What is Keyword Cannibalization?
Keyword cannibalization might sound ominous, but its concept is straightforward in the realm of Search Engine Optimization (SEO). It refers to a situation where multiple pages from the same website compete for the same or similar keywords in search engine results pages (SERPs). This internal competition can potentially dilute the SEO value of your pages, making it harder for any single page to rank well.
Imagine you own a website that sells handmade shoes. You have separate pages for “handmade leather shoes” and “artisanal shoe designs.” If both these pages are optimized for the keyword “handmade shoes,” search engines may get confused about which page to rank higher when someone searches for that term. Instead of one strong page that could rank at the top, you end up with two weaker pages that might rank lower.
What Causes Keyword Cannibalization?
| Content Overlap | This is the most common cause. If you have multiple articles or pages on similar topics, it’s easy for keyword overlap to occur. |
| URL Structure | Poorly structured websites might have different URLs for slight variations of the same content, leading to unintentional cannibalization. |
| Meta Information Overlap | Sometimes, even if the content on two pages is different, having similar meta titles and descriptions can cause them to compete for the same keywords. |
| Internal Linking with Inconsistent Anchor Text | Using different anchor texts pointing to different pages can sometimes confuse search engines about which page is more relevant for a particular keyword. |
Understanding keyword cannibalization is the first step to identifying it on your website. By being aware of this phenomenon, you can ensure that your SEO efforts are streamlined and that you’re not inadvertently pitting your pages against each other.
Google About Keyword Cannibalization
John Mueller, a Google Search Liaison, has tweeted about keyword cannibalization on several occasions. Here are a few of his key insights:
- Keyword cannibalization happens when multiple pages on your website target the same keyword. This can confuse Google and make it difficult to determine which page is the most relevant to a particular search query. As a result, both pages may rank lower than they would if they were targeting different keywords.
- Keyword cannibalization is not a black hat SEO tactic. Google does not penalize websites for keyword cannibalization. However, it can still have a negative impact on your rankings.
- The best way to avoid keyword cannibalization is to carefully plan your content strategy. Make sure that each page on your website targets a unique keyword or set of keywords. If you have multiple pages that cover similar topics, try to differentiate them by focusing on different aspects of the topic or by targeting different audiences.
- If you think you may have keyword cannibalization on your website, you can use a variety of tools to identify the affected pages. Once you have identified the problem, you can fix it by merging or redirecting the affected pages, or by rewriting the content on one or more of the pages to target a different keyword.
Here are some specific examples of John Mueller’s tweets about keyword cannibalization:
Seeing a list like that as a target for content makes me worry that you're not going to get a lot out of your work, or that your work is going to be quite superficial.
I'd look for topics that match your expertise & passion. Where can you contribute that isn't already covered by lots of others, and do so in ways that provide something new & useful?
Why SEO Keyword Cannibalization is Harmful
Keyword cannibalization isn’t just a buzzword; it poses genuine challenges for your website’s SEO. When multiple pages on your website vie for the same keyword, they end up competing against each other in the search results. This internal tug-of-war can lead to several negative impacts on your website’s overall search performance. Let’s delve into why keyword cannibalization can be detrimental.
Search Engines Get Confused
When several pages on your site target the same keyword, search engines can have difficulty determining which page is the most relevant for a particular search query. Instead of promoting one strong, definitive page, search engines might flip-flop between the pages, leading to fluctuating rankings and unpredictability in your site’s SERP performance. This confusion can prevent your most valuable content from achieving the high rankings it deserves.
It Weakens Off-Page Optimization
Backlinks are a cornerstone of off-page SEO. When external sites link to your content, they usually choose the page they find most relevant or authoritative. However, if you have multiple pages targeting the same keyword, these backlinks can get scattered among these pages. Instead of one page accruing strong backlink authority, the link juice gets distributed, weakening the potential ranking power of each page.
Internal Linking Weight Diminishes
Internal linking is a powerful SEO tool, as it helps distribute page authority throughout your site. However, if multiple pages target the same keywords, your internal linking strategy can become convoluted. You might end up linking to different pages with the same anchor text, leading search engines to question the true relevance and authority of each page. This can dilute the SEO value of your internal links and diminish the potential of your pages to rank.
Users Behavior Gets Worse
From a user experience perspective, encountering multiple pages on the same topic can be confusing and redundant. If visitors find similar content spread across different pages, they might struggle to locate the exact information they’re after. This can lead to increased bounce rates, reduced time on site, and overall dissatisfaction, which search engines might interpret as your site being less valuable or relevant.
Crawl Budget Gets Wasted
Search engines allocate a specific crawl budget to each website, which determines how often and how deep a site gets crawled. If you have multiple pages with similar content, search engines might waste their crawl budget on these redundant pages instead of discovering and indexing other valuable content on your site. Over time, this can impede the visibility of your website’s diverse content in search results.
In essence, while targeting a variety of keywords and topics is essential for SEO, it’s equally crucial to ensure that your efforts are not cannibalizing your own rankings. Recognizing and rectifying keyword cannibalization can lead to a more cohesive SEO strategy and improved search performance.
Is Keyword Cannibalization Always Bad?
Keyword cannibalization is often discussed in cautionary terms within the SEO community. The idea of your own pages competing against each other in search results can indeed have several negative implications, as we’ve explored. However, it’s essential to approach this concept with nuance. Keyword cannibalization isn’t always detrimental, and in some cases, it might even be indicative of a robust content strategy. Let’s examine when keyword cannibalization might not be as bad as it’s made out to be.
Multiple Intents for a Single Keyword
Sometimes a keyword can have multiple user intents behind it. For instance, the search term “apple” could refer to the fruit, the tech company, or even a music record label. In cases like these, having different pages optimized for each intent can be beneficial. A user might find a general overview page, a detailed guide, a comparison, or even an opinion piece—all targeting different aspects of the same keyword but serving different user needs.
Dominating the SERP
In some instances, having multiple pages rank for the same keyword can allow a website to dominate the search engine results page (SERP). This can increase the likelihood of a user clicking on one of your links, effectively pushing down competitors and occupying more real estate on the SERP.
Content Freshness and Evolution
As websites grow and evolve, new content gets created, and older content gets updated. This evolution can sometimes lead to accidental keyword overlap, especially if newer articles address topics similar to older ones. However, this overlap might not always be problematic. Search engines often prioritize fresh content, and if your newer content starts ranking higher, it might be an indication for you to revisit and update older articles.
Opportunity for Content Consolidation
Recognizing keyword cannibalization can present an opportunity. Instead of viewing it as a problem, see it as a chance to consolidate, refine, and strengthen your content. Merging overlapping articles or interlinking them to provide a broader perspective can enhance user experience and SEO performance.
What to Look for: Keyword Cannibalization Red Flags
Recognizing keyword cannibalization early on can prevent a lot of SEO troubles down the road. While you might not see an immediate drop in your overall traffic, subtle shifts and patterns in your analytics can hint at underlying issues. Here are some red flags that suggest your site might be experiencing keyword cannibalization:
URL Rankings Constantly Change
If you notice that different URLs from your site alternate positions for a specific keyword over a short period, it’s a classic sign of cannibalization. Instead of a stable, high-ranking URL for that keyword, search engines are frequently re-evaluating which of your pages is the most relevant. This constant shuffle can prevent any of your pages from achieving a strong, consistent position in the SERPs.
Ranking Fluctuations
Minor fluctuations in keyword rankings are typical and can result from a multitude of factors like algorithm updates or increased competition. However, if you observe significant swings in rankings for a specific keyword—where one week you’re in the top 5 and the next you’re beyond the top 20—it could suggest that search engines are struggling to determine the best page from your site for that keyword.
Ranking Queries Don’t Move Up in the SERP
You’ve optimized a page, built backlinks, and promoted it extensively. Despite these efforts, the page doesn’t seem to move up the rankings. If other pages from your site appear for the same keyword, they might be siphoning off the SEO value, effectively stagnating the rise of your primary page in the SERPs.
The Wrong URL is Ranking for the Right Keyword
Say you’ve crafted a comprehensive guide on “Organic Farming Techniques,” but when you search for that keyword, your blog post on “The History of Organic Farming” ranks instead. This mismatch indicates that search engines might be confused about the relevance and intent of your pages. It’s a sign that multiple pages on your site are competing for the same keyword, and not necessarily the one you intended.
How to Find Cannibalized Keywords
Identifying keyword cannibalization is crucial before taking steps to resolve it. If you’re unaware of the problem, you can’t address it. Fortunately, there are several tools and methods to help you pinpoint instances of keyword cannibalization on your website. Let’s discuss some effective techniques:
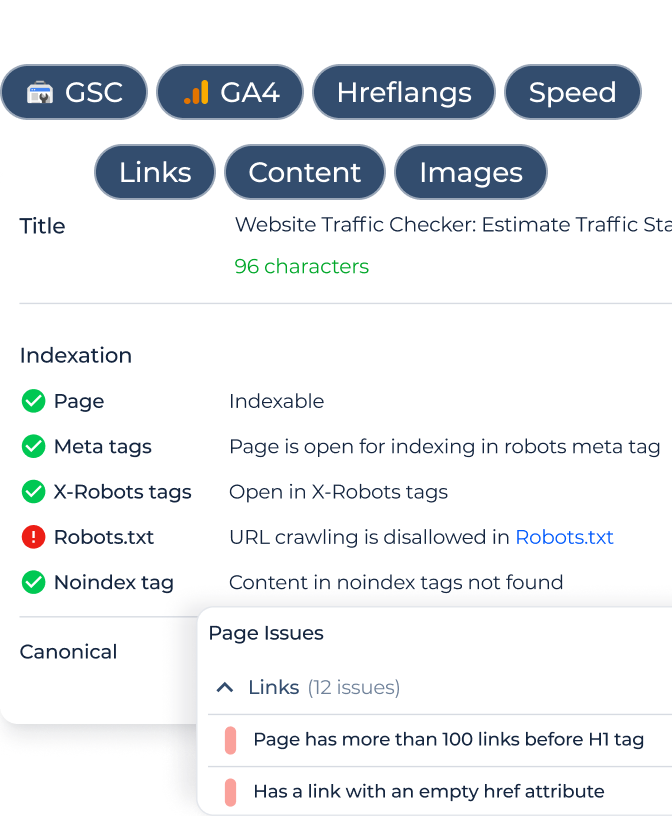
Google Search Console
Google Search Console (GSC) is a free tool from Google that offers a plethora of insights about your website’s search performance. Here’s how you can use it to detect keyword cannibalization:
-
Performance Report: Navigate to the ‘Performance’ section of GSC. Here, you’ll see a list of queries for which your website has appeared in the search results.
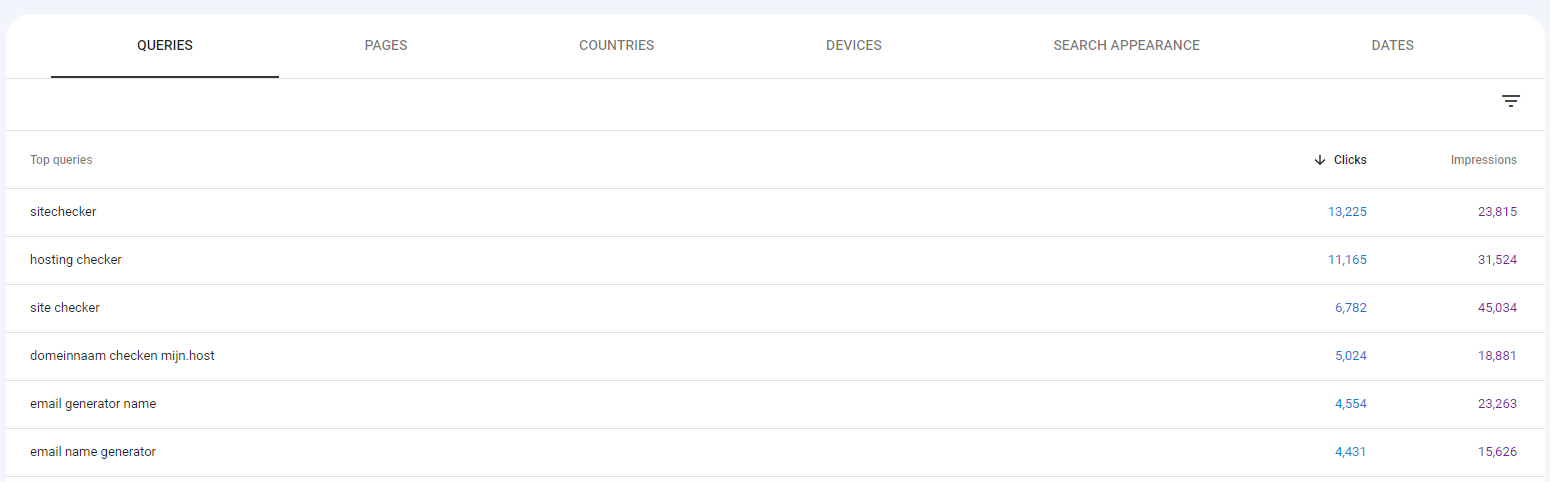
-
Check Multiple URLs: For each query, you can see the number of clicks, impressions, average CTR (click-through rate), and average position. By clicking on a specific query, you’ll be able to see which URLs from your site are ranking for that keyword.
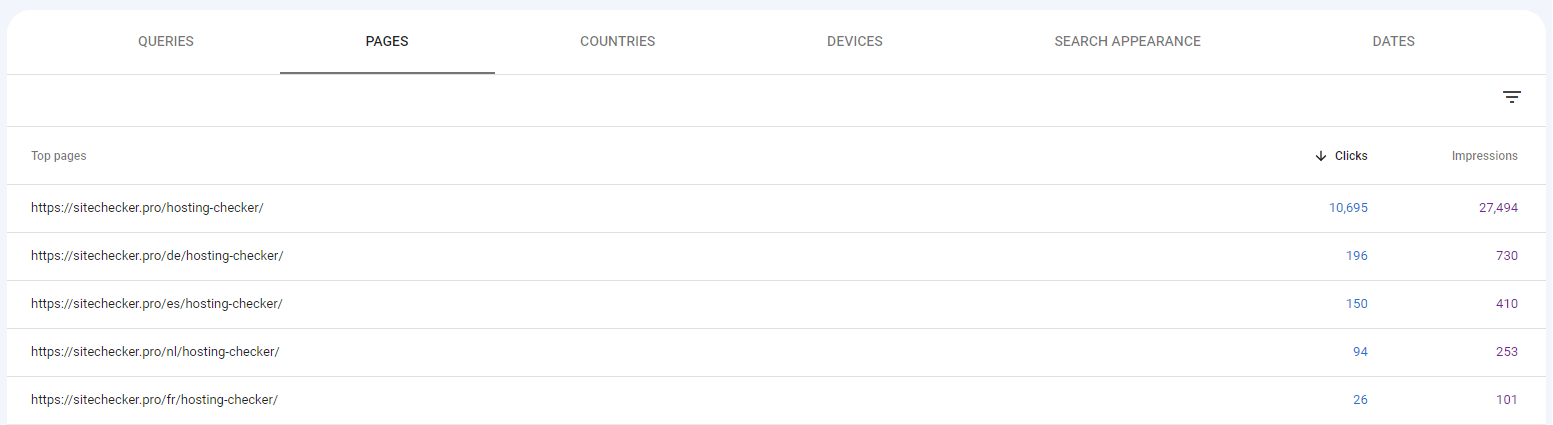
- Identify Overlaps: If more than one URL from your site is appearing for a single query, it’s an indication of potential cannibalization. Take note of these queries and corresponding URLs.
- Analyze Position Data: If the positions of these URLs frequently change or if they’re closely ranked, it further confirms the cannibalization issue.
Search Your Site
A straightforward way to identify overlapping keyword targets is by manually searching your site:
- Site: Search on Google: Use the “site:” operator followed by your website’s domain and the keyword in question. For example: “site: yourwebsite.com keyword”. This will display all the pages from your site indexed by Google for that keyword.
- Review Titles and Meta Descriptions: By looking at the search results, check if multiple pages have similar titles or meta descriptions targeting the same keyword.
- Analyze Content: Click through to the pages to ensure that they indeed have overlapping content. Sometimes, pages might appear in the search results due to a single mention of the keyword, which might not necessarily indicate cannibalization.
- Internal Search: If your website has a search function, use it! Input your target keywords to see how many pages come up. This can be especially helpful for large websites with vast amounts of content.
By combining the insights from Google Search Console and manual site searches, you can effectively identify cannibalized keywords and begin the process of strategizing how best to address them. Remember, the goal isn’t necessarily to eliminate all instances of overlap but to ensure that your pages are as optimized as possible for user intent and search engine clarity.
How to Fix Keyword Cannibalization
Once you’ve identified keyword cannibalization on your website, it’s crucial to address it effectively to maximize your SEO potential. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to tackle this issue:
Redirects
Utilizing 301 redirects is a handy method when you have two pages that serve nearly identical purposes:
- Choose the Strongest Page: Determine which of the conflicting pages has better traffic, more authoritative backlinks, or is more aligned with the user’s intent.
- Redirect: Implement a 301 redirect from the lesser page to the stronger one. This way, you consolidate the SEO value, and users are led to the most relevant content.
Canonical Tags
Canonical tags signal to search engines which version of a page is the “master” or preferred one:
- Implement Tag: If two pages have very similar content but both need to exist (e.g., due to targeting different audiences), you can use a canonical tag on the non-preferred page pointing to the preferred page.
- Search Engines Respect: This way, search engines will prioritize the canonical page in search results, reducing competition between the two.
Optimize Links and Content
- Re-evaluate Internal Links: Ensure that internal links use appropriate anchor text and direct users to the most relevant page for their query.
- Update Content: Modify the content on each page to better target distinct keywords or user intents.
Content Creation
When adding new content:
- Keyword Research: Always conduct fresh keyword research to ensure you’re not unknowingly targeting keywords already covered.
- Gap Analysis: Identify topics or areas you haven’t addressed yet and focus on those.
Noindex Tags
For pages you don’t want search engines to index (but you still want to keep on your site):
- Add Noindex: Implement a “noindex” tag, instructing search engines not to index that specific page.
Remove, Merge, and Redirect Non-Primary Pages
- Evaluate Value: If you have several weaker articles on the same topic, consider merging them into a comprehensive, authoritative piece.
- Redirect as Needed: Use 301 redirects to lead users from old URLs to the new, consolidated content.
Canonicalize Non-Primary Pages to the Primary Page
As previously discussed, utilize canonical tags to consolidate ranking signals.
Blocking Non-Primary Pages from Indexing
Beyond the “noindex” tag, you can also:
- Use Robots.txt: Prevent search engine crawlers from accessing certain pages or directories.
Rework Internal Linking
- Prioritize Linking: Ensure that the most important pages get the bulk of internal links.
- Avoid Conflicting Anchors: Don’t use the same anchor text to link to different pages about the same topic.
Differentiate Intents
- User Intent Analysis: Dive deep into what users are looking for with specific queries and tailor your content to match those needs.
- Diversify Content Formats: For the same keyword, one page could be a long-form guide, while another could be an infographic or video, serving different user intents.
Addressing keyword cannibalization requires a mix of technical and content-driven strategies. Regularly reviewing your site’s content and performance can help you stay ahead of potential cannibalization issues and maintain a strong SEO position.
How to Prevent Keyword Cannibalization
Strategies for Avoiding Keyword Overlap
Avoiding keyword overlap is crucial to prevent cannibalization before it even starts. Here are some strategies to ensure your pages maintain distinct keyword targets:
- Use Keyword Mapping: For every piece of content you produce, assign primary and secondary keywords. Maintain a centralized document that tracks which keywords are targeted by which pages.
- In-depth Keyword Research: Before finalizing content topics, delve deep into keyword research. Utilize tools to find related keywords, synonyms, and variations. This ensures you have a comprehensive understanding of the keyword landscape.
- Understand User Intent: Recognize that the same keyword might have different user intents. For example, someone searching for “apple” might be looking for the fruit or the tech company. Differentiating the intent allows you to craft unique content for each scenario.
Regular Audits of Keyword Performance
Regularly checking your site’s keyword performance can help identify potential overlap and other issues early on:
- Scheduled Checks: Set a regular schedule (monthly, quarterly) to review keyword performance using tools like Google Search Console, SEMrush, or Ahrefs.
- Look for Drops: If a page suddenly drops in rankings or traffic for a specific keyword, it could indicate that another page is cannibalizing its traffic.
- Monitor New Content: Whenever you add new content to your site, check how it impacts your existing content’s keyword performance.
Refined Content Strategy to Avoid Similar Topics
Being strategic about the content you produce can help you steer clear of unintentional overlaps:
- Content Calendar with Keyword Focus: When planning your content calendar, assign specific keywords to each piece. This helps you visually spot any potential overlaps before the content is even produced.
- Gap Analysis: Regularly review your existing content to identify topics or areas you haven’t covered yet. This ensures you’re always producing fresh, unique content.
- Encourage Collaboration: Ensure that writers, SEOs, and content strategists collaborate. Open communication can help identify potential overlaps and clarify content direction.
Utilize Different Formats: Even if you’re covering a similar topic, you can differentiate by using different formats. For instance, if you already have a blog post about a topic, consider creating a video or infographic for a different perspective.
Keyword Suggestion Tool to Find Profitable Keyword Ideas for SEO
The Keyword Suggestion Tool from SiteChecker is a crucial companion for digital marketers aiming to sharpen their SEO and PPC strategies. By inputting a primary keyword, the tool effortlessly churns out a list of related keywords, complete with vital statistics like search volume and competition level. This not only aids in identifying high-potential keywords for campaign targeting but also helps in uncovering new, untapped opportunities within your niche.
Additional features of this tool elevate its utility, offering deeper keyword analysis that includes seasonality trends and cost-per-click data for PPC. It also suggests long-tail keywords, which are invaluable for targeting more specific queries that could lead to higher conversion rates. With its comprehensive approach, the Keyword Suggestion Tool from SiteChecker empowers users to craft more effective and data-driven SEO and PPC campaigns.
Get Top Keyword Suggestions!
Start building more effective SEO and PPC strategies today.
Conclusion
Keyword cannibalization is an often-overlooked aspect of SEO that can significantly hamper a site’s performance in search rankings. By ensuring that individual pages on your site aren’t competing against each other for the same keywords, you can optimize each page’s potential to rank well and provide clear, distinct value to users. Regular monitoring, strategic content planning, and a keen understanding of user intent are pivotal in preventing and addressing cannibalization issues. Remember, the aim is to provide the best possible content for each query, and ensuring your pages aren’t stepping on each other’s toes is a big part of that. Stay vigilant, adapt, and continually refine your approach to keep your content distinct and valuable.