Understanding Google’s URL removal process
Managing what appears in Google’s search results is crucial for maintaining your online presence. Whether you want to remove outdated content, protect sensitive information, or manage SEO strategy, knowing how Google indexes and ranks pages will help you take the right approach.
Google’s indexing process follows three key steps:
- Crawling: Googlebot discovers new pages through links, sitemaps, and previous crawl data.
- Indexing: Once a page is crawled, Google processes its content, extracting text, metadata, and other relevant information.
- Ranking: Indexed pages are evaluated based on relevance, quality, and ranking signals to determine their position in search results.
When managing content visibility, it’s essential to understand how to remove or hide URLs from Google Search, whether temporarily or permanently. The following sections outline different methods to control URL visibility effectively.
Overview of Google’s removal policies
Temporary hiding
Through Google Search Console, site managers can temporarily shield pages from appearing in search results – a tactical pause for content updates, without lasting impacts. This temporary concealment lasts approximately six months.
Ensuring permanent removal
To permanently erase a URL from search indices, the page must either be inaccessible (indicated by a 404 or 410 status) or explicitly blocked via a robots.txt file or noindex tag. Following these changes, a re-crawl request via Google Search Console can expedite the removal from Google’s index.
Navigating legal removals
Google demands a formal procedure for content removal under legal constraints. Requesters need to provide substantial legal justification to support the removal of URLs infringing on copyright or privacy.
Launch Sitechecker’s GSC Dashboard to boost your Search Console reporting!
Expand GSC Data Limits
Bypass Google’s 1,000-row cap and unlock up to 36 months of Search Console history in a single dashboard.
Temporary removal & permanent removal
To effectively manage your content’s visibility on Google, it’s crucial to understand the distinct approaches of temporary and permanent URL removal. The table below highlights the differences between these two methods, helping you choose the right strategy based on your specific needs.
Comparison of temporary vs. permanent URL removal in Google Search Console
| Temporary Removal | Permanent Removal | |
| Duration | Conceals the URL for approximately six months, providing a window for making changes without public visibility. | Removes the URL indefinitely, ensuring it does not reappear in search results, barring re-indexation under new conditions. |
| Use Cases | Best suited for content updates, website redesigns, or sensitive issues needing immediate but temporary action. | Removes the URL indefinitely, ensuring it does not reappear in search results, barring re-indexation under new conditions. |
| Mechanism | Executed via Google Search Console, this process doesn’t delete the URL from Google’s index; it simply hides it from search results for a set period. | Achieved by ensuring the URL returns a 404 or 410 status, implementing a noindex directive, or blocking it via robots.txt. A subsequent re-crawl request through Google Search Console solidifies the removal from the index. |
Understanding these distinctions is critical for effectively managing how your content appears online, ensuring that your approach to URL visibility aligns seamlessly with your broader digital strategy.
Using Google Search Console for removal
Google Search Console is an indispensable tool for website administrators aiming to control their site’s visibility in Google search results. It offers robust options for temporary and permanent page removal from Google’s index. Whether you need to quickly hide a page or remove it indefinitely, here’s how to effectively use Google Search Console for various removal scenarios:
Temporary removals in Google Search Console
Temporary removals in Google Search Console allow you to quickly hide web pages from Google’s search results while you address content updates or other issues. This feature is particularly useful for managing content visibility without permanently altering your site’s Google index status. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to perform a temporary removal:
1. Log into Google Search Console
2. Select the property
Navigate to the specific property (website) you want to manage. Make sure you are working on the correct version of your site, considering variations like https vs. http and www vs. non-www.
3. Access the removals tool
Find the ‘Removals’ section in the left sidebar menu. This tool is dedicated to handling requests related to content visibility.
Click on ‘New Request’. You will be prompted to input the URL of the page you wish to remove temporarily:
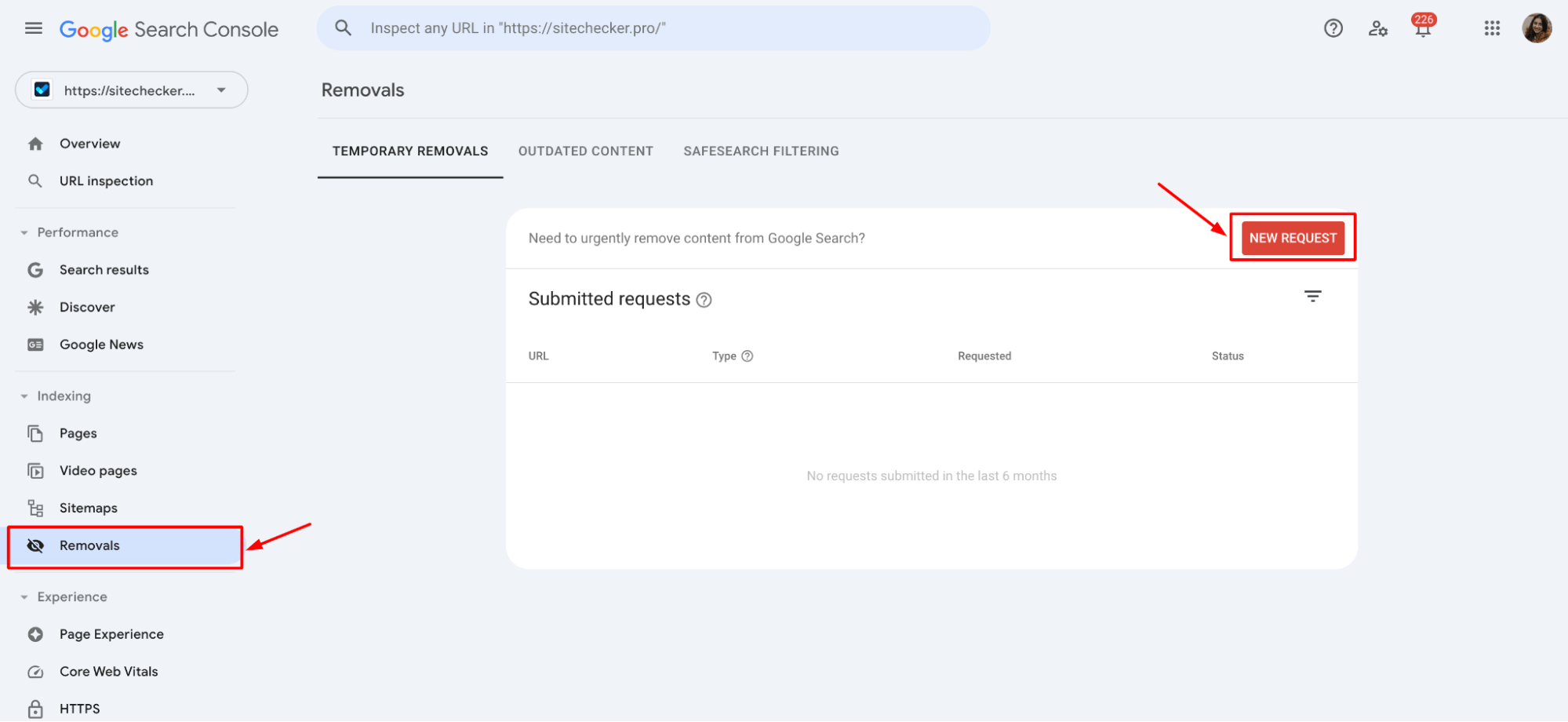
You can temporarily remove the URL, which hides the page from search results.
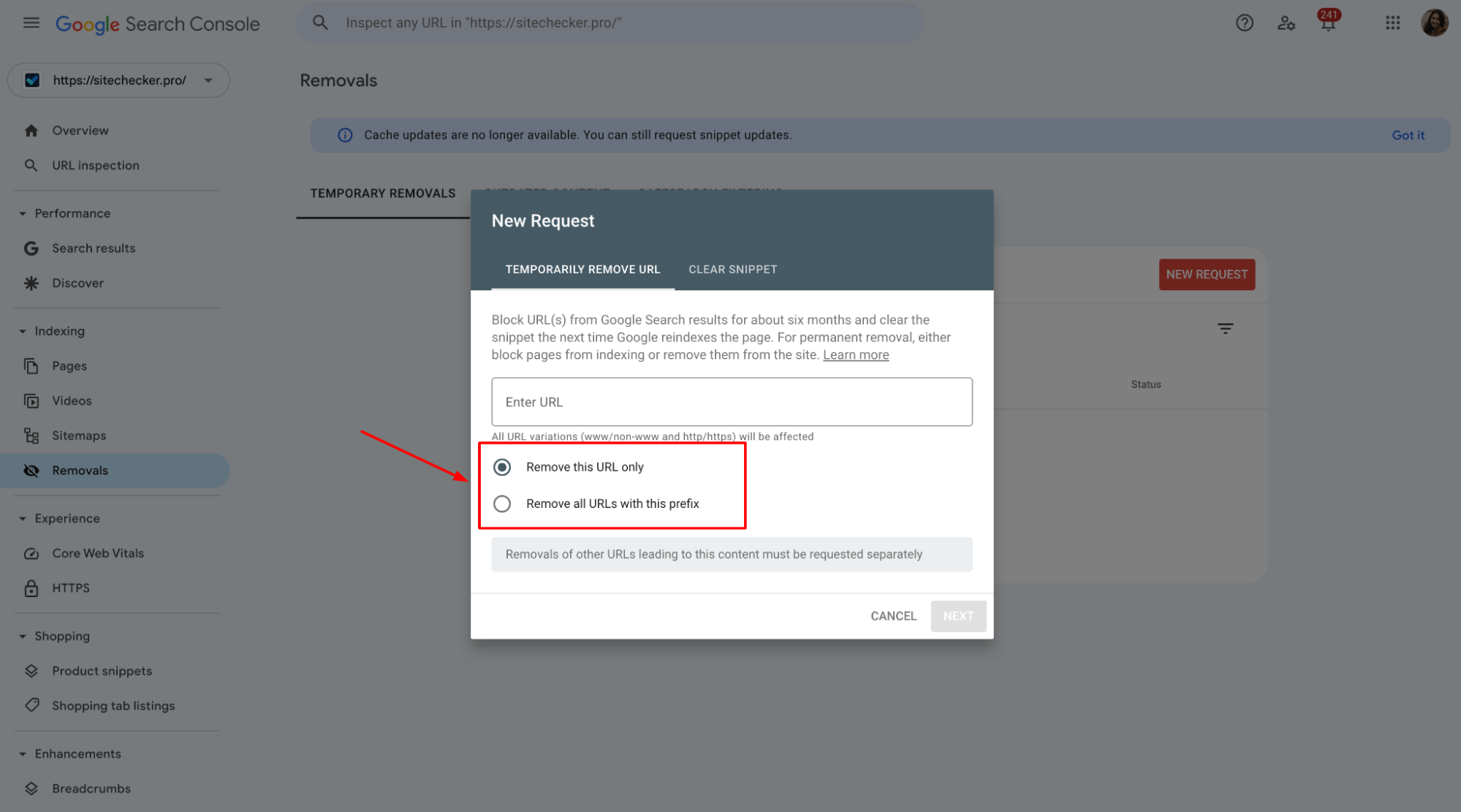
4. Specify the type of removal
The “Clear Snippet” option removes the cached page and snippet from search results while keeping the URL indexed. This is useful if sensitive or outdated content needs to be updated but the page itself remains accessible.
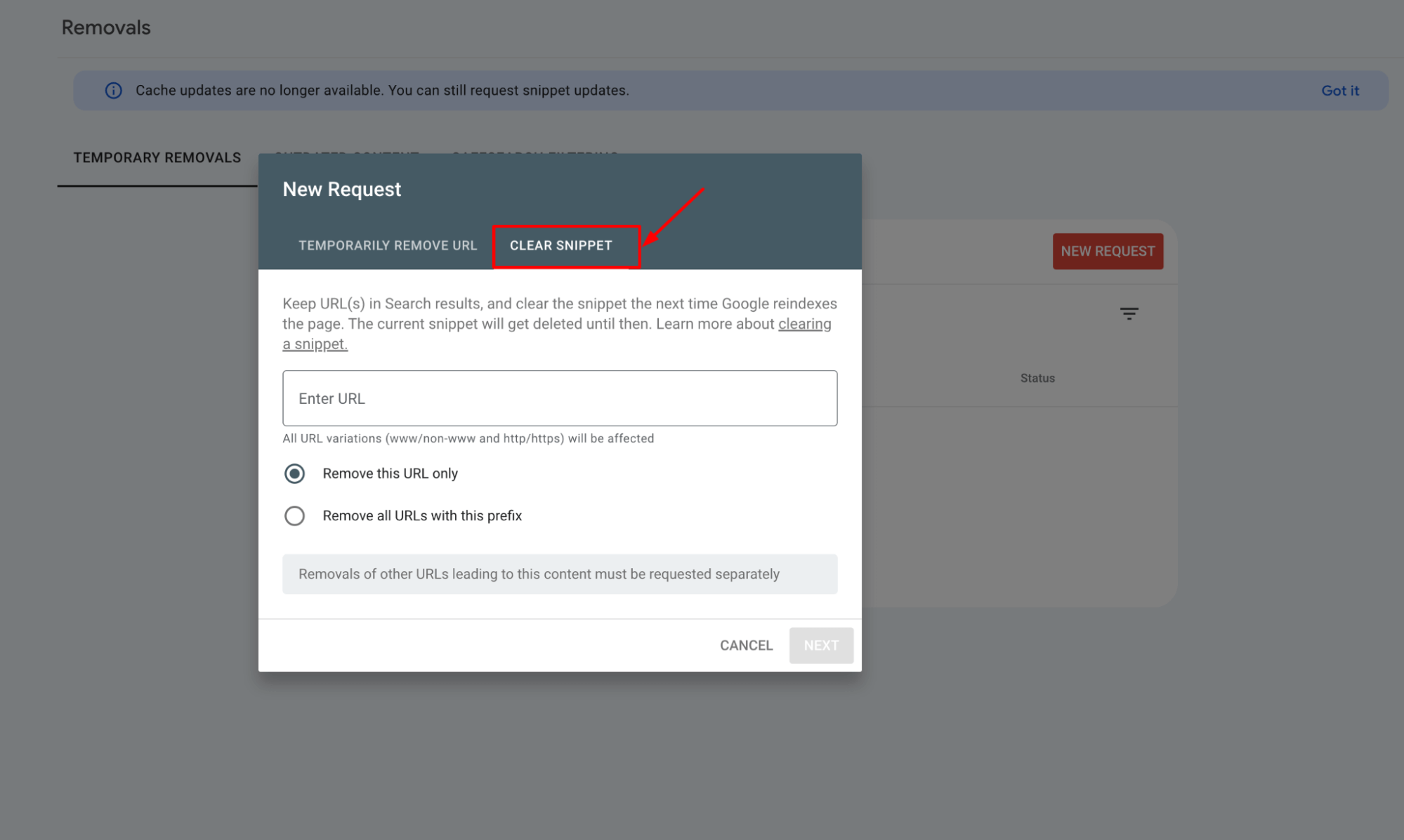
5. Submit the request
After entering the URL and choosing your removal type, submit your request. Google will process this and typically act on it quickly, usually within about a day, though it can take longer.
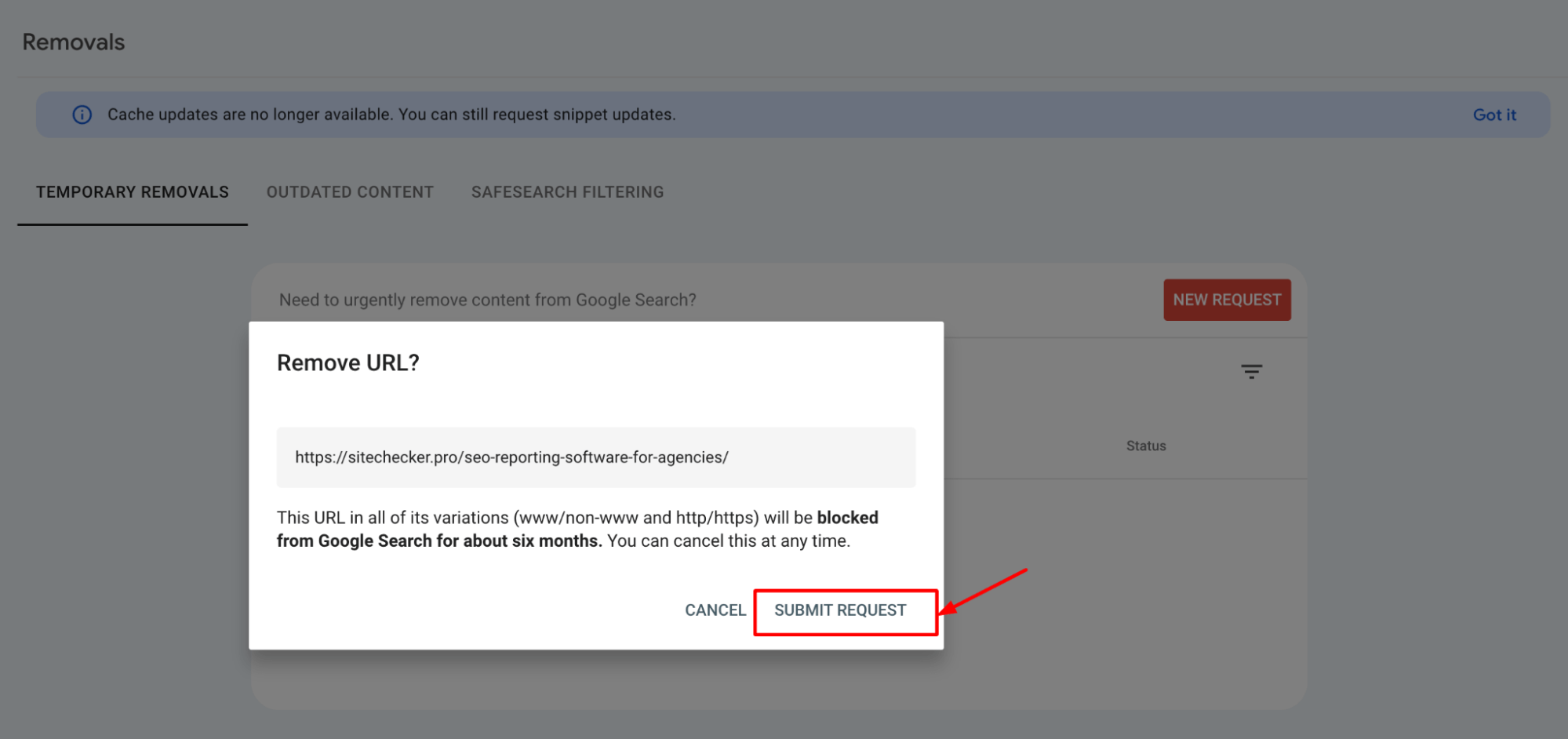
6. Review the status
Once submitted, you can track the status of your removal request in the ‘Removals’ section. It’s important to monitor this to ensure the content is hidden as expected.
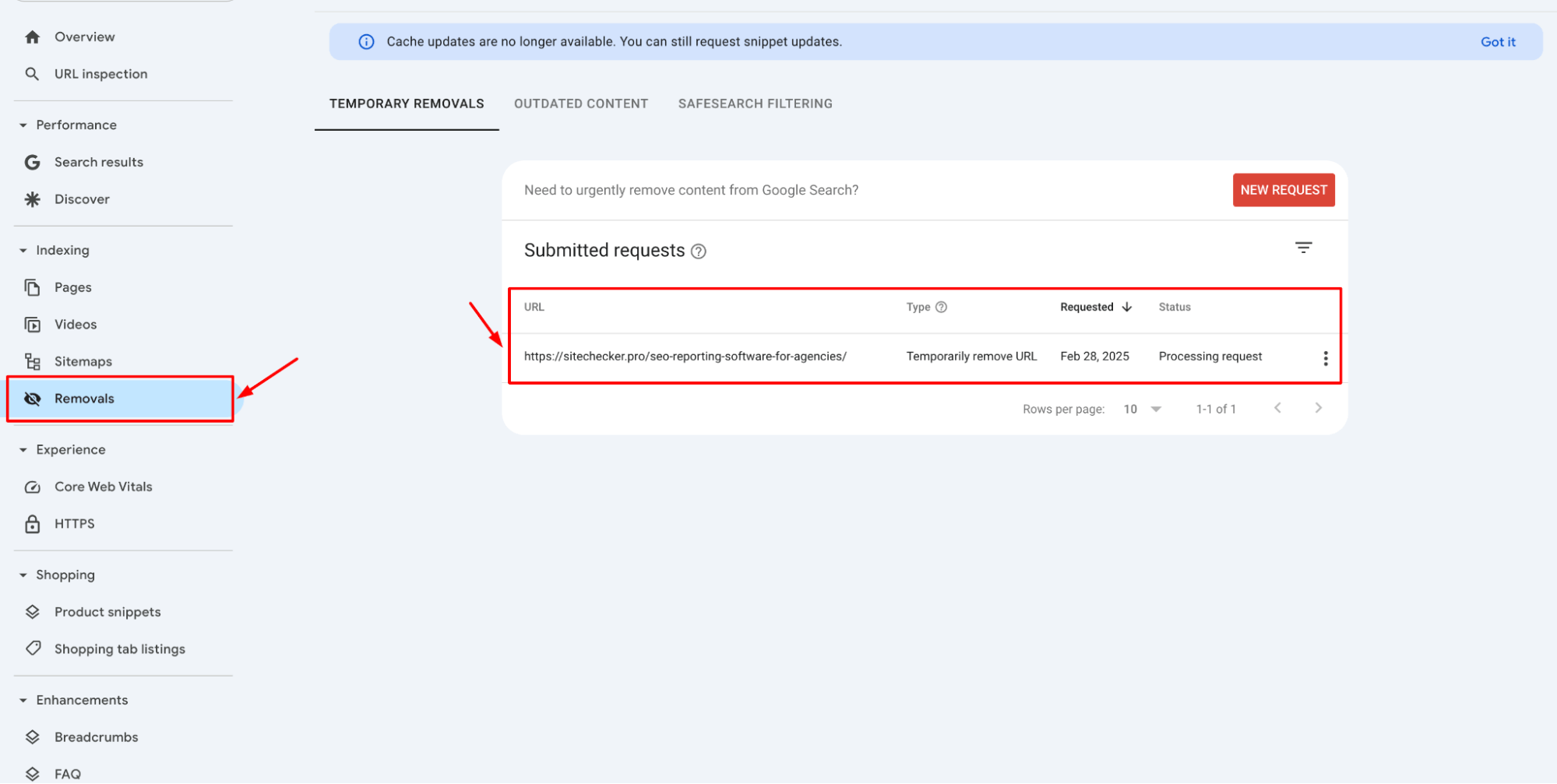
This temporary removal is effective for about six months, providing a considerable window to make necessary changes. After this period, the URL can reappear in search results unless further action is taken.
This feature is vital for SEO and content management strategies, allowing flexibility and control over how your content is presented in Google search during transitions or sensitive updates.
Permanent removals in Google Search Console
For situations requiring that a URL be removed from Google’s search results indefinitely, permanent removals via Google Search Console provide a lasting solution. This process ensures that the content does not reappear in search results, ideal for handling outdated, sensitive, or incorrect information.
Here’s how to ensure a URL is permanently removed
Before requesting a permanent removal, ensure that the URL you want to remove meets one of the following conditions: the page returns a 404 (Not Found) or 410 (Gone) HTTP status code, indicating it no longer exists.
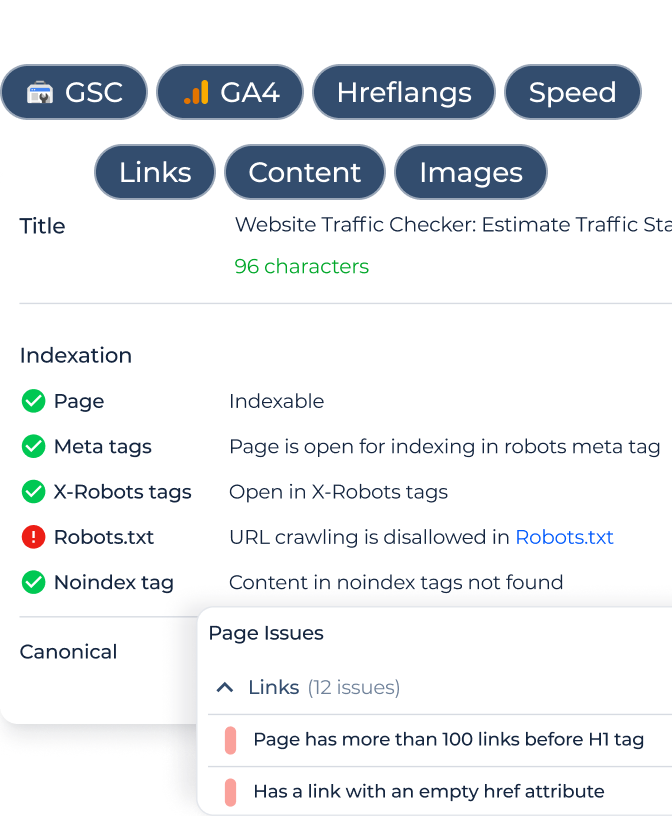
To do this, simply open the Sitechecker app and go to ‘All HTML Pages’ in the Site Audit section. Here, you can check the status of all website pages or find specific pages using the ‘Filter URL’ option.
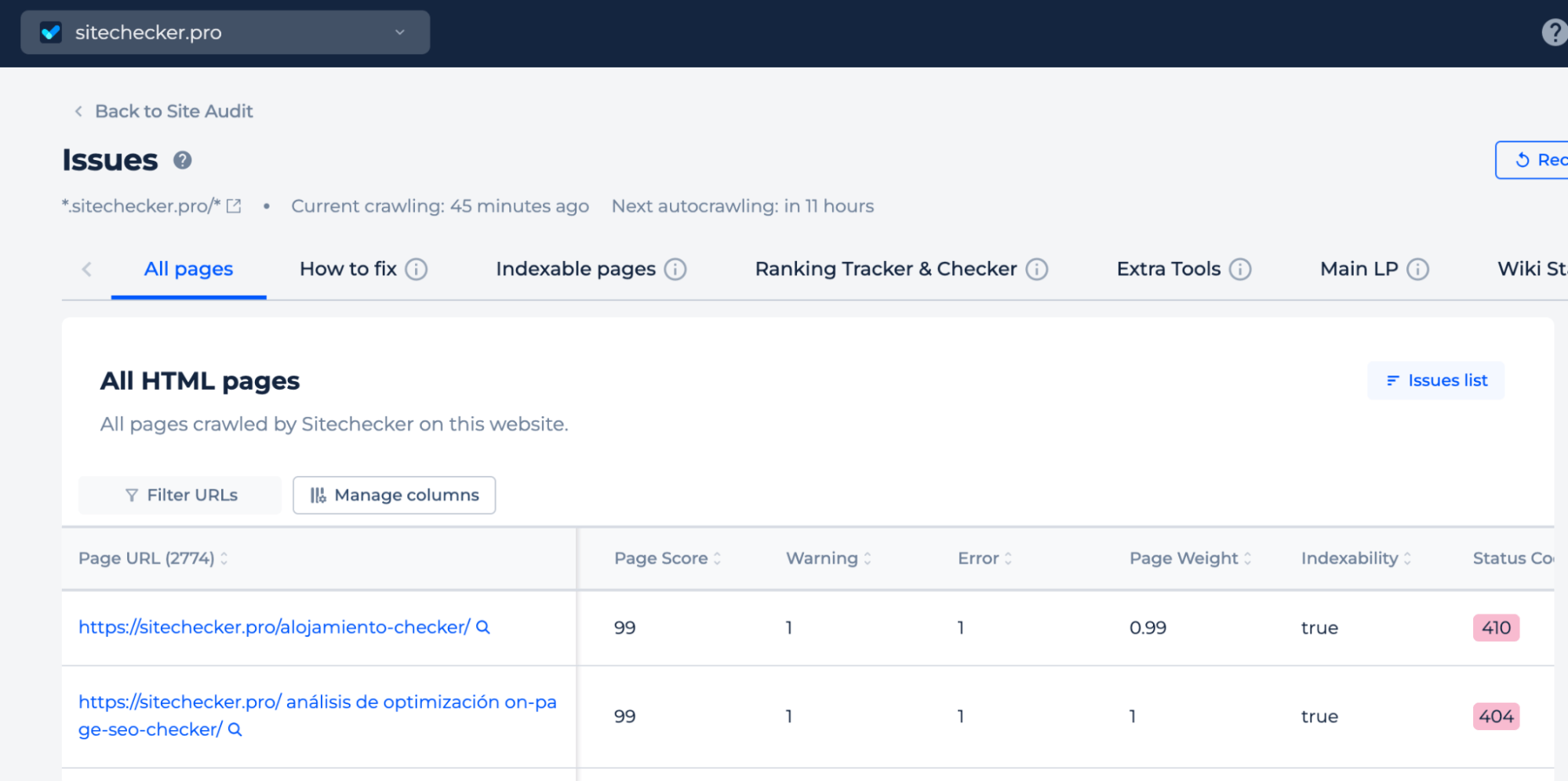
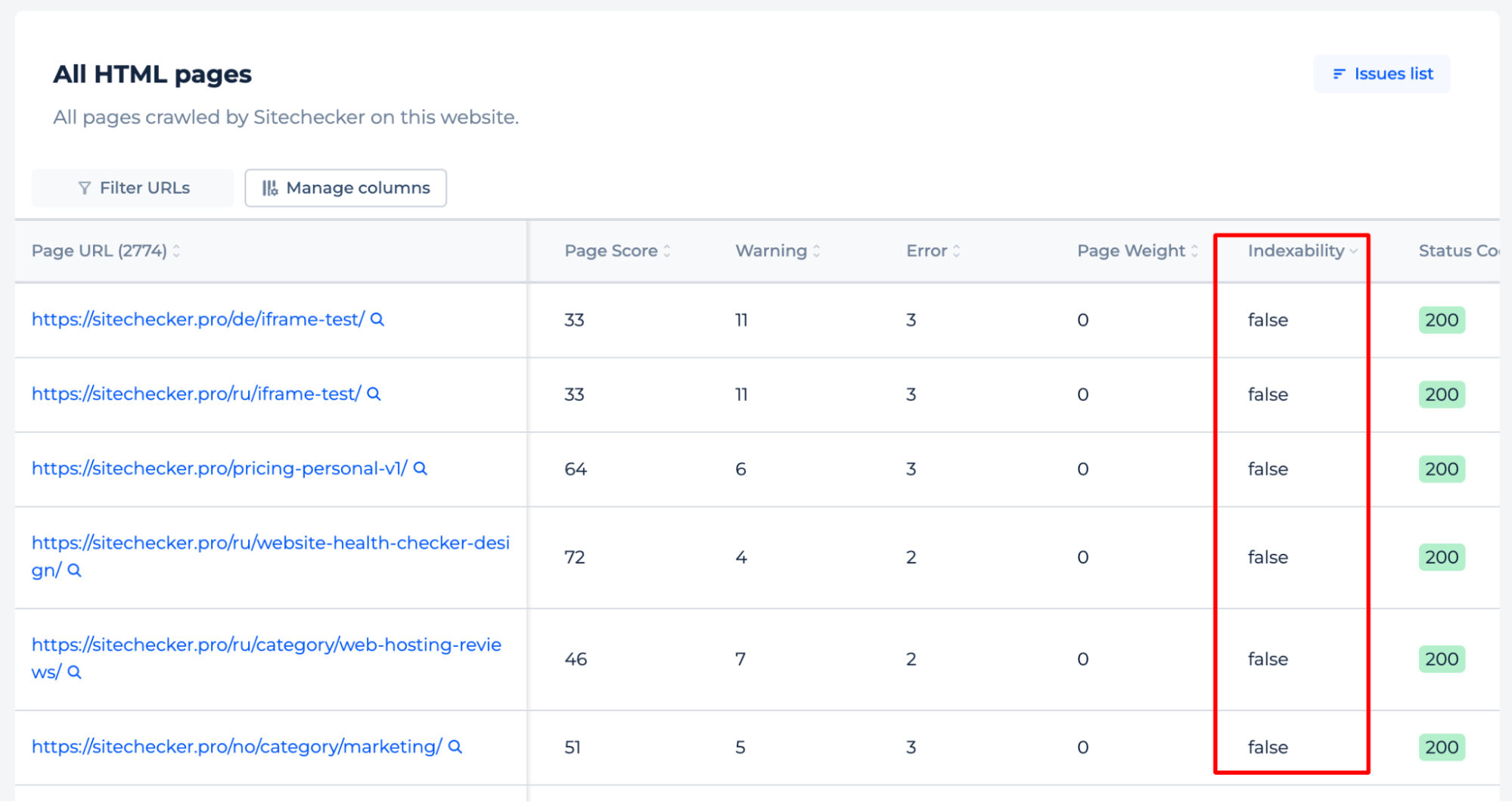
Here, you can also check the list of pages blocked from crawling by the robots.txt file or those that include a noindex tag, which tells search engines not to index the page.
How to permanently remove content in GSC
1. Log into Google Search Console
Access your account and select the appropriate property related to the URL you wish to remove.
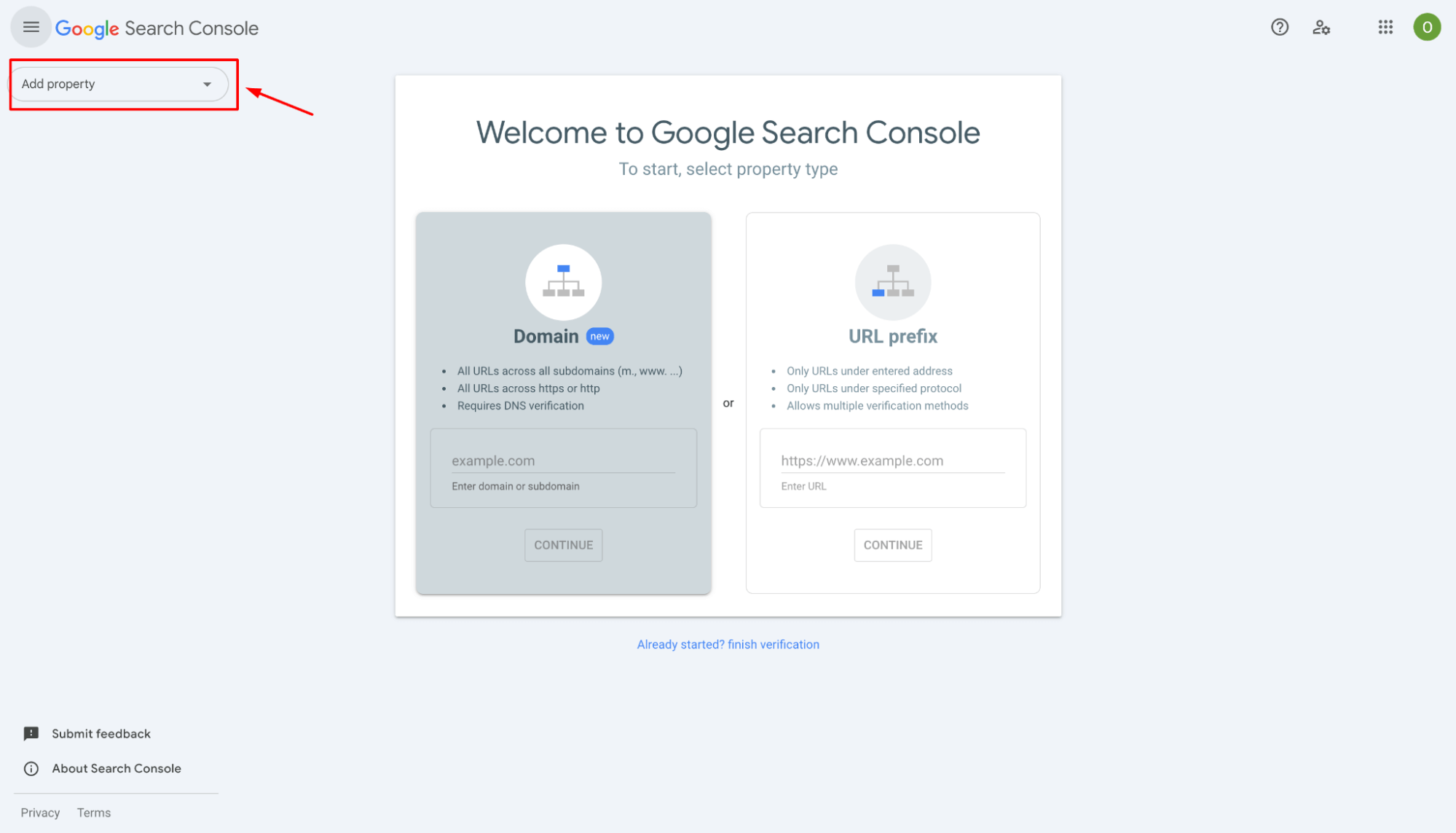
2. Use the URL Inspection tool within Google Search Console to check the current status of the URL
This will confirm whether the page is accessible, blocked, or correctly returning a status that makes it eligible for removal.
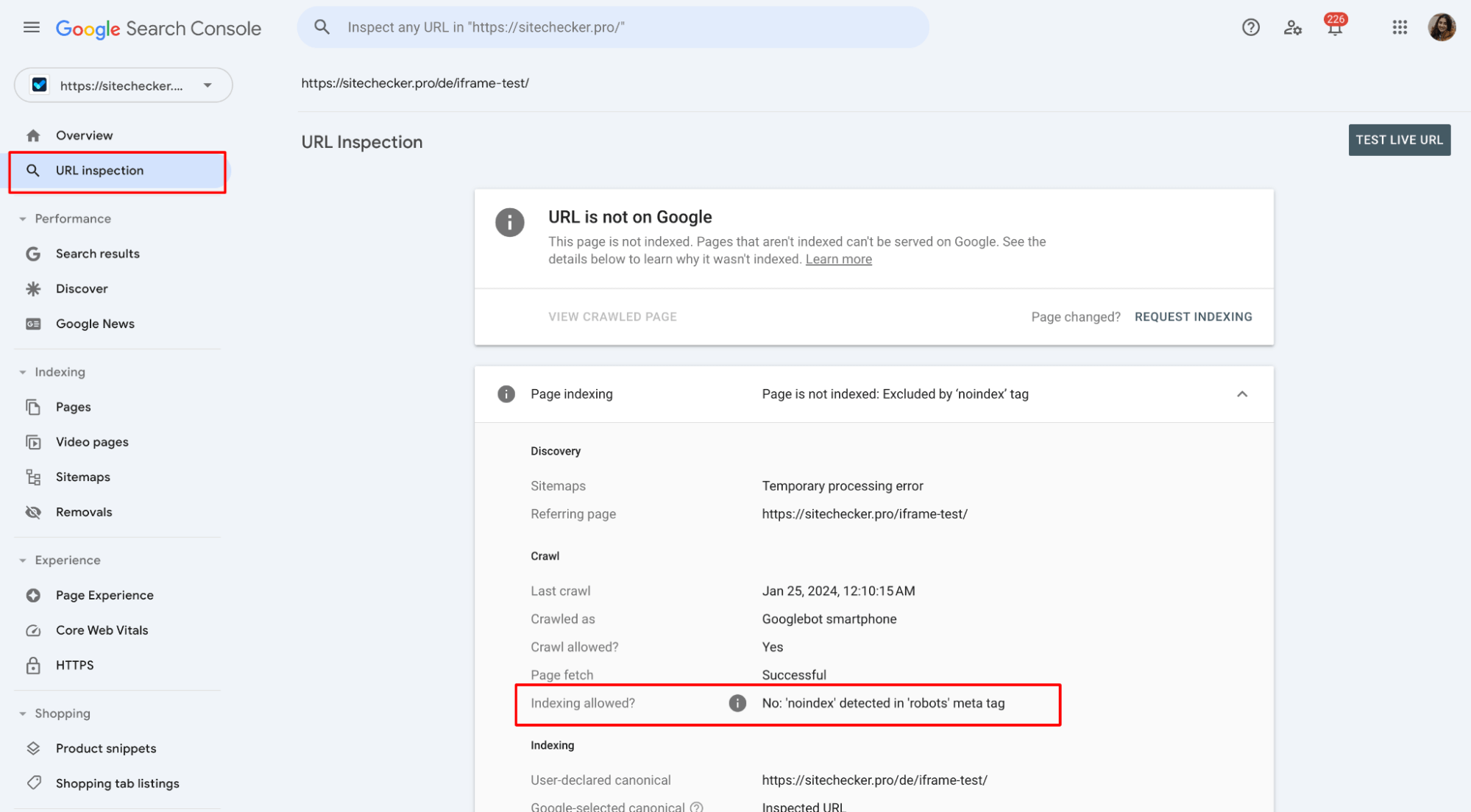
If you have updated the page to meet removal criteria, such as adding a noindex tag or ensuring it returns a 404/410 status, request a re-crawl of the URL. This will prompt Google to update its index based on the page’s current state.
3. Once the URL meets the removal criteria, formally request its removal by navigating to the ‘Removals’ section and submitting the URL
Monitor your removal request in the ‘Removals’ section to ensure that the URL is permanently removed from Google’s index.
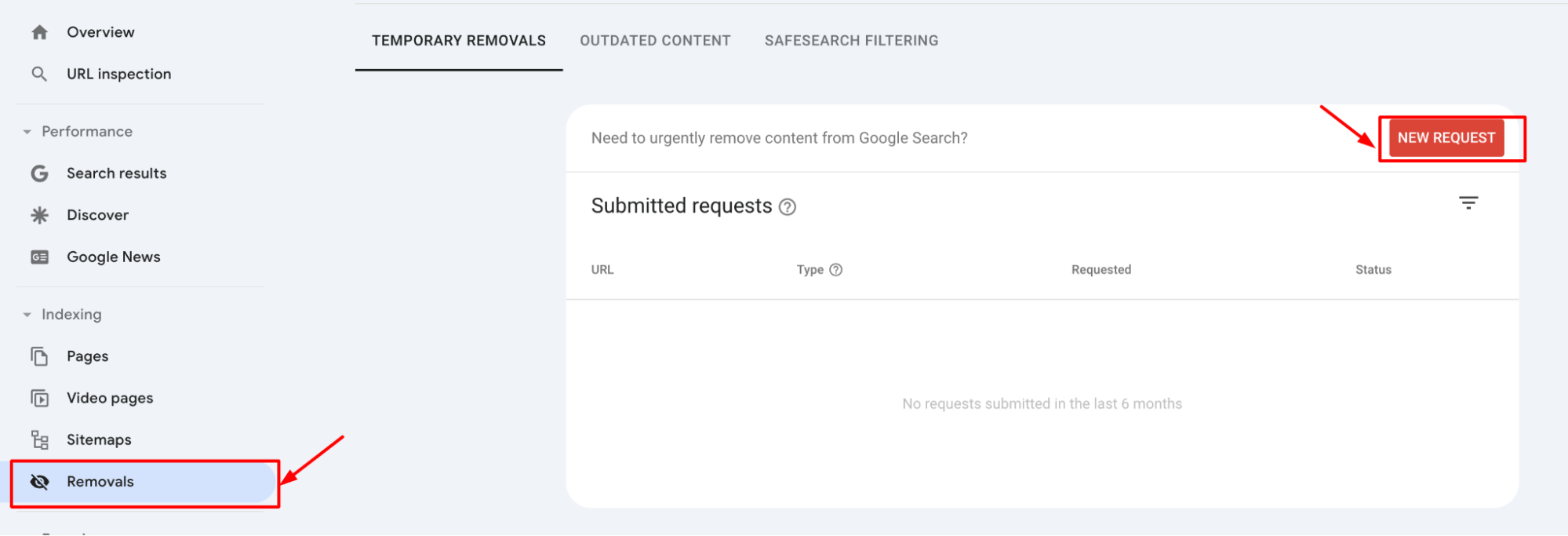
4. Periodically verify that the URL has not reappeared in search results by checking its status in Google Search Console and performing searches on Google.
Permanent removal requires consistent adherence to Google’s non-indexing criteria, making it more complex than temporary removal. This is essential for effectively managing your online content and maintaining its accuracy and relevance on Google search.
Manual content update or removal
When managing your website’s presence on Google, you may sometimes need to update or remove content manually. This can be crucial for maintaining the accuracy and relevance of your website in search results.
Here’s how you can effectively handle manual content updates or removals:
Update the content on your website
1. Direct Editing. If the information on a page is outdated or incorrect, update the content directly on your website. This includes text, images, and any other multimedia elements.
2. Complete Removal. If a page should no longer be accessible (e.g., outdated promotions, expired content, or irrelevant posts), remove it entirely from your website.
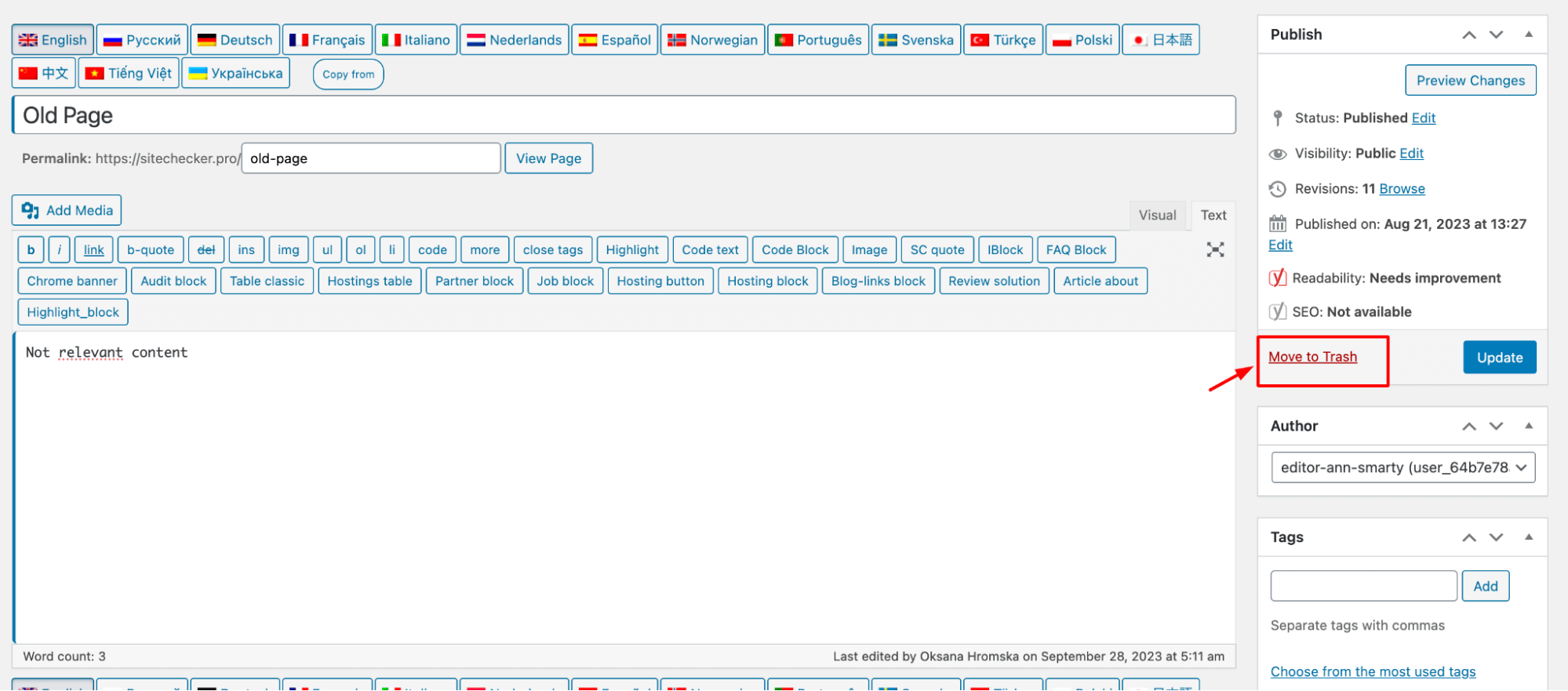
Apply changes to Google’s index
After making changes, use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console to request a re-crawl of the updated or removed page. This action prompts Google to update its index to reflect your changes.
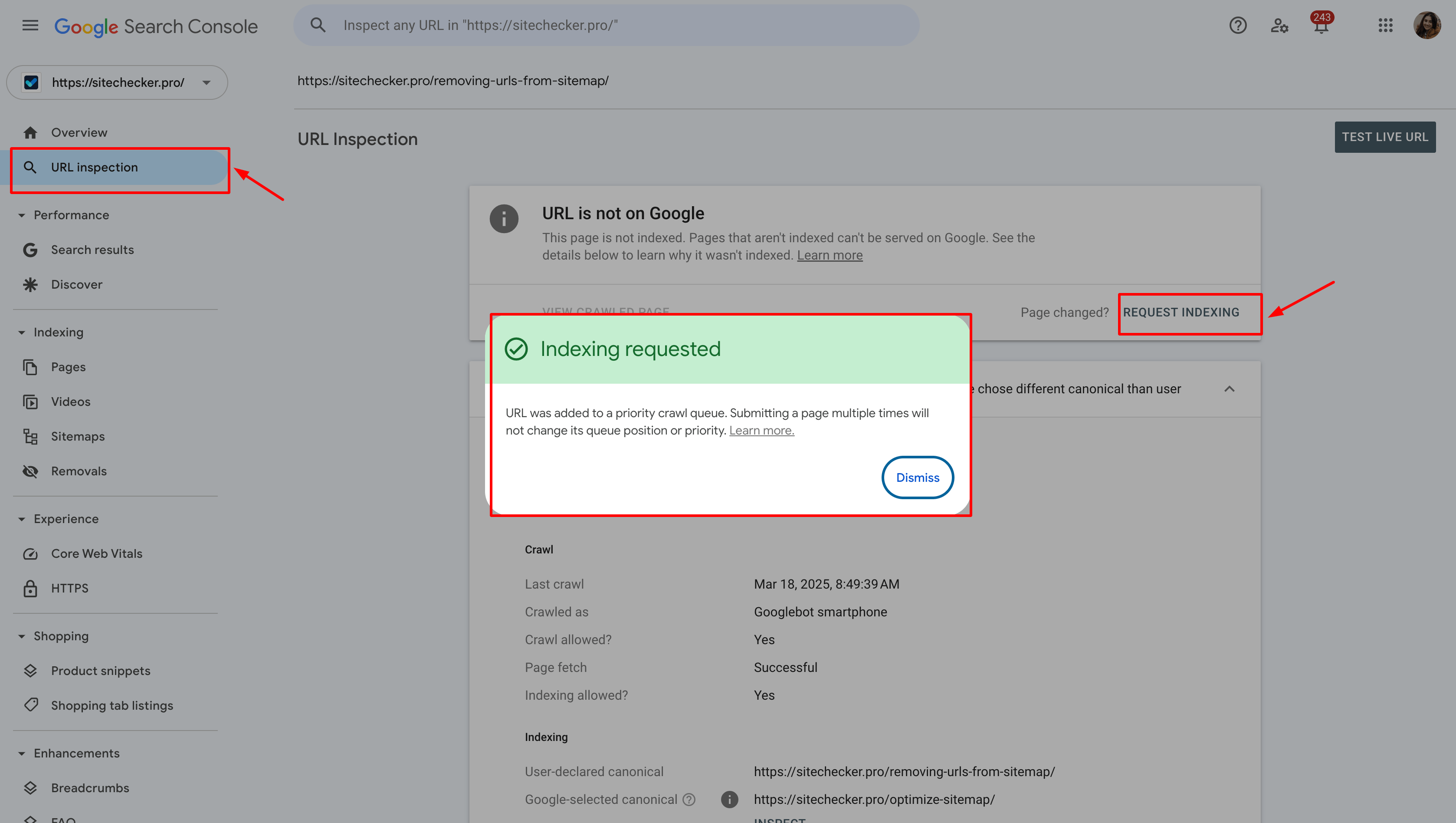
For removed pages, ensure they return a 404 (Not Found) or 410 (Gone) status code to inform search engines that the page no longer exists. No special status code is needed for updated pages as the content remains live.
Monitor search results
Regularly check how your updated or removed content appears in search results. This can help you verify that Google has recognized changes and that outdated or unwanted content is no longer visible.
If urgent removal of content from search results is necessary (e.g., for legal or privacy reasons), consider using Google’s content removal tools and updating your site.
Maintain regular updates
Periodically review your website content to ensure it remains accurate and relevant. This proactive approach can prevent the need for emergency content removals and maintain a positive user experience.
Get a comprehensive evaluation of your website’s content quality, identifying issues like missing or duplicate titles, low word count, outdated elements, and weak content structure.
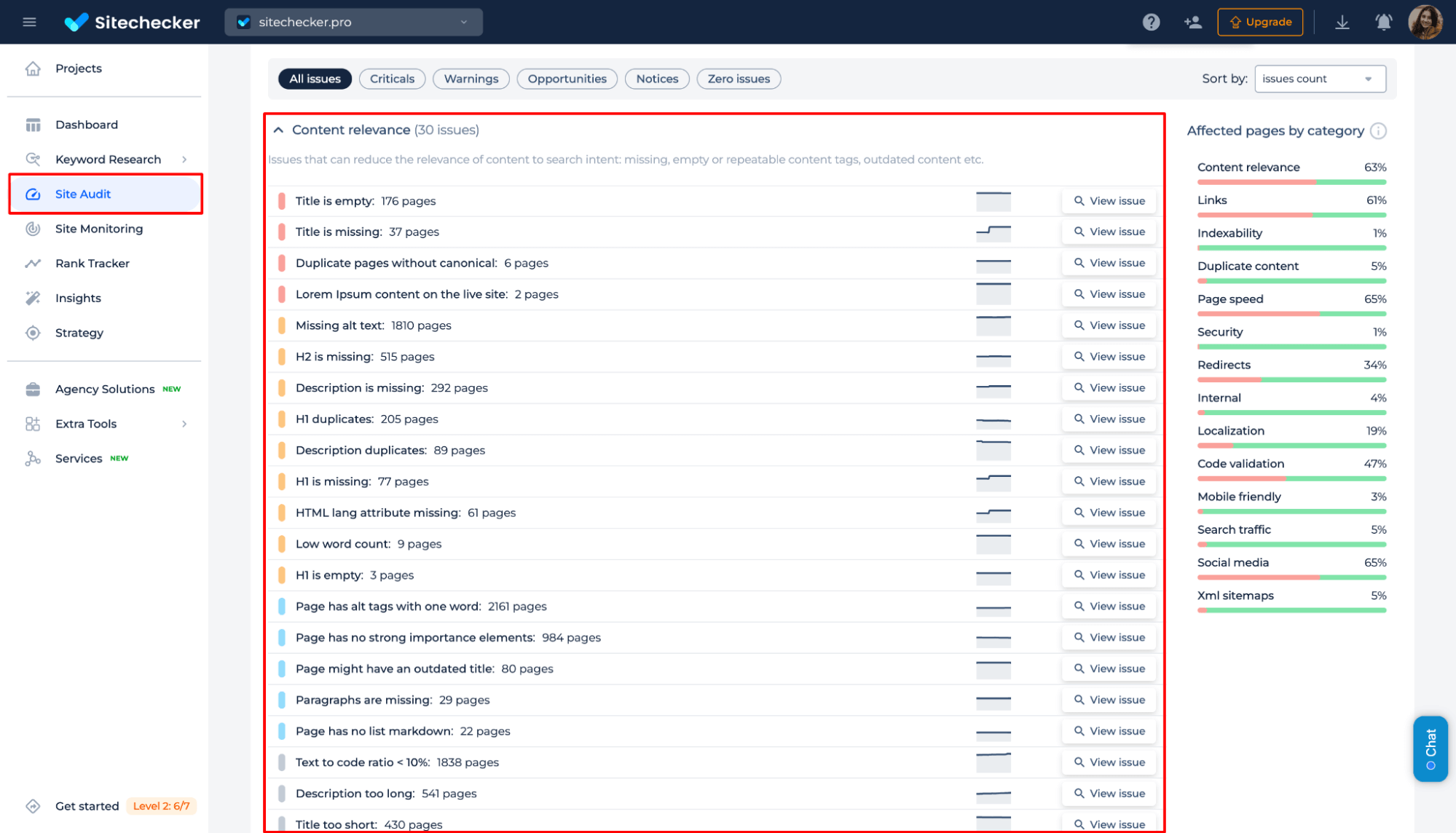
Optimize Your Content for Search!
Identify duplicate, missing, or weak content that affects SEO. Get insights instantly!
Legal removal requests
Handling legal removal requests involves navigating specific procedures to comply with legal standards and protect privacy. When content on Google violates laws or infringes on personal rights, it may need to be removed from search results through a formal legal process. Here’s how to manage legal removal requests effectively:
Identify the legal basis

Determine if the content in question violates specific laws, such as copyright infringement, defamation, or privacy breaches. Understanding the legal foundation is crucial before proceeding.
Submit a legal removal request to Google
Google provides different forms based on the type of legal issue involved. Select the appropriate form that corresponds to your specific legal concern.
Provide all required documentation and evidence supporting your claim. This may include court orders, identity verification documents, or detailed explanations of how the content violates legal standards.
Follow up on your request
After submitting the request, Google will review the information provided. This process may take some time, depending on the complexity of the legal issues and the volume of requests Google is handling.
Keep track of your submission and be prepared to provide additional information if Google requires further clarification to process your request.
Monitor the outcome
Once Google has processed your request, they will inform you of the outcome. If the request is approved, the offending content will be removed from search results.
Regularly check to ensure that the content remains removed. If it reappears or is reposted, you may need to submit a follow-up request.
Consider further legal action
In cases where Google does not comply with the removal request, or if the content continues to cause harm, consider seeking legal counsel to discuss further actions, which could include formal legal proceedings against the content publisher or continued engagement with Google.
Legal removal requests are a serious matter that requires careful documentation and a clear understanding of both legal implications and Google’s policies. By methodically approaching this process, you can effectively manage the removal of legally sensitive content from Google search results.
Using robots.txt and meta tags to control crawling
Effectively managing how search engines interact with your website can significantly impact your site’s visibility and privacy. Robots.txt files and meta tags are two critical tools that help control the crawling and indexing of your website content by search engines like Google. Here’s how to use these tools effectively:
1. Using robots.txt
The robots.txt file is used to prevent search engines from accessing certain parts of your website.
Place the robots.txt file in the root directory of your server. This ensures it’s the first file a search engine encounters when visiting your site
https://www.example.com/best-seo-practices-for-urls
to
https://99lh.short.gy/Bb0U
Specify user-agents (search engine crawlers) and directories or files to be excluded. For example, to prevent all crawlers from accessing a specific folder, your robots.txt might include:
Dealing with third-party content
Managing how third-party content related to your brand or personal information appears in search results can be challenging. Whether it’s unauthorized use of your content, incorrect information, or negative publicity, taking control requires a strategic approach. Here’s how to effectively handle third-party content:
1. Identify the content
Regularly use search engines to monitor what is being said or shared about you or your brand. Tools like Google Alerts can automate this process, sending you notifications when new content is published.
Determine whether the content is harmful, misleading, or potentially infringing on your rights or privacy.
2. Contact the website owner
If you find problematic content, try contacting the website owner or the author directly. Politely request the modification or removal of the content. Contact information can typically be found on the site’s “Contact Us” page or via a domain lookup service.
Explain how the content affects you and suggest reasonable modifications. Sometimes, website owners are not aware of the content’s impact and may be willing to cooperate.
3. Use legal and formal requests
If the content infringes on your copyright, you can submit a DMCA takedown notice to the website or the host to have the content removed.
For content that may be defamatory or violates other legal statutes, consider seeking legal advice. You may need to send a formal cease-and-desist letter or pursue further legal action.
4. Request removal from search engines
If contacting the website owner doesn’t work, you can use tools provided by search engines like Google’s legal removal request process for sensitive personal information, copyright violations, or other legally sensitive issues.
Keep records of your communications and submissions, as this information might be necessary if the issue escalates or for legal processes.
5. Reputation management and SEO strategies
Develop and publish positive content that ranks well in search engines to counteract negative third-party content.
Optimize your online presence through SEO best practices to help ensure that positive content about you or your brand appears higher in search results.
6. Monitor and adjust strategy
Keep an eye on the situation by continuing to monitor online mentions and the search results for your name or brand.
Depending on the outcome, adjust your strategies. This might include more aggressive SEO tactics, additional legal action, or continued outreach to website owners.
Handling third-party content effectively requires a combination of direct communication, legal actions, and strategic online reputation management. By actively managing how you are represented online, you can significantly influence public perception and protect your brand integrity.
Monitoring and maintaining URL visibility
Maintaining control over how URLs appear in search results is essential for managing your digital presence effectively. Whether you are dealing with changes on your own website or responding to how third-party sites represent your brand, consistent monitoring and proactive management can help ensure your online visibility aligns with your goals.
How to monitoring and maintaining URL visibility
1. Set Up regular monitoring
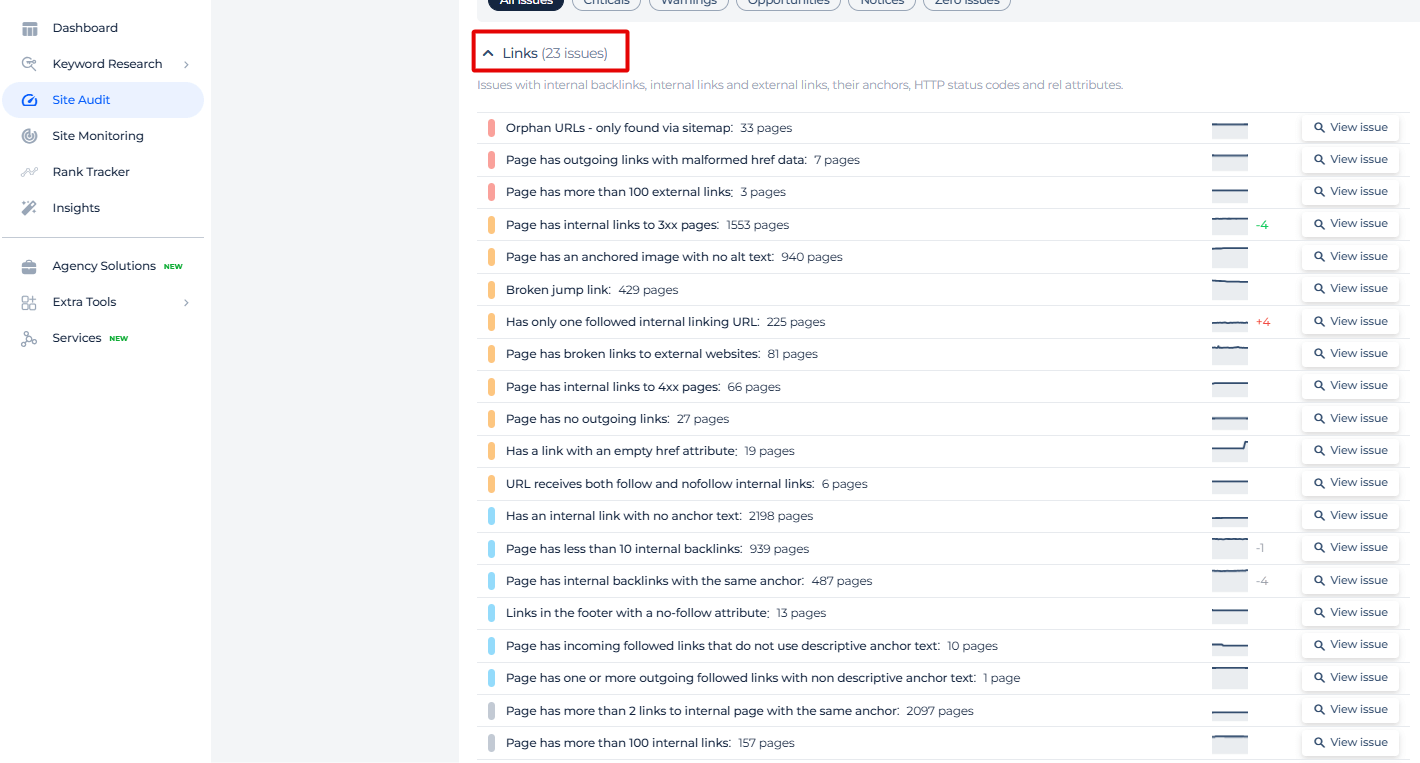
Utilize tools like Sitechecker to track the performance of your URLs in search results. The tool provides insights into visibility, traffic, and any issues affecting your site.
Monitor Your URLs: Take Control Now!
Ensure your website's visibility is managed effectively. Start monitoring today!
Set up alerts to notify you of any significant changes, such as sudden drops crawl errors that could affect your site’s performance.
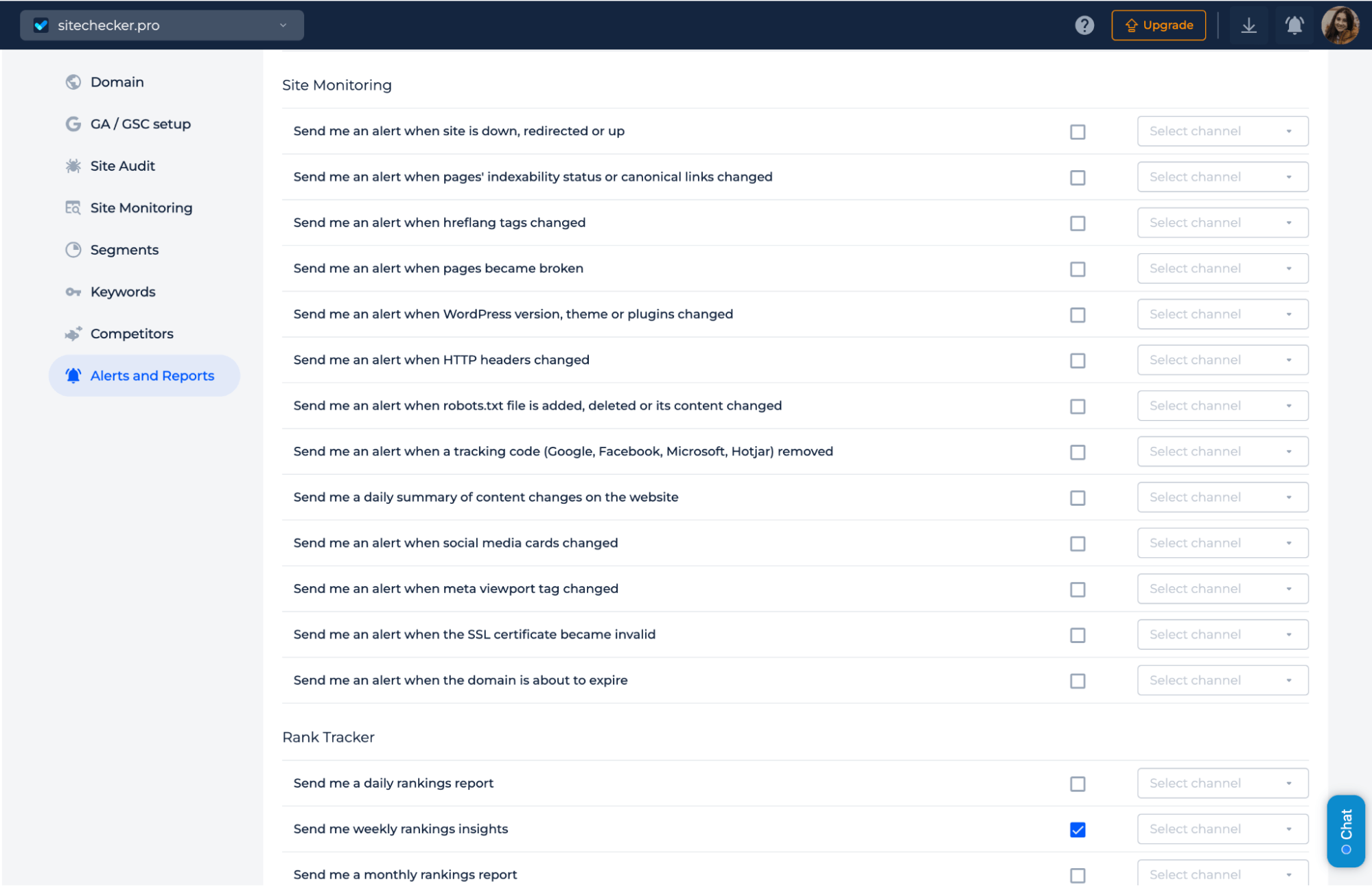
When you set up URL monitoring with the Sitechecker tool, you receive real-time alerts about crucial changes and updates to your website.
This includes notifications when your site’s status changes (such as going offline or coming back online), alterations to indexability and canonical links, updates to HTTP headers, changes in hreflang and robots.txt files, modifications to social media cards, and shifts in WordPress configurations.
2. Inspect individual URLs
Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool allows you to check specific URLs to see how Google views these pages. It shows whether a URL is indexed, any crawling or indexing issues, and the last crawl date.
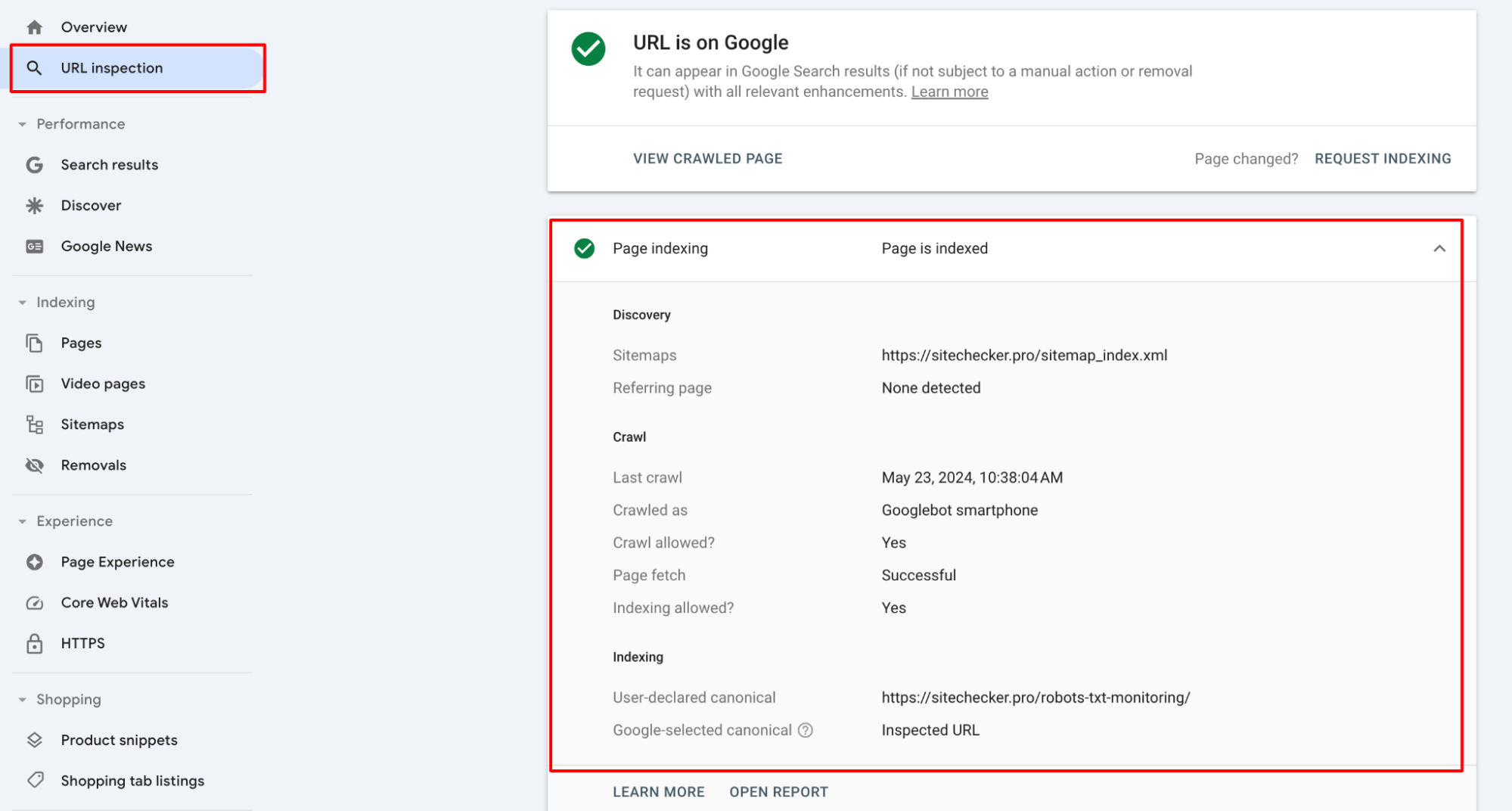
Regularly perform searches in Google to see how your URLs are ranking and whether any outdated or unwanted content is appearing.
3. Analyze and respond to changes
Regularly review any changes in your website’s traffic or rankings and investigate potential causes. This could include website updates, algorithm changes, or external factors like increased competition.
Based on your findings, adjust your SEO strategy. This might involve updating content, improving on-page optimization, or resolving technical issues that could impact your visibility.
4. Manage URL removals and updates
If necessary, use Google Search Console to temporarily remove URLs from search results while you make updates or resolve issues.
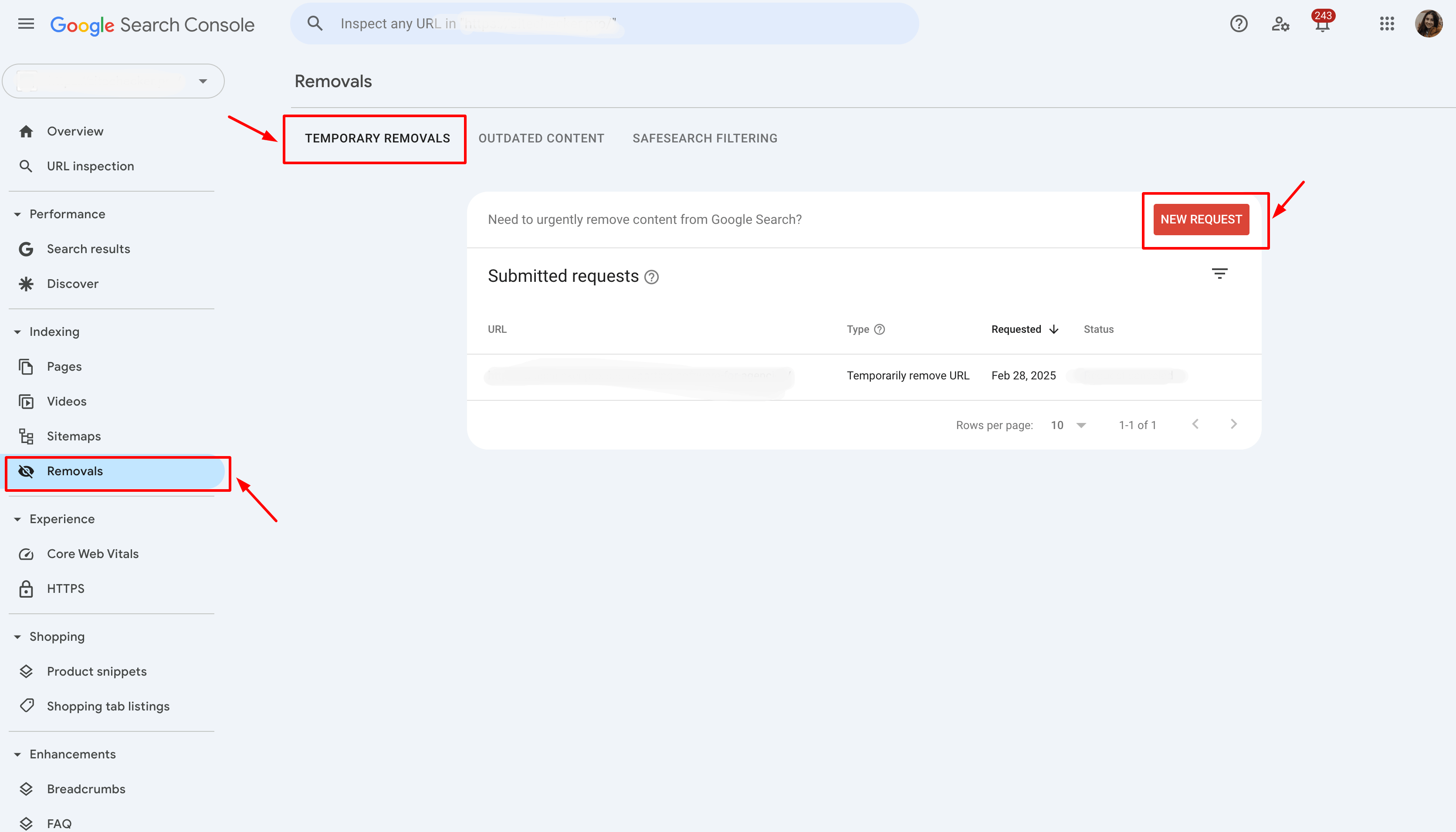
For URLs that need to be removed permanently from search results, ensure they return a 404 or 410 status code, and use the Removals tool in Google Search Console to request a permanent removal.
5. Engage in proactive reputation management
Regularly develop and publish new content that positively reflects your brand and addresses potential negative content that might appear in search results.
6. Continuously evaluate performance
Regularly monitor key SEO performance indicators such as page rankings, click-through rates, and average position in search results. This helps you understand the effectiveness of your current strategies and identify areas for improvement.
Final idea
Managing URLs in Google search results involves understanding temporary and permanent removal options. Temporary removal hides URLs for six months, useful for content updates, while permanent removal ensures URLs are indefinitely erased. Google Search Console is key for handling both processes. Additionally, managing third-party content and using tools like robots.txt or noindex tags helps control your online presence.