Exactly, a 401 status code, officially labeled as “Unauthorized,” is a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) status code that the server sends back to the client (for example, your web browser) when the client’s request lacks valid authentication credentials to access the requested resource.
In simpler terms, when someone tries to access a specific web page and receives a 401 status code, it means the server does not recognize the user’s provided credentials (if any were given), or no credentials were provided, and the resource requested requires them.
Typically, the website will present the user with a login screen, where they can enter their credentials (username and password) to gain access to the resource. If the credentials are not valid or not provided, the server returns the 401 status code, preventing the user from accessing the requested content.
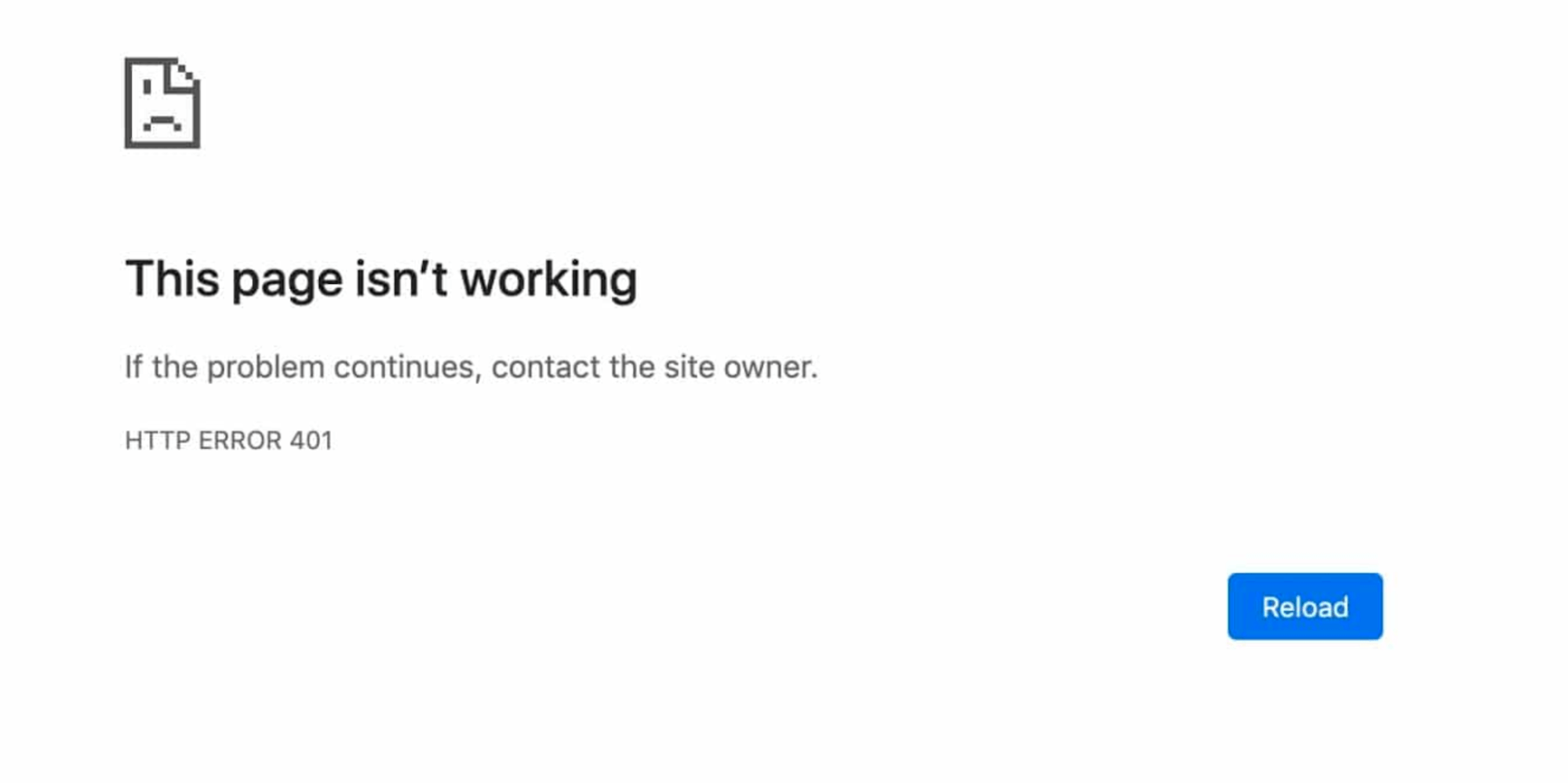
For instance, while using browsers like Chrome or Edge, you’re likely to encounter a graphic icon accompanied by a brief message indicating that the requested page is malfunctioning. At the bottom, the text “HTTP Error 401” will be displayed and a suggestion to reach out to the site’s owner if the issue continues:
In certain situations and with different browsers, you might receive a more austere warning, represented by a blank page displaying a “401 Authorization Required” message:

Nginx’s error message for 401 Authorization Required
Error message indicating 401 Authorization Required
Some other variants include:
“HTTP 401 Error – Unauthorized”
“401 – User Unauthorized”
“Access Denied”
In terms of SEO, excessive 401 errors can indicate to search engine crawlers that many of your site’s pages are protected and not accessible, which could limit your site’s visibility in search engine results if not managed correctly. That’s why it’s crucial to properly control access to your web content and make sure all public content is easily accessible to search engines.
Main Reasons Why a Server Might Return a 401 Status Code
Navigating the web, you might sometimes stumble upon a 401 status code. This signifies an unauthorized request, but what triggers this response? Let’s take a brief look at the key reasons why a server might return a 401 status code:
| Incorrect Credentials | This is one of the most common reasons for a 401 error. If a user enters incorrect login details, the server cannot verify the user’s identity and therefore refuses access to the requested resource. |
| Lack of Necessary Authorization | Sometimes a user might have some level of authorization, but not enough to access a specific resource. For example, they might be a standard user trying to access an admin-only area. |
| Session Expiration | When a user logs into a site, they often start a “session” where they can move around the site without having to log in again. However, for security reasons, sessions often expire after a certain period. If a user’s session has expired, they’ll need to log in again, and if they try to access a resource without doing so, they might encounter a 401 status code. |
| Incorrectly Configured Authentication | If the authentication on a server or website is set up incorrectly, it could mistakenly return a 401 status code even when the user provides correct credentials. |
| Issues with Cookies | If a user’s browser is set to not accept cookies or to delete them regularly, it could interfere with the site’s ability to remember the user’s login details, leading to a 401 error. |
Remember, a 401 status code doesn’t necessarily mean something is wrong with the website. Often, it’s working exactly as it should, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized users. However, when these errors start cropping up where they shouldn’t be, it might indicate an issue that needs addressing.
How a 401 Status Code Can Impact SEO
The 401 status code can indeed impact your SEO, though its effect is more nuanced than simply blocking search engine bots. When a page requires authentication, it’s often because the information on that page isn’t meant to be publicly accessible. So, in a sense, these pages shouldn’t necessarily be crawled or indexed by search engines in the first place.
However, problems may arise if your publicly accessible pages are mistakenly configured to require authentication or return 401 status codes. In such cases, search engines like Google will be unable to access these pages, which means they can’t be crawled, indexed, or ranked. This could significantly impact your site’s visibility in search engine results.
Furthermore, user experience is an important factor for SEO, and encountering a 401 status code can be confusing or frustrating for users, especially if the reason for the error isn’t clear. If a user encounters a 401 error, they might choose to leave your site and go elsewhere, which can increase your bounce rate and potentially harm your site’s overall SEO performance.
For these reasons, it’s important to monitor your site for 401 errors and to fix them where necessary. You should also make sure that any pages you want to be publicly accessible do not require authentication unless absolutely necessary.
Common Issues Related to 401 Status Code in SEO and Their Respective Fixes
Unidentified 401 Errors
401 errors that are going unnoticed, impacting both user experience and SEO.
Unresolved 401 Errors
Identified 401 status codes that obstruct site accessibility.
Incorrect Public Page Configuration
Publicly accessible pages are wrongly configured to require authentication leading to unnecessary 401 errors and preventing search engines from accessing these pages.
Poor User Experience
Users are encountering 401 errors without sufficient guidance, leading to confusion and a higher bounce rate.
Recurring Server Errors
Server issues are leading to recurring, unwarranted 401 errors
Identifying and resolving 401 errors is vital to the success of your SEO efforts. These errors, when not addressed, can lead to reduced site visibility, poor user experience, and overall lower SEO performance.
Sitechecker Pro offers an HTTP Status Code Checker that can help identify 401 issues. It scans each page of your website, simulating the behavior of search engine bots, and as it navigates through your pages, it identifies and lists any HTTP status codes encountered, including 401 status codes. This allows you to see exactly where these issues are occurring so that they can be addressed.
The tool also offers insights into other website performance metrics, making it a comprehensive solution for site audit and SEO optimization.
A 401 status code, also known as “Unauthorized,” is an HTTP status code that can impact user experience and SEO. It’s returned when the server can’t authenticate the client’s request. Common reasons include incorrect credentials, session expiration, or issues with cookies.
Conclusion
In terms of SEO, 401 errors on publicly accessible pages can block search engine bots, reducing your site’s visibility. Therefore, It’s crucial to identify and resolve these issues using tools like Google Search Console or Sitechecker Pro.
Additionally, to avoid 401 errors, managing server performance, configuring public pages appropriately, and guiding users effectively are important. With these steps, you can manage 401 status codes, improve your website’s SEO, and enhance user experience.