not follow the correct format. Google relies on the BCP 47 format for language codes and, optionally, ISO 3166-1 Alpha 2 for country codes. For example, an incorrect code might be “en-UK” instead of the correct “en-GB” for English content targeted to the United Kingdom. Such mistakes can lead Google to ignore the hreflang tags, as it cannot accurately match the pages with the users’ language and location preferences.
Wrong language attributes
Wrong language attributes refer to situations where the hreflang attribute specifies a language or locale that does not match the content on the page. For instance, if a page contains content in Spanish but is marked with an “en-US” hreflang tag for English, USA, this misalignment can confuse search engines and users. It’s crucial to ensure that each hreflang tag accurately reflects the page content’s language and region to avoid misleading search engines and diminishing the user experience.
Simultaneous use of sitemap and page tagging
Using hreflang annotations both in a sitemap and directly on pages (via HTML tags) is generally acceptable but can lead to inconsistencies if not managed carefully. Google advises maintaining consistency across these implementations to prevent conflicts. For example, if the hreflang entries in the sitemap do not match those in the HTML of the pages, Google might encounter conflicting signals about which version of the content is relevant for specific languages or regions. Consistency is key to ensuring that search engines correctly interpret and apply your hreflang annotations for the best international SEO results.
Language Code Errors
Language code errors occur when the hreflang attribute uses incorrect or unsupported language codes. Google relies on BCP 47 language tags to interpret the intended audience for each page. A common mistake is using incorrect codes that don’t adhere to this standard (for example, using “EN” instead of “en” for English). Such errors can prevent Google from correctly understanding and serving the content to the intended language or regional audience. Ensuring that all hreflang tags use the correct BCP 47 language codes is essential for the effective internationalization of your site.
Final Thoughts
Mastering hreflang tags is crucial for websites targeting a global audience, ensuring users are directed to content that matches their language and regional preferences. Proper implementation, whether through HTML, XML Sitemaps, plugins, or tools like Linguise, enhances user satisfaction and search engine optimization by addressing common issues such as incorrect language codes and inconsistencies. Recognizing when and how to use hreflang tags—especially for multilingual sites, country-specific content, and e-commerce platforms—is key to avoiding duplicate content penalties and improving international visibility. Effective management and regular verification of hreflang tags solidify a website’s global presence, making a meticulous approach to their application essential for a successful international SEO strategy.