Code minimization, or minimizing, removes all unnecessary characters from JavaScript source code without changing its functionality. It involves removing extra spaces, extra comments, and other elements and introducing short variable and function names. Minifying JavaScript code results in compact file size.
You can get advice on minifying in our free Minify JS tool. We created this tool to analyze your source code and find points that need possible intervention and code size reduction. We will tell you how you can use the tool to optimize your code.
Here are some tips about site performance by LevelUpTuts:
Using JavaScript Minification Test: a Step-by-Step Guide
Well, it’s important to know how you can optimize your site’s pages. One way to speed up the loading of your site’s pages is to minimize the source code. Remove unnecessary code elements so that your code is optimized. It will positively affect search engine rankings and the user experience of your site.
Let’s look at how to use our JS minifier to optimize the source code of your site pages. We used our sitechecker.pro site as an example. In two normal steps, you can get useful hints.
Step 1: Insert your URL and start free trial
You don’t need a credit card to use our free trial. All you have to do is confirm your email address or use your Google account. Quick and easy to get started.
Step 2: JS minify results analysis
We will analyze your site, including the URL you added to the tool. It will take just a few seconds, and once the analysis is complete, we’ll provide suggestions on which pieces of code you could improve. Use these suggestions to minify your js code and speed up loading times. We’ll also give you a page SEO audit that highlights any issues your page has.
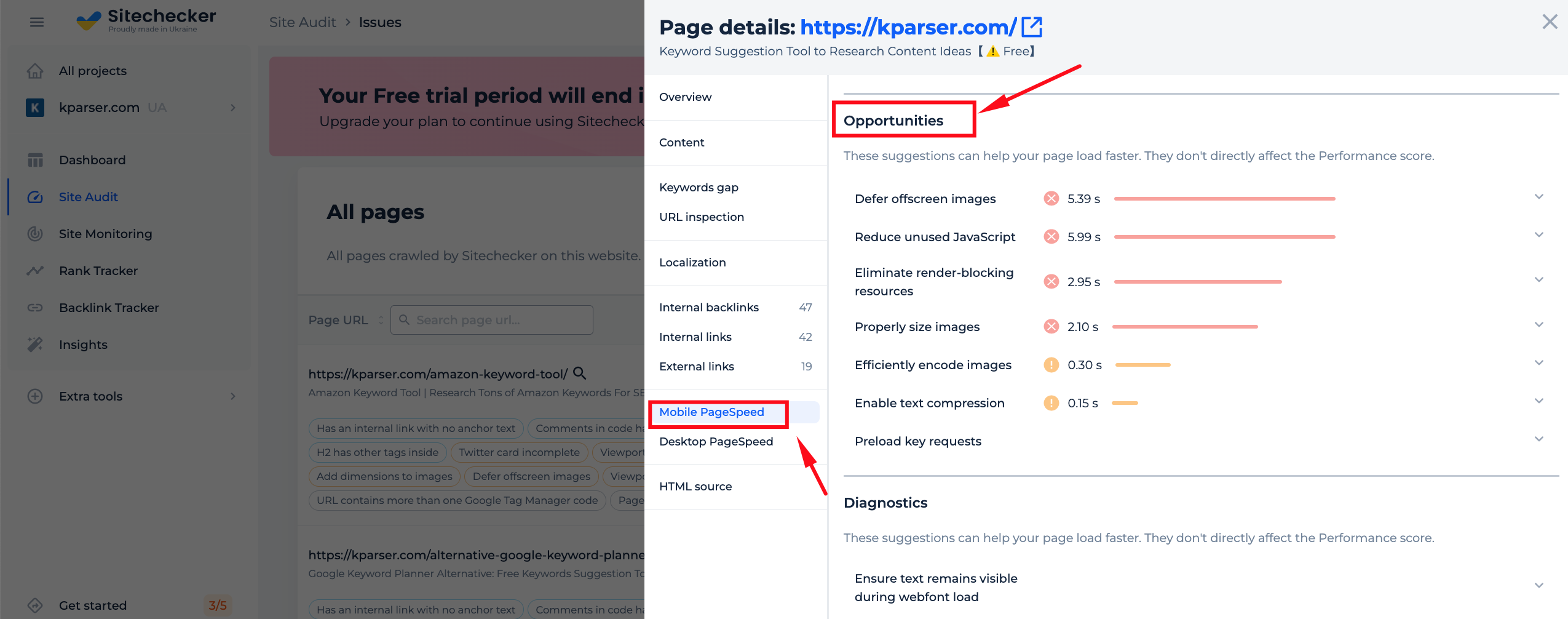
Features of JS Minification Checker
Full-site audits can help you identify various types of problems and list the URLs where those issues occur. This service can provide you with instructions and video guides on how to fix them, which can be an invaluable resource for improving your website’s performance and ranking.
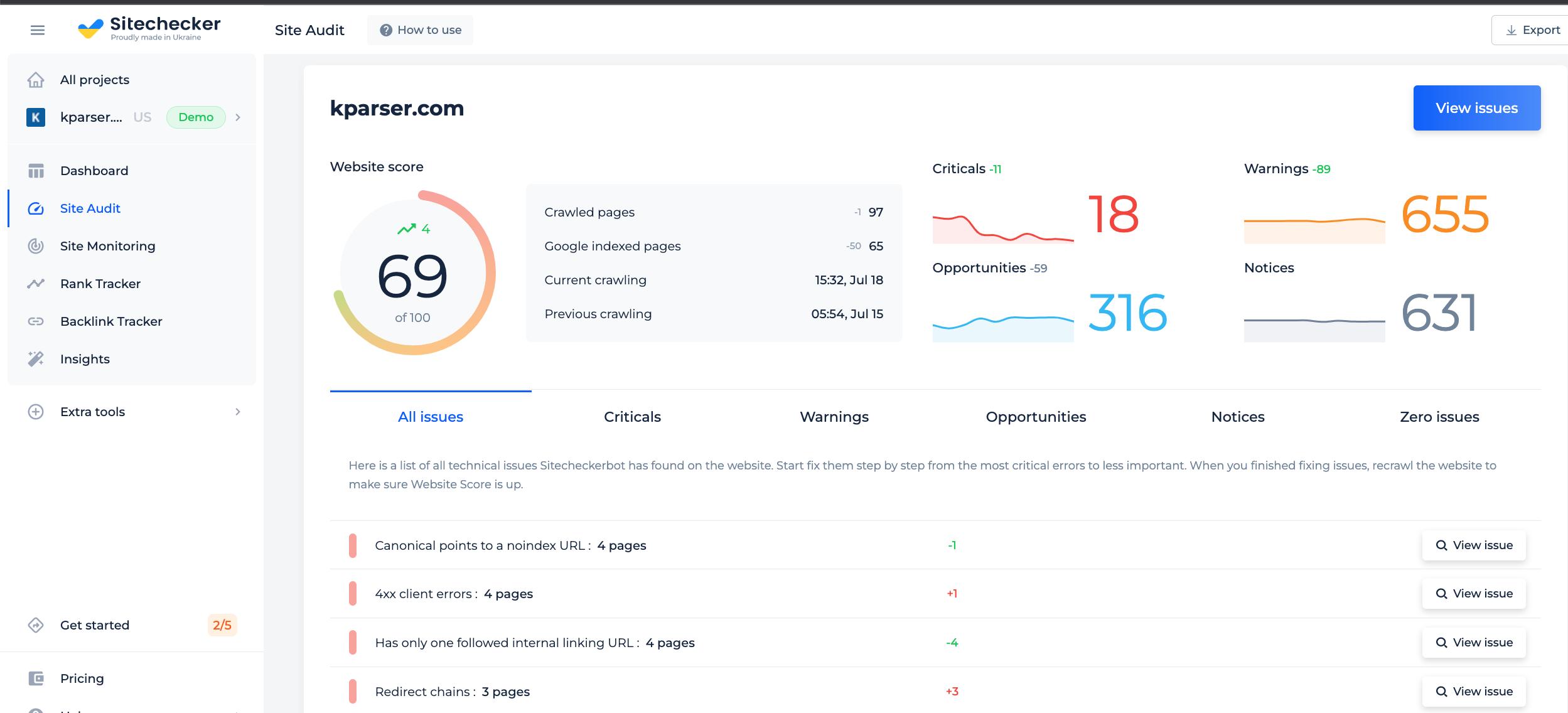
The “Page Speed” section of Full Audit is a great way to identify any potential issues with your site’s speed. You can also set up notifications to receive alerts if any of these problems occur in the future. If you want to keep your site running smoothly for all users, it is important to stay on top of potential speed bumps. By being proactive and addressing these issues, you can ensure that your website remains accessible and user-friendly.
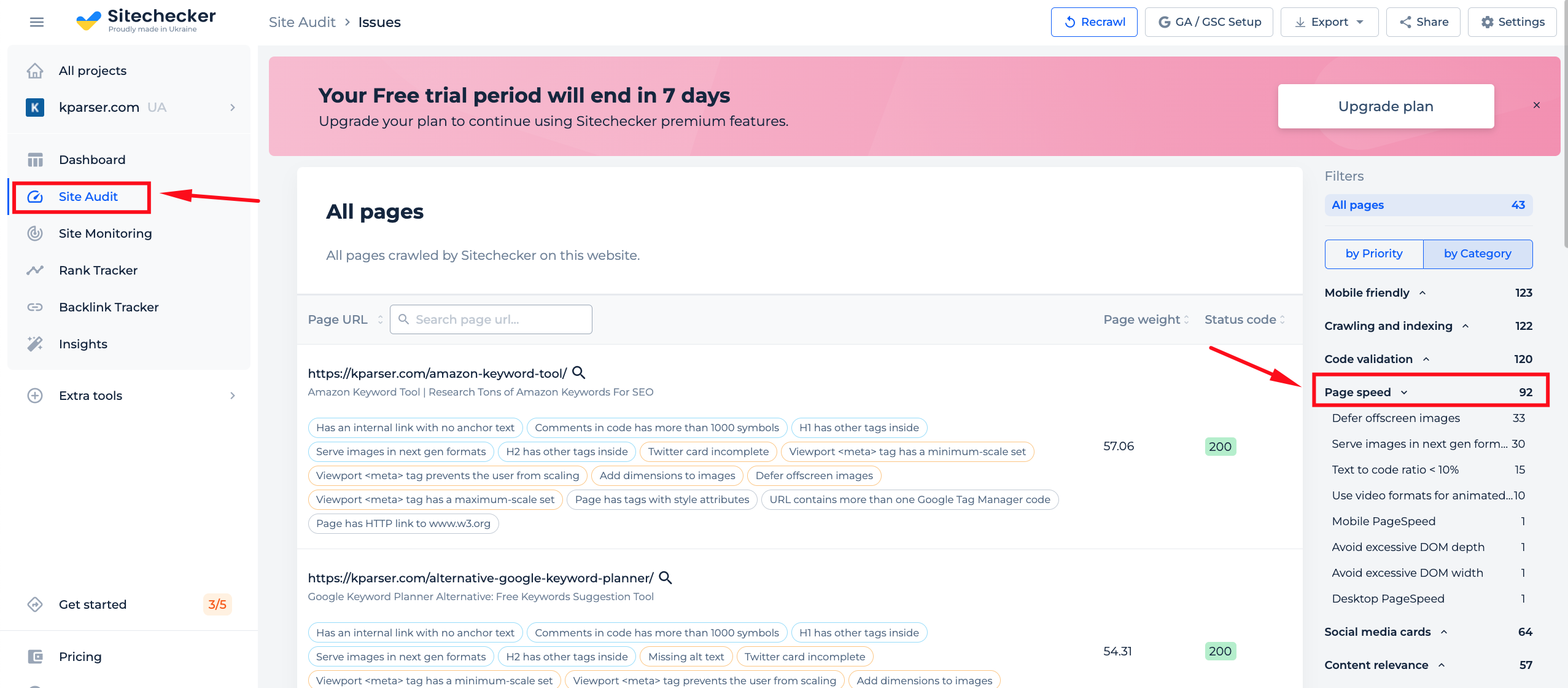
If you’re worried about potential JS code errors, our on-page checker tool can help. This tool will help you ensure everything is set up correctly, and avoid any problems that might occur in the future.
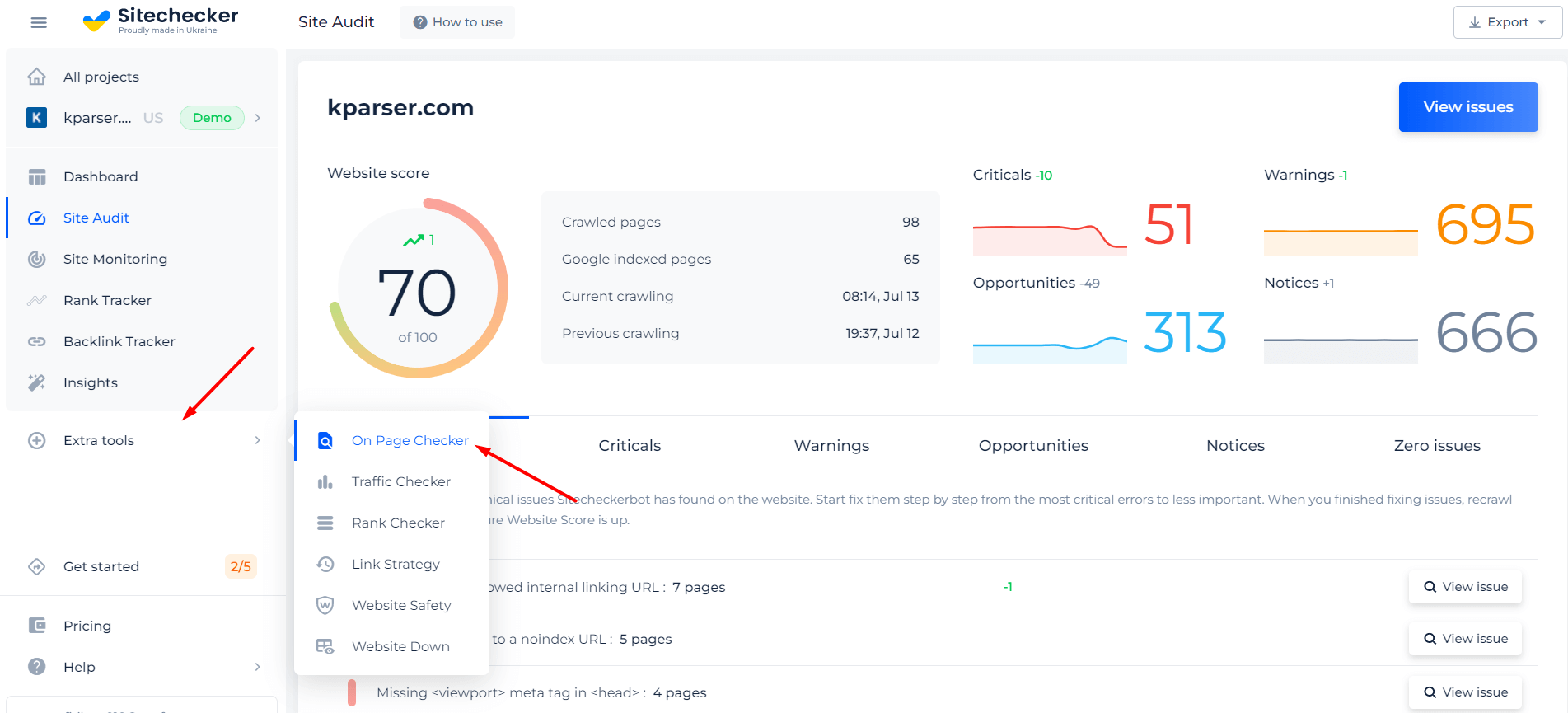
Analyze not only JS Minification but the entire site!
Make a full audit to find out and fix your technical SEO in order to improve your SERP results.
What Is Minification In JavaScript?
Let’s find out what minification is. It is the process of minimizing the source code and markup in web pages and script files. This method allows you to reduce scripts loading time and bandwidth usage on websites. Minifications significantly speed up your website, and this, in turn, has a positive effect on Google rankings. It’s also very useful for users who browse your site from mobile devices and want to save their mobile traffic. You can minify JS, HTML, CSS, PHP, node NPM, etc.
We designed the JavaScript minification test for your convenience. It’s free and quick! Use the tool to find potential optimization moments.
Why Is It Bad For Site & SEO
Source code minification can disrupt the operation of complex censors on your site, such as themes, plugins, gulp, and add-ons. In addition, you should do minification in conjunction with advanced performance tweaks. Keep in mind that if you do not act comprehensively, you’re unlikely to get a good visual result. As for the optimization for search engines, the introduction of minification in your source code can not do any harm, in itself, not good.
Use this method only if you know how to do it. Otherwise, you can cause great harm to the site. You may make mistakes that will interfere with the promotion in search networks. You can make mistakes that will be difficult to concat. To avoid this, ask experienced professionals who will optimize the code for your WordPress or Shopify website.
Common Reasons & Problems That Make JS Too Big
You might think that JavaScript source code is pretty straightforward. Nevertheless, it is worth bearing in mind that this programming language has many nuances and peculiarities, and you need to keep all of these features in mind while minimizing them. JavaScript Closure Compiler tweaks lead to several common mistakes, one of which is large code. To keep your code optimized on the site’s pages, use the minimization toplevel method.
When you start optimizing and minifying your code in the studio, it will lose its functionality and original form. Just in case, we recommend that you save a copy. It will help you go back to the previous step if you inadvertently make mistakes while changing the source code version. The sizes of the code are affected by how much redundancy you will use. Remove unnecessary comments that have no value. Remove spaces and compress semicolons. And don’t forget about Grunt – a task manager for auto routine operations.
How to Minify Your JavaScript Files
Check whether your webpage needs JS compressing using the tool above. It is advisable to use minification when the JavaScript file size is over 25 KB. If the page has some unoptimized parts of JavaScript, you will see a similar note as in the picture below. It is advisable to use minification when the JavaScript file size is over 25 KB.

In addition, you must know the logic of modern minifiers:
- Tools parse JavaScript code into a syntax tree (like Magento).
- Analyze and optimize the code.
- Write the resulting code from the syntax tree.
Should you minify JavaScript?
Does minification improve performance?
How is minification different from obfuscation, compression, encryption, or uglification?
- Uglify is JavaScript library documentation for minimizing JavaScript files, like jQuery. This un method allows you to improve performance by reducing readability significantly.
- Encryption is the process of converting samples of data into encrypted data.
- Obfuscator is used to obfuscate business logic and make reverse engineering more difficult.
- Data compression is a process that reduces the number of bits needed to represent API data.