What Does the “Bad URL Redirect” Issue Mean?
The “Bad URL redirect” issue refers to a situation where redirects lead to URLs that result in 4xx or 5xx HTTP status codes. These status codes indicate errors that prevent users from accessing the intended content.
Causes of “Bad URL Redirect (4xx and 5xx)” Issues
- Outdated Links: Forwardings pointing to pages that have been removed or moved without updating the redirect rules.
- Incorrect Redirect Rules: Misconfigured server or CMS settings leading to improper forwarding targets.
- Server Issues: Problems with the server hosting the destination page, causing it to return 5xx errors.
- Permissions Issues: Pages that require authentication or have restricted access leading to 401 or 403 errors.
How to Check the Issue?
You can check this issue with online or offline tools that scan your site. They can identify page resource URLs that redirect, where the destination URLs return HTTP status codes of 4XX or 5XX.
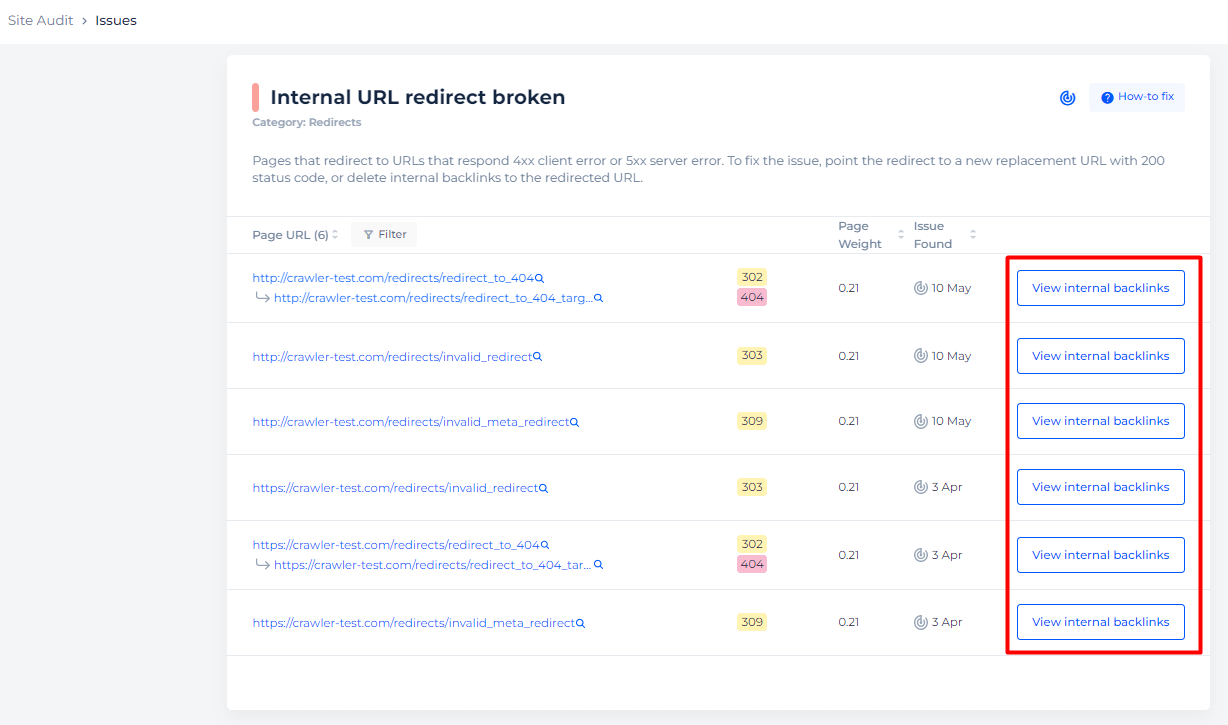
For example, Sitechecker keeps track of pages that redirect to URLs that respond 4xx client error or 5xx server error.
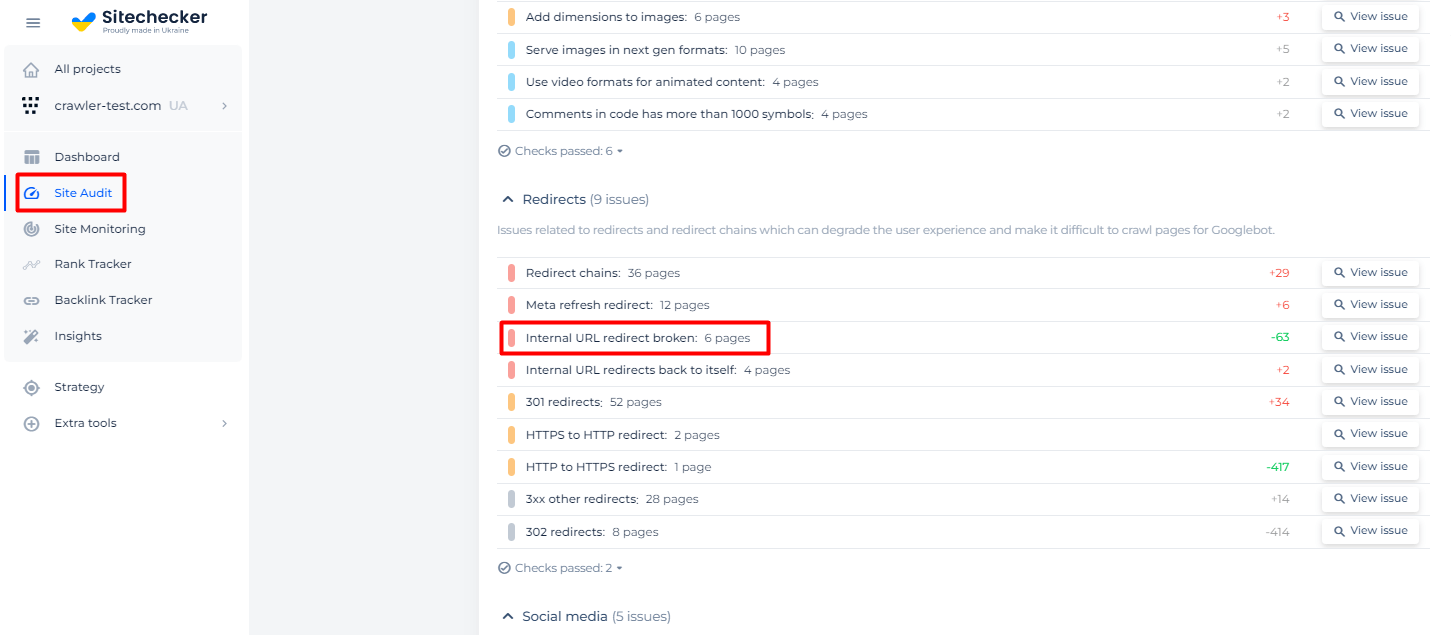
You can receive a list of such pages with ability to view their internal backlinks.
Checking Broken redirects is important for your site’s health!
Conduct a full audit to find out and fix your technical SEO.
How to Fix the Issue?
Fixing a “Broken Redirect” issue involves several steps to identify and correct the problem. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you resolve such issues:
1. Identify Broken Redirects
Utilize Sitechecker to identify broken forwardings.
2. Diagnose the Cause
Ensure there are no typos in the redirect URLs. Verify that the destination URLs still exist and have not been changed or deleted.
Check the web server or CMS settings to ensure forwardings are properly configured.
3. Fix the Redirects
Edit any URLs with typos or incorrect paths. If the destination page has moved, update the redirect to point to the new URL. Ensure you are using the correct HTTP status codes (e.g., 301 for permanent redirects, 302 for temporary).
4. Implement Proper Redirects
In your web server configuration (e.g., .htaccess file for Apache, nginx.conf for NGINX), set up proper redirect rules.
Apache Example (.htaccess):
Redirect 301 /old-page.html http://www.example.com/new-page.html
NGINX Example:
rewrite ^/old-page.html$ http://www.example.com/new-page.html permanent;
If using a CMS like WordPress, use redirect plugins (e.g., Redirection, Yoast SEO) to manage and set up redirects.
5. Test Redirects
Use a web browser to manually test the redirects and ensure they are functioning correctly.
Use Sitechecker to re-crawl your site and verify that all redirects are working.