What is a “Page with redirect” in the GSC?
A “Page with Redirect” in Google Search Console (GSC) refers to a URL that automatically forwards visitors to another page. When a page is rerouted, the original URL points to a different one. If the redirection is not set up correctly, Googlebot may be unable to index the original page properly.
This error typically appears in GSC, where Google flags redirected pages but does not index them.
Common reasons for redirect issues in Google Search Console
⛔ Incorrect setup: using the wrong redirect type (e.g., 302 instead of 301).
⛔ Redirect chains: multiple forwards before reaching the destination, confusing search engines.
⛔ Redirect loops: URLs pointing back to each other, creating endless loops.
⛔ Temporary redirects: Google treats temporary (302 status codes) differently, impacting indexing
Launch Sitechecker’s GSC Dashboard to boost your Search Console reporting!
Expand GSC Data Limits
Bypass Google’s 1,000-row cap and unlock up to 36 months of Search Console history in a single dashboard.
How to fix a page with a redirect error in Google Search Console
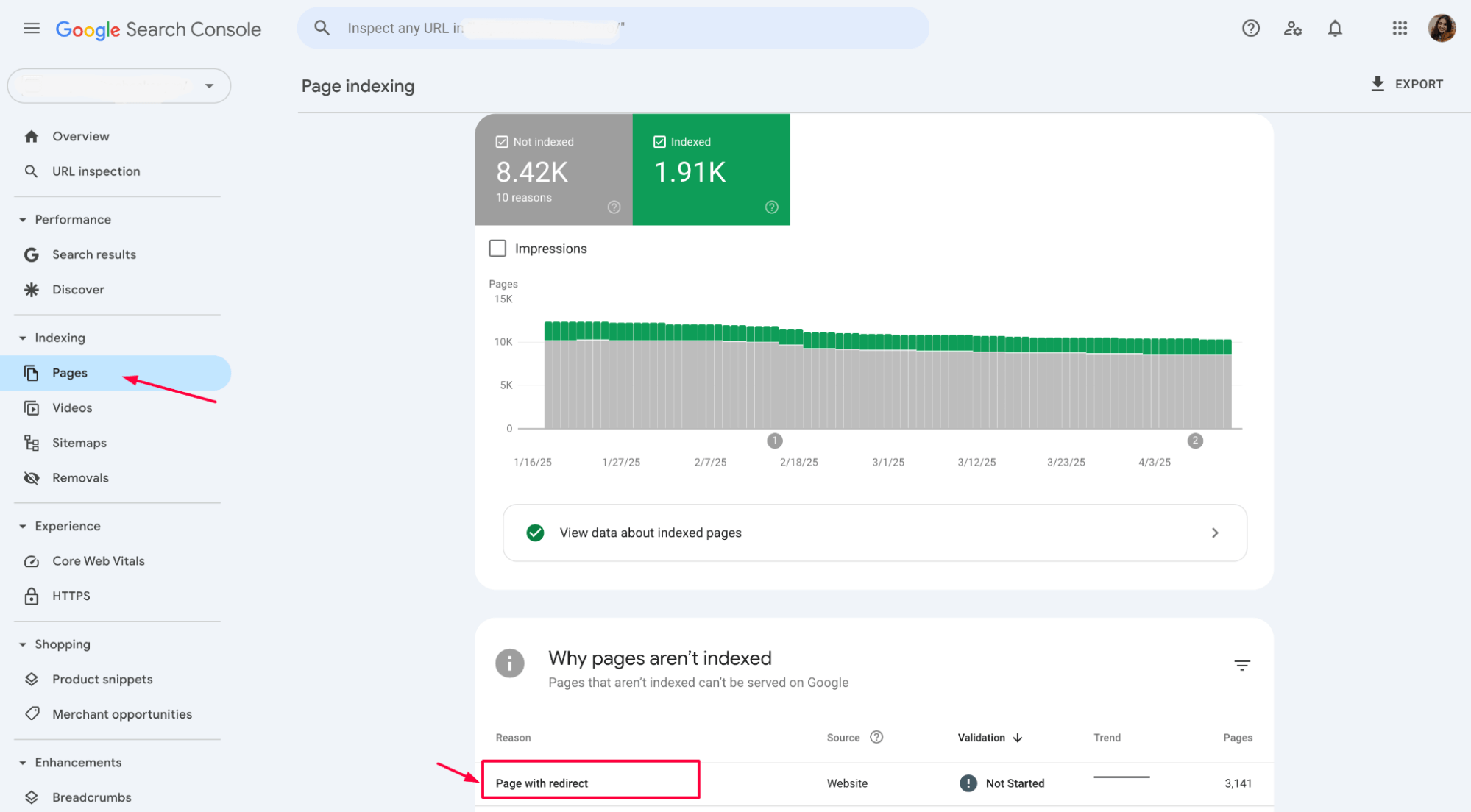
1. Identify the list of redirected pages
In Google Search Console, go to the Pages section and find the “Why pages aren’t indexed” category. Export the data into Google Sheets, Excel, or CSV for further analysis.
Alternatively, it is helpful to use URL Redirect Checker to easily identify pages, track their paths, and check the associated status codes.
While GSC provides a list of URLs, it lacks detailed status code information, making the troubleshooting process more complex and challenging to interpret.
Redirect Checker simplifies this by providing clear insights and organized data, allowing quicker identification and resolution of issues.
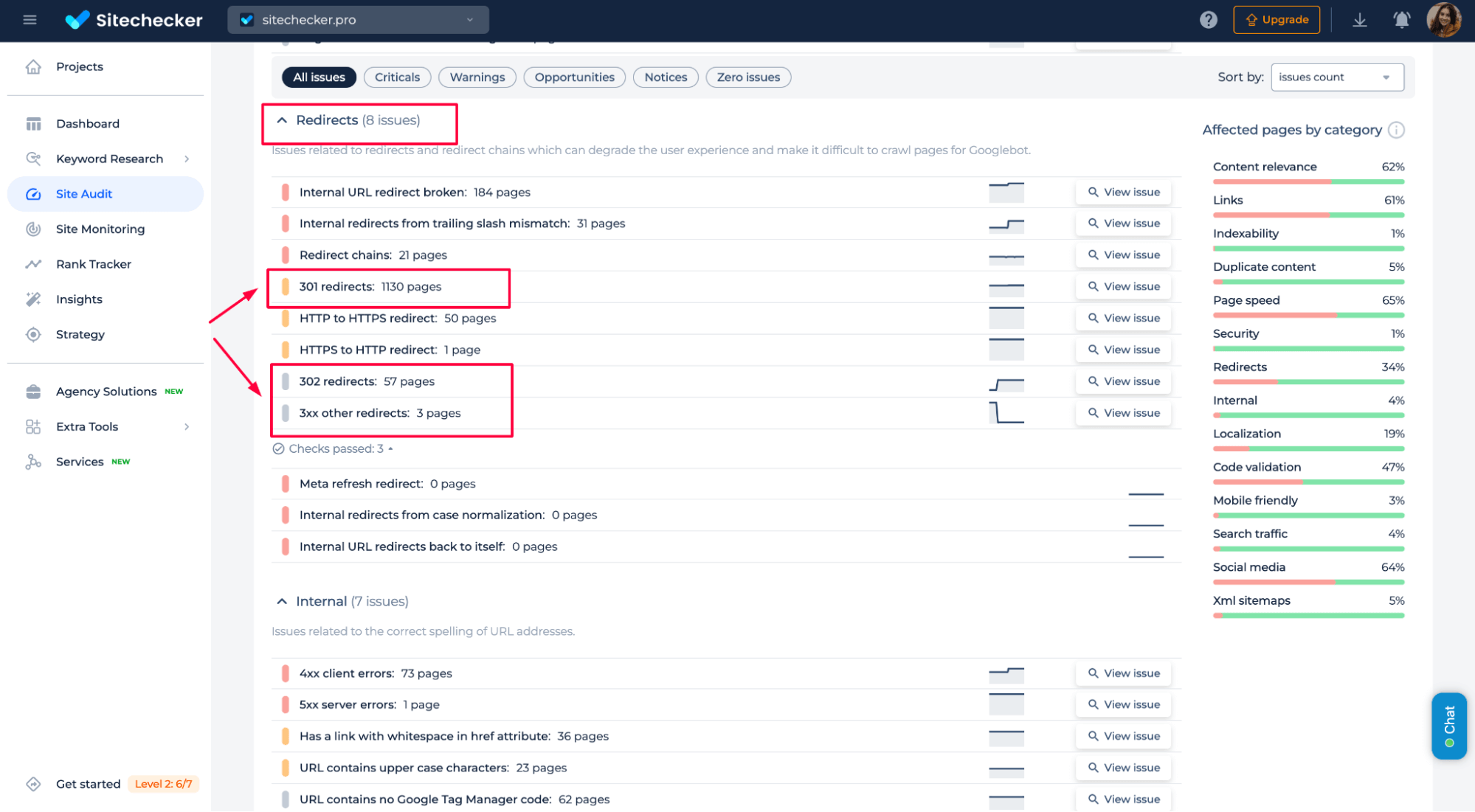
The tool allows you to see both the redirect paths and the corresponding status codes, making it much easier to resolve the issues efficiently.
2. Fix redirect correctness
Ensure the routes are intentional and properly configured:
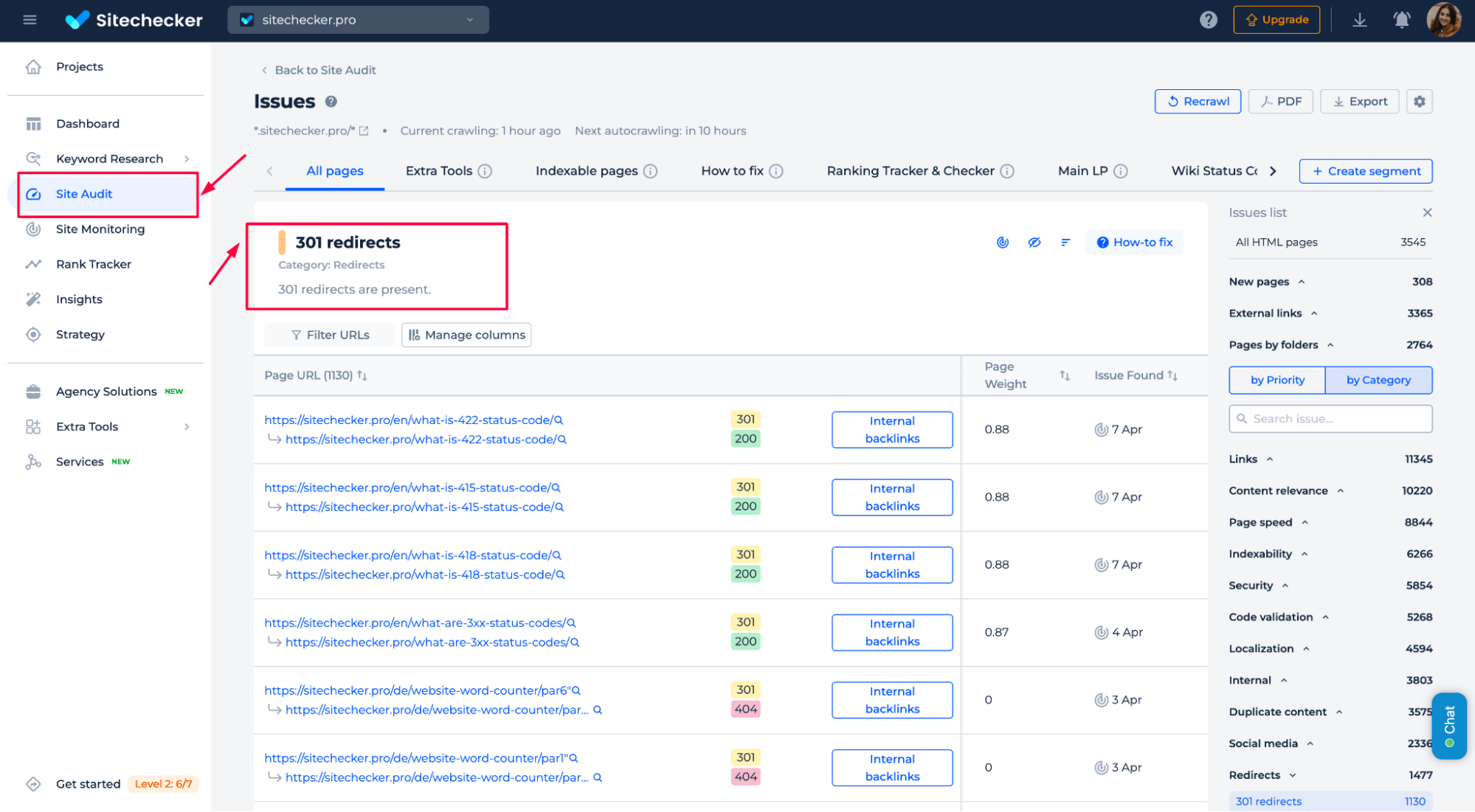
301 status codes
These are permanent redirects used when a page has been permanently moved.
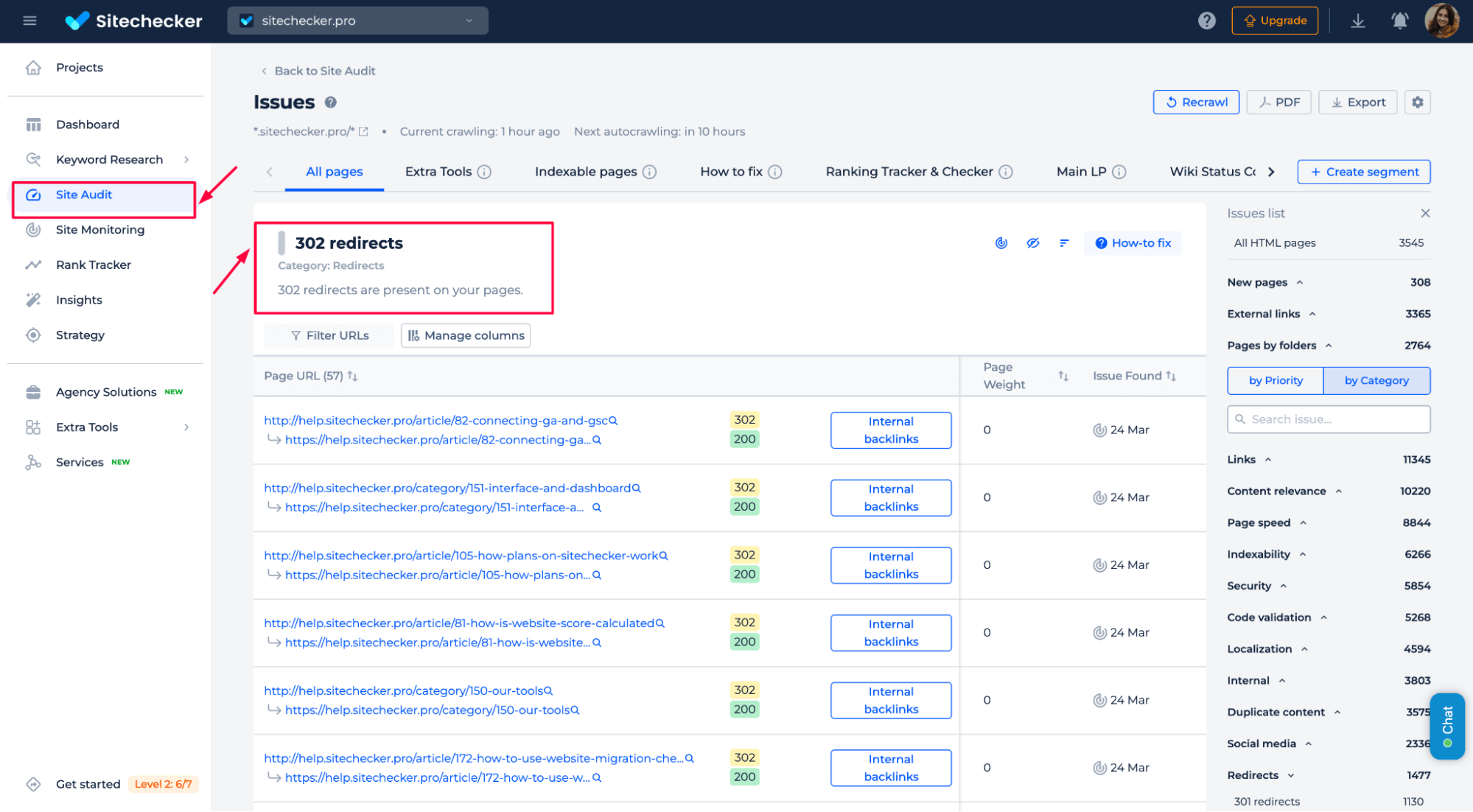
302 status codes
These are temporary redirects. If they last longer than a month, Google might treat them as 301, affecting rankings.
Redirect chains
It occurs when a page is routed through several other pages before reaching the final destination, confusing search engines.
https://example.com/old-page -> https://example.com/redirect-page ->
-> https://example.com/intermediate-page -> https://example.com/final-destination-page
Fixing chains improves crawl efficiency by allowing Googlebot to reach the final page directly, which saves crawl time and budget. It also enhances user experience by reducing unnecessary redirects, leading to faster page load times.
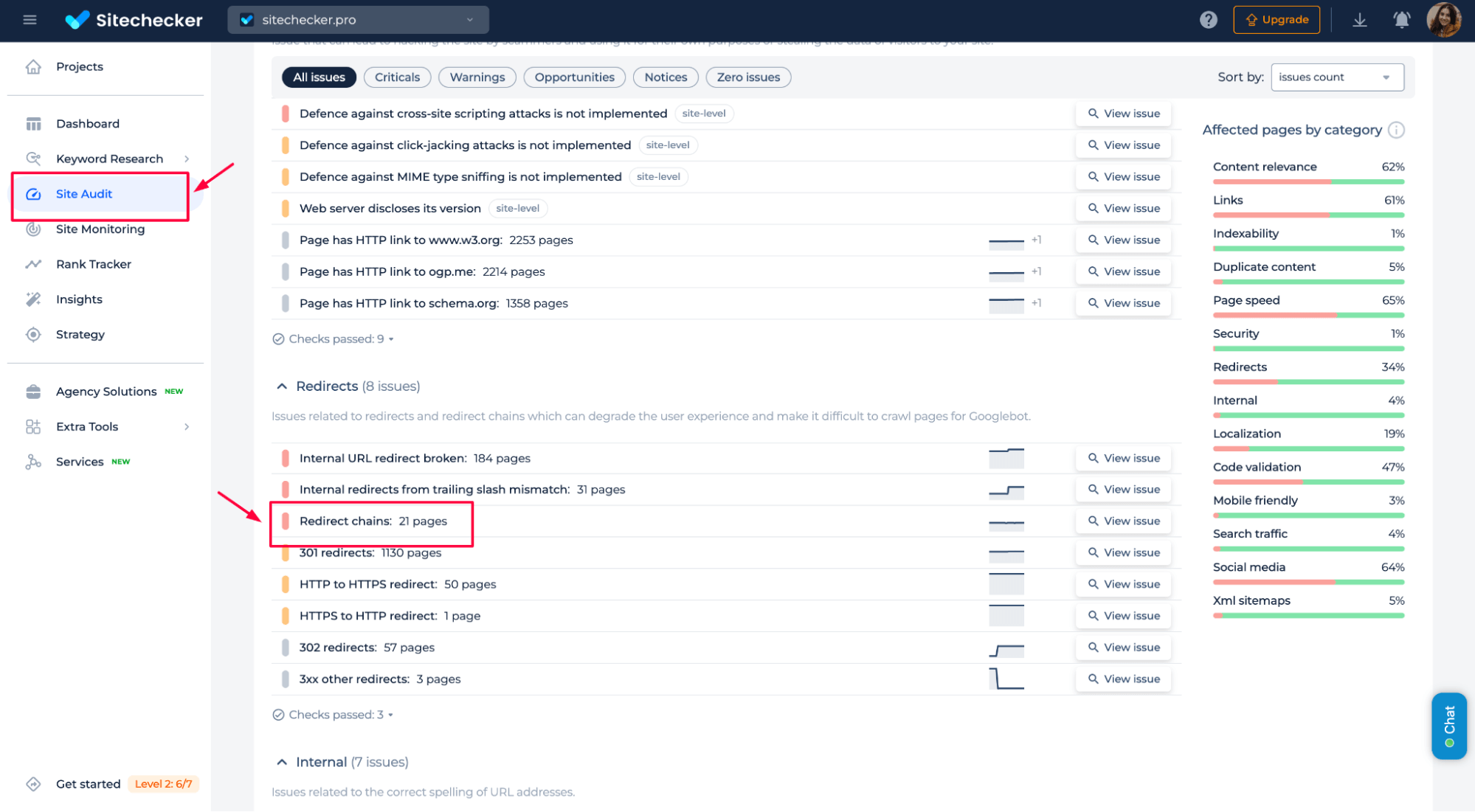
The tool can review and analyze all the errors, including 301 status codes, HTTP to HTTPS mismatches, chains, and more. This tool helps you identify and resolve issues, ensuring your site is optimized for better SEO and user experience.
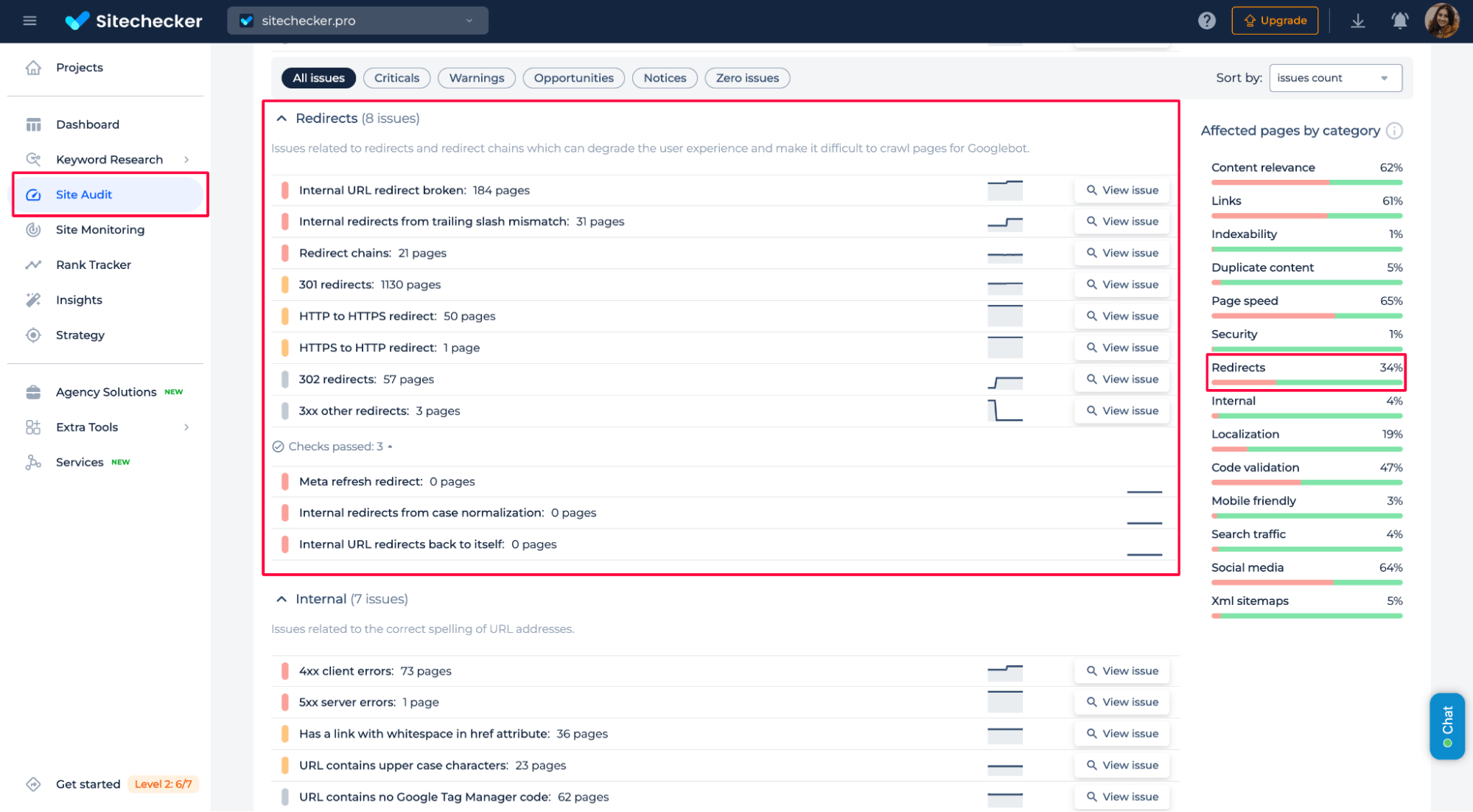
Redirects to important pages
If important pages are mistakenly forwarded, you must identify the forwardings and ensure they lead to the correct destination.
First, check whether the forwardings are intentional or if there’s an error causing key pages to be turned. If a crucial page, such as a product or service page, is redirected, update the forwarding rule to point to the correct and most relevant page.
Stop Redirect Errors in Google Search
Use Redirect Checker to fix problems with Google Search Console indexing.
3. Review your XML sitemap
Ensure that your XML sitemap doesn’t contain redirects. If they are present, remove them and add their final destination pages to the sitemap.
3.1 Check your sitemap for redirects
Open your XML sitemap and look for redirecting URLs. If a URL is redirected to another page, the sitemap should contain the final destination URL, not the rerouted one.
3.2 Remove redirected URLs from the sitemap
If you find any URLs in your sitemap that are currently being redirected, remove them.
You can detect redirects in your XML sitemap using the XML Sitemap Tool. The tool helps you identify pages with redirects in your sitemap, allowing you to resolve any issues with incorrect or broken links quickly.
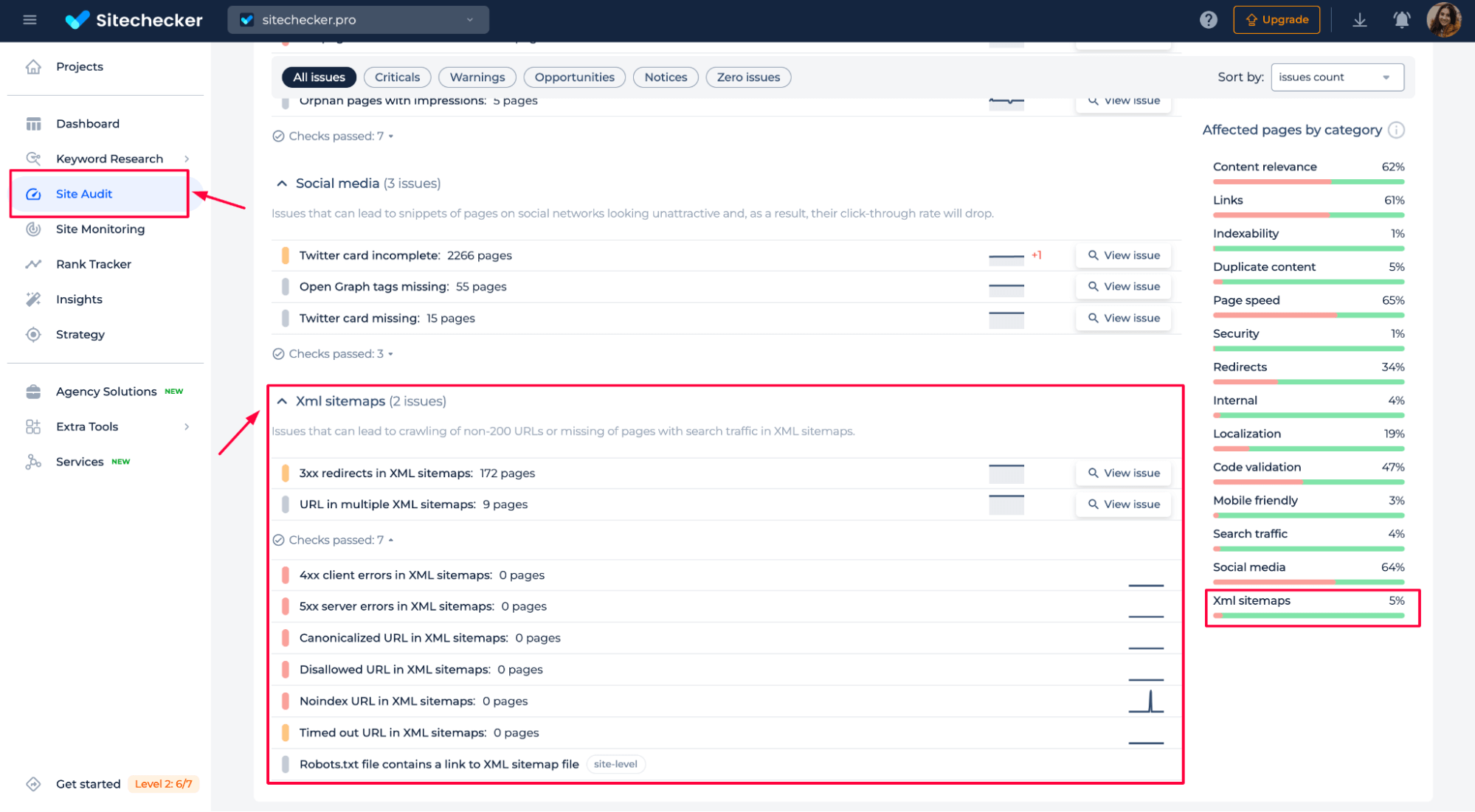
By reviewing your sitemap, you can ensure that it contains only the correct, non-redirected URLs for better crawling and indexing by search engines.
3.3 Add final destination pages
Ensure that your sitemap lists the final destination URLs (the ones the redirects point to).
3.4 Re-submit the updated sitemap
Once you’ve updated your sitemap, resubmit it to Google Search Console. This will ensure Google uses your sitemap’s latest version when crawling your site.
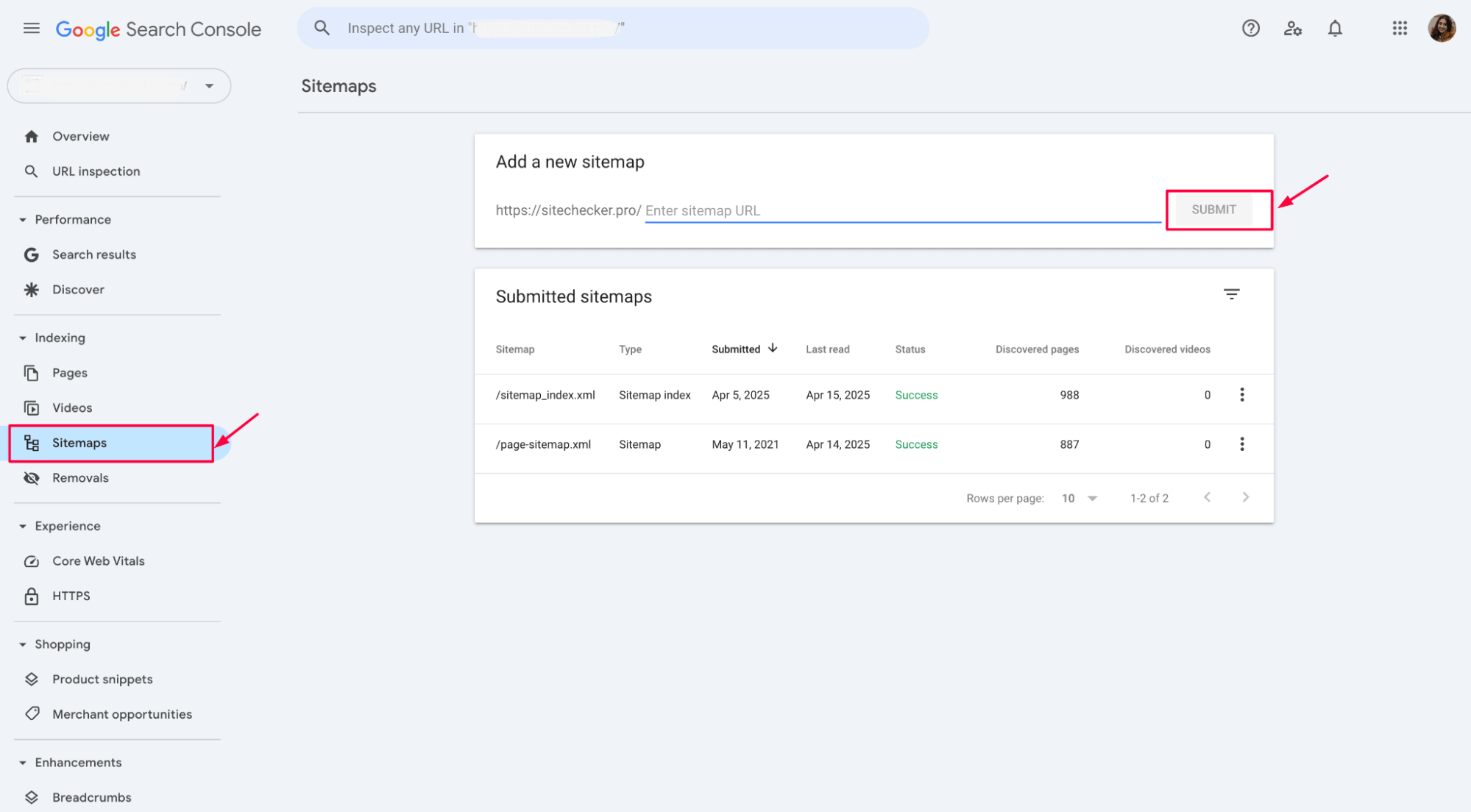
4. Use the Removal Tool (Optional)
If a page with a redirect contains outdated or irrelevant information, or if you need to stop its indexing until the redirect issue is temporarily resolved, you can use the Removal Tool in GSC. This tool temporarily removes the page from search results, allowing you time to fix the redirect.
Go to Google Search Console and navigate to the Removals section. Choose Temporary Removals and enter the URL that you want to remove temporarily:
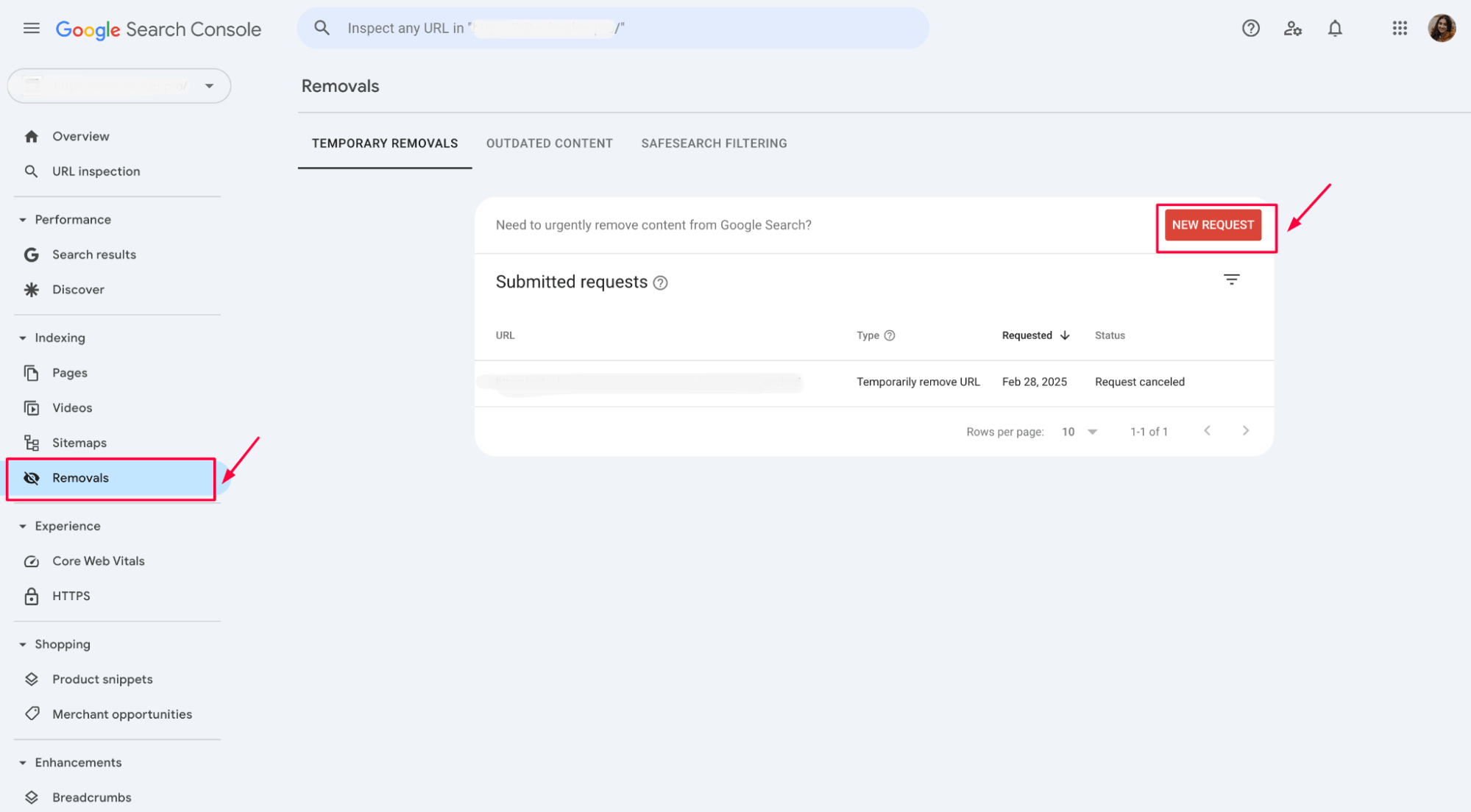
This action will last about 6 months, giving you time to fix the redirect permanently.
Watch this tutorial to understand how to manage your removal requests effectively:
5. Check and update canonical tags
Ensuring that the canonical tag on the forwarded page points to the correct final destination is essential when managing URL forwarding. This helps search engines identify the primary version of the page, avoiding duplicate content issues and preserving SEO value.
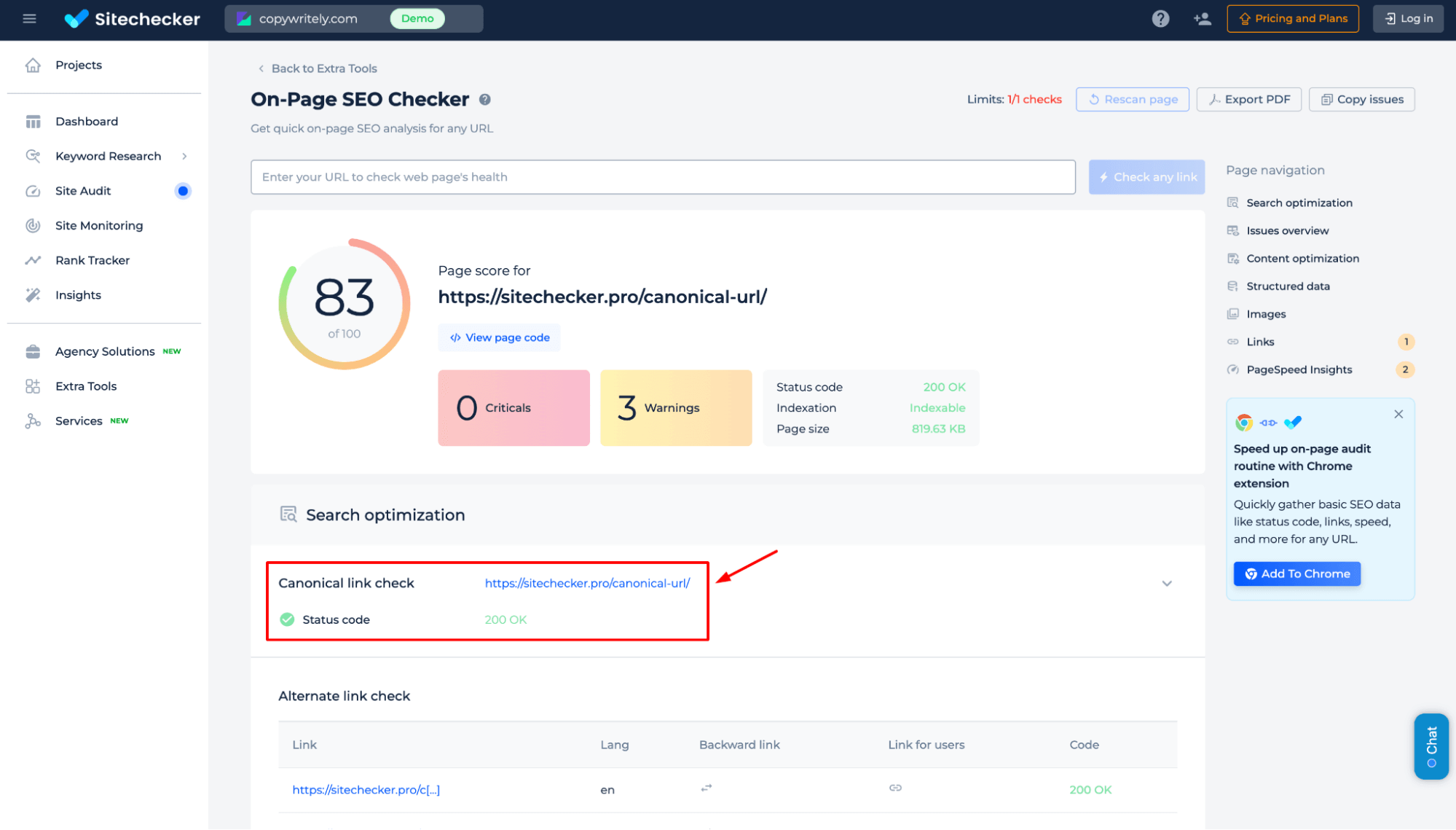
Ensure the canonical tag on the redirected page points to the correct final destination URL, not to another page.
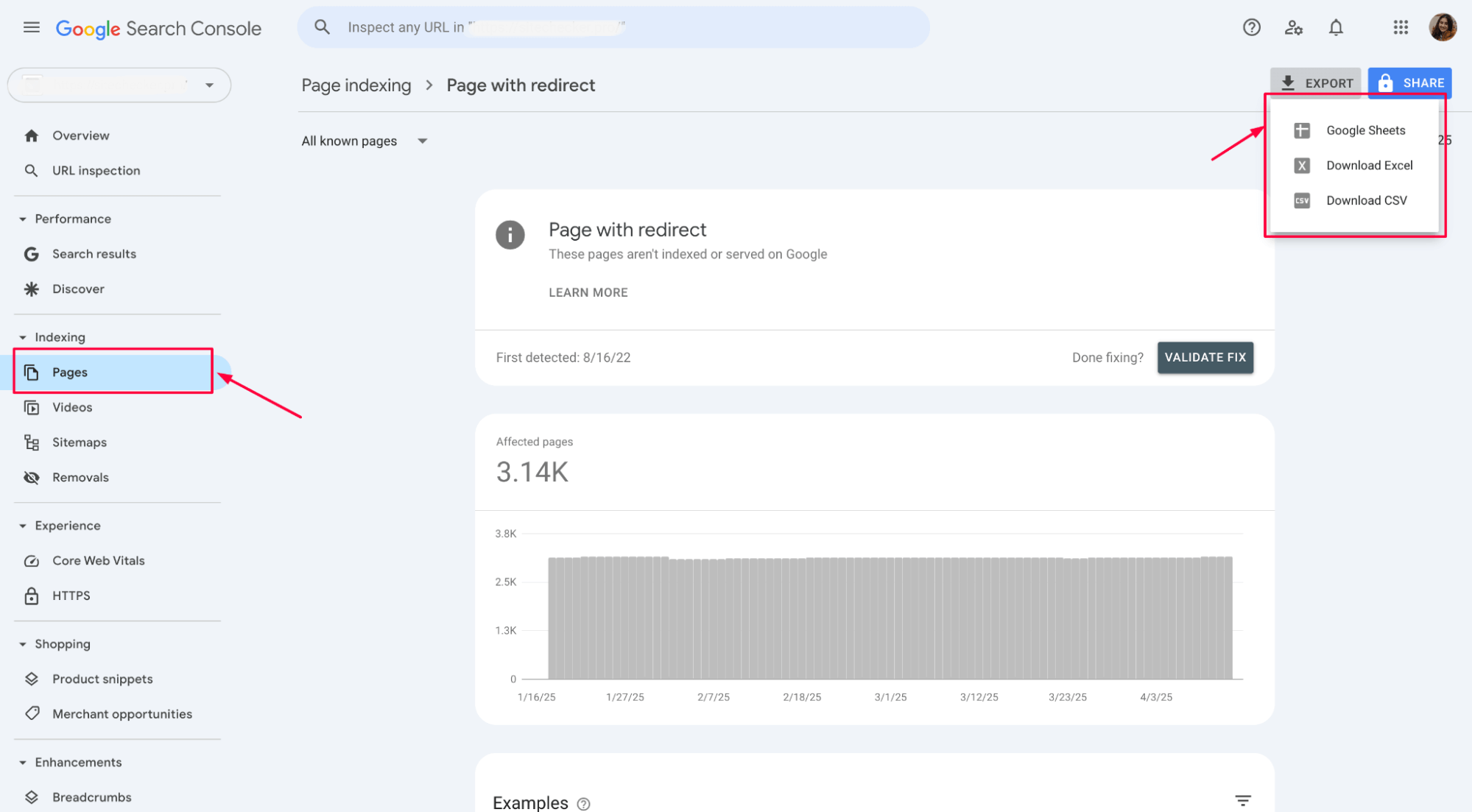
6. Validate and confirm fixes in Google Search Console
After you have resolved all redirect issues, updated the canonical tags, and ensured proper redirects, you can use the “Validate Fix” feature in Google Search Console to confirm the problems are resolved.
Once you’ve addressed the “Page with Redirect” error, click the “Validate Fix” button in the Google Search Console interface. This action triggers Google to re-crawl the affected pages to ensure the redirects are now correctly configured and that the pages are indexed properly.
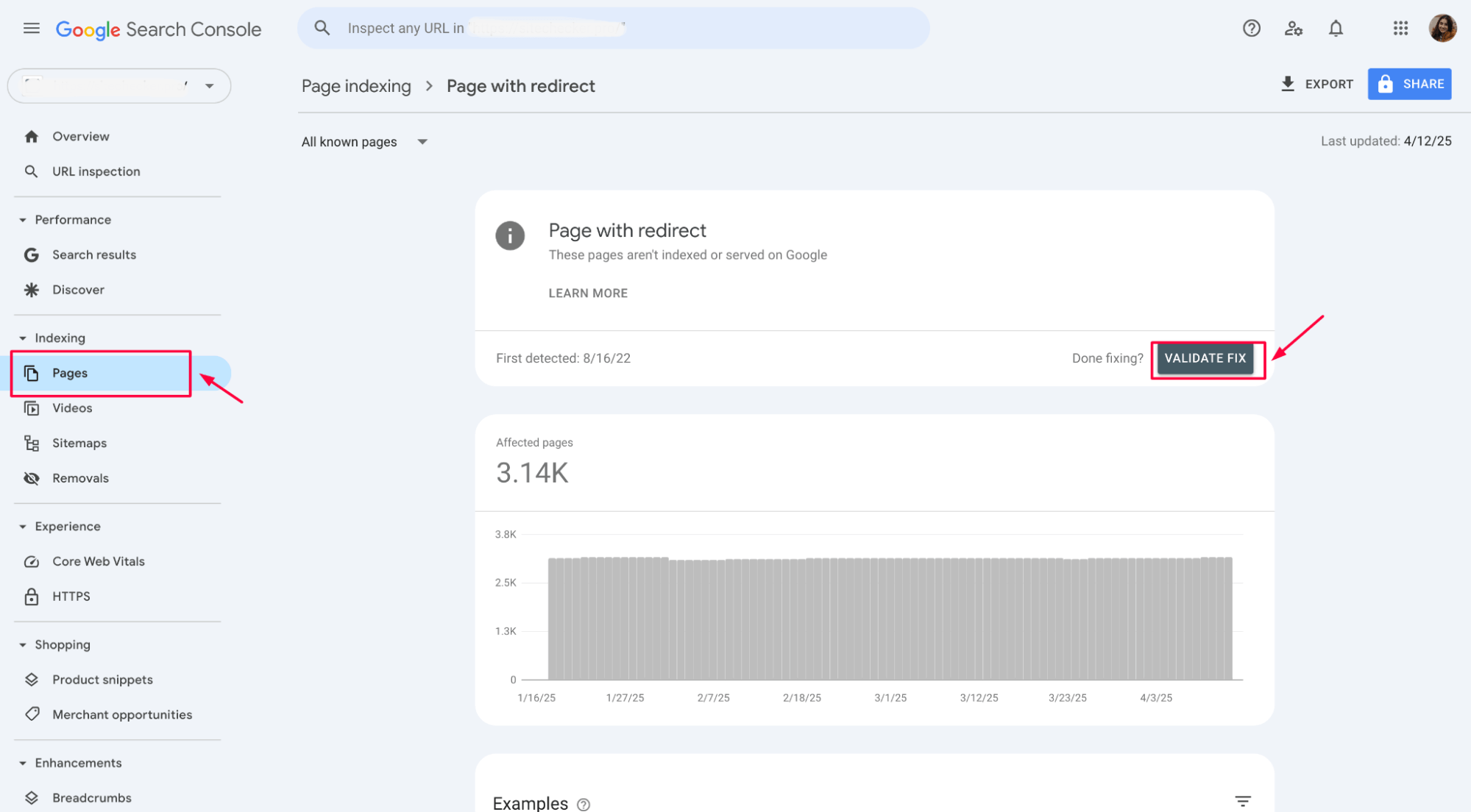
If Google detects that the issues have been fixed, the error status will be updated, and the affected pages will no longer be flagged.
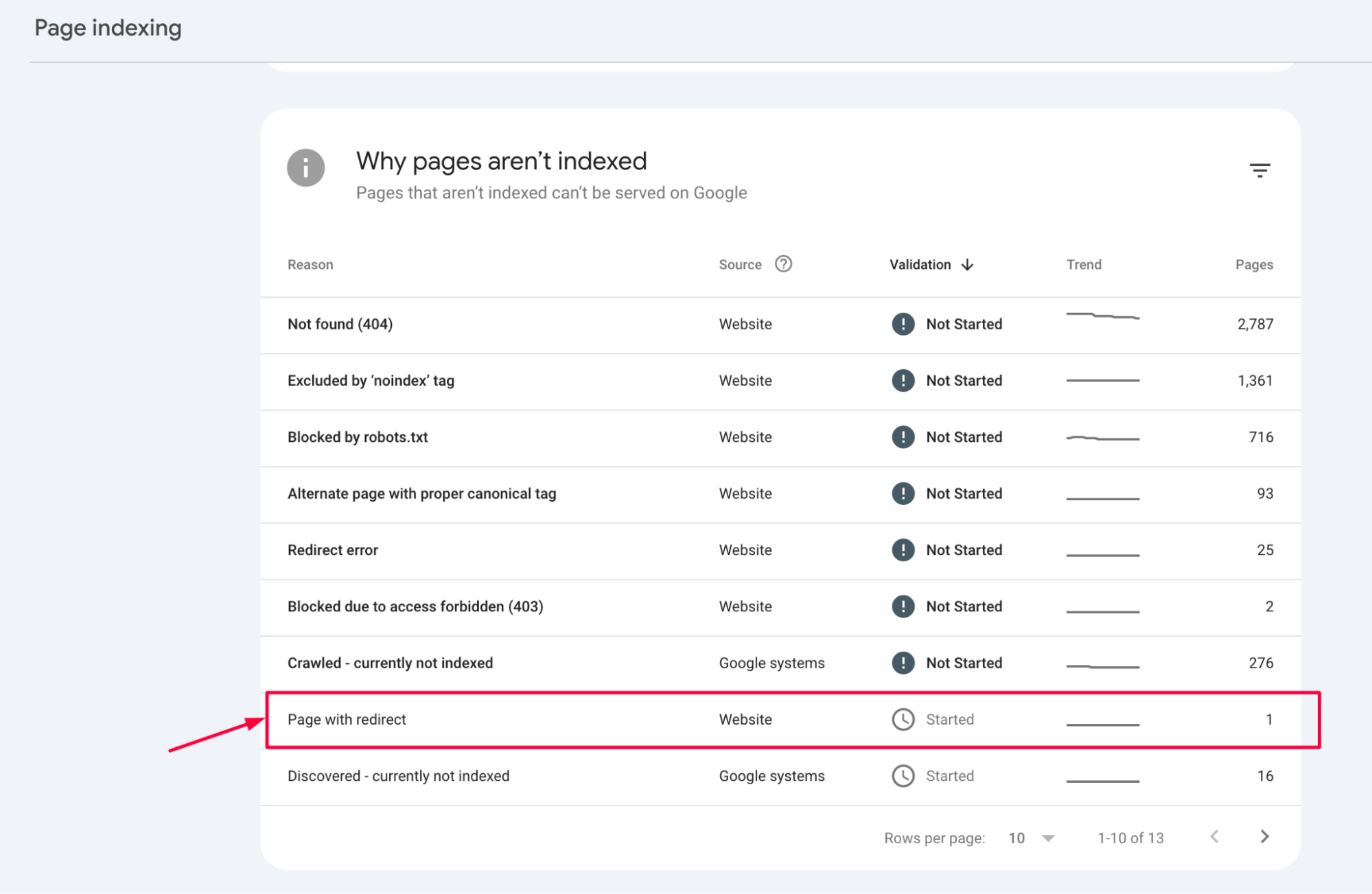
The validation process typically takes 1-2 weeks, depending on the number of pages and your website’s crawl frequency.
Once Google confirms that the issues have been resolved, the error status will be updated, and the affected pages will no longer be flagged.
Regularly monitor redirects and canonical tags
You can use Website Monitoring to detect when redirect issues and canonical tag problems occur on your website. This tool continuously monitors your website for any changes or errors, including:
- Redirect chains: Identifies when multiple redirects occur before reaching the final destination.
- Pages with 3xx status codes: Highlights pages with redirects, potentially indicating issues with indexing or SEO.
- Incorrect or missing canonical tags: This detection system detects pages with improperly configured or missing canonical tags, which could cause duplicate content issues.
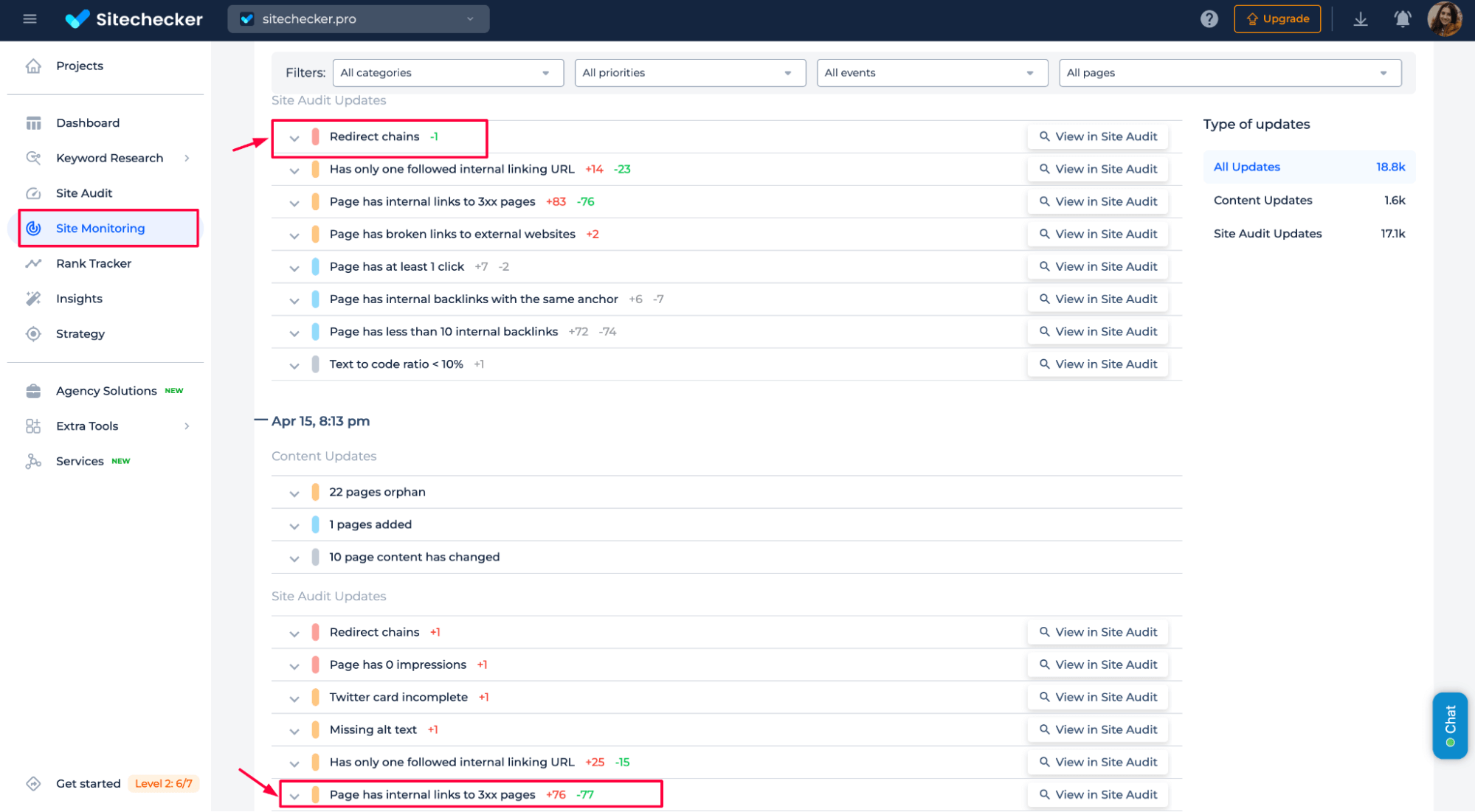
By regularly using this tool, you can easily spot these issues, address them, and quickly optimize your site for search engines.
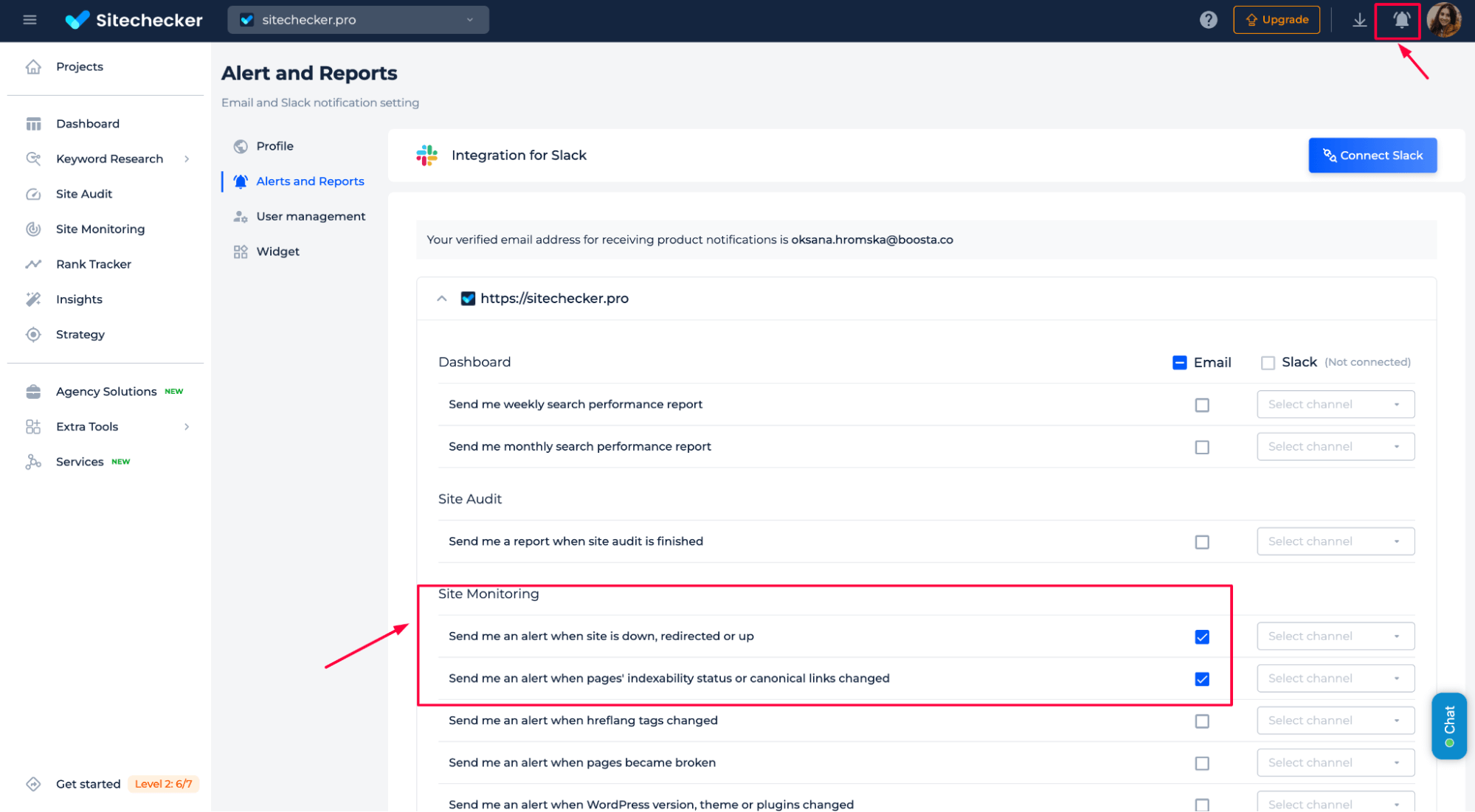
The SEO Alerts feature allows you to set up monitoring for redirect errors and canonical tag issues.
To set up monitoring for redirect and canonical errors, you can configure alerts to notify you via email or Slack when:
- Pages are redirected incorrectly.
- Canonical tags are misconfigured or changed.
- Indexing issues arise due to redirect or canonical errors.
This ensures that you are immediately informed of any problems and can take action to fix them, keeping your website optimized for search engines.
Conclusion
To resolve the “Page with Redirect” error in GSC, identify and fix issues like incorrect forwarding, loops, and chains. Ensure the proper types of forwarding (301 for permanent, 302 for temporary) and update canonical tags to the correct destination. Review your XML sitemap to remove forwarded URLs and include the final destination pages.
You can also use the Removal Tool to temporarily remove outdated pages. GSC’s “Validate Fix” feature helps confirm your fixes.
Regularly monitor your site with tools like SiteChecker to detect and address forwarding and canonical tag issues.