Understanding Whitespace in URLs
When it comes to URLs, whitespace can be a surprisingly common issue. Although it might seem minor, whitespace can cause technical challenges and affect SEO. This section covers what whitespace entails and explores the typical causes of whitespace in links.
What Constitutes Whitespace Characters?
Whitespace characters include any character used to create space within text but are invisible. Common examples include:
Spaces

The most typical whitespace character, often inserted by users unintentionally in URLs.
Tabs
Though rare in URLs, tabs are another form of whitespace that can slip into text through copying and pasting.
Line Breaks
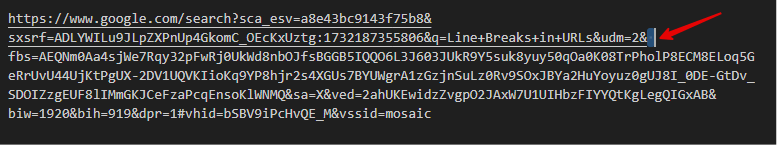
Occasionally, line breaks or carriage returns may appear in URLs, particularly if the URL is handled across multiple lines in text or code.
These characters are usually invisible but have significant impacts in a URL, often causing errors or unintended behavior when accessed on the web. Because URLs do not handle whitespace directly, each whitespace character must be encoded to avoid issues. Spaces, for example, are encoded as %20 in links.
Common Causes of Whitespace in URLs
Whitespace can end up in URLs due to a variety of causes. Here are some of the most common scenarios:
Manual URL Entry Errors
When users manually type URLs, spaces may be inserted by mistake, especially if they are unfamiliar with URL encoding standards. This can lead to broken links or accessibility issues on certain browsers.
Improper Filename Handling
Filenames containing spaces, such as “My Document.pdf,” can lead to whitespace in URLs when uploaded to the web without proper handling. When uploaded, the space is often replaced with %20, which can make URLs appear cluttered or confusing.
Dynamic URL Generation Issues
Many websites and applications generate links dynamically based on user inputs or database entries. If input validation is not implemented, whitespace can slip into the generated URLs, leading to inconsistent or incorrect link behavior.
Implications of Whitespace in URLs
Whitespace in URLs can lead to several issues that affect both the technical functionality of websites and their visibility in search engines. Addressing these issues is essential for maintaining a well-functioning and search-friendly site.
Technical Challenges
Whitespace in URLs can introduce multiple technical challenges, including:
Broken Links
When whitespace is improperly encoded or handled, URLs may not resolve correctly, leading to broken links. For example, a URL containing an unencoded space might break, causing visitors to encounter 404 errors. Additionally, if a whitespace character appears at the end of a link by mistake, many browsers and servers may interpret this as an invalid URL, resulting in page load failures.
Inconsistent Browser Behavior
Different browsers handle whitespace in URLs in slightly different ways, which can lead to inconsistencies. Some browsers may automatically encode spaces as %20, while others may fail to load the page altogether. This variation can create unpredictable user experiences, especially when URLs are shared across different devices or platforms.
Compatibility Issues with Third-Party Tools
Whitespace in URLs can also interfere with third-party tools, such as analytics software, URL shorteners, and social media sharing platforms. If these tools cannot process links with whitespace properly, they may record incorrect data or fail to link correctly, leading to inaccurate analytics and loss of traffic.
These technical issues highlight the importance of addressing whitespace in URLs at both the development and maintenance stages to ensure that links remain functional across platforms and browsers.
SEO Considerations
Whitespace in URLs can also impact a site’s SEO performance in various ways:
Search Engine Interpretation
Search engines require URLs to be clean and properly formatted to interpret and index them effectively. URLs with whitespace may be misinterpreted if not encoded correctly, leading to indexing issues or even exclusion from search results. For example, a link with a %20 in place of a space may be indexed separately from the intended page, which can fragment search traffic.
Impact on Rankings
URLs that contain encoded whitespace (e.g., %20) can appear unprofessional or cluttered, potentially affecting user trust. When users see complex URLs with multiple encoded characters, they may be less likely to click on the link. This reduced click-through rate (CTR) can indirectly influence search rankings, as CTR is a known factor in Google’s ranking algorithm.
Duplicate Content Concerns
In some cases, URLs with and without whitespace might lead to the same page, creating duplicate content in the eyes of search engines. This duplication can dilute page authority, as search engines may divide ranking signals between multiple URLs pointing to the same content.
By understanding and mitigating these SEO implications, website owners can ensure their URLs are both user-friendly and optimized for search engines. A clean URL structure, free of unnecessary whitespace, helps improve both user experience and search engine visibility, ultimately enhancing a site’s performance.
Best Practices for Handling Whitespace in URLs
Effectively managing whitespace in URLs is key to ensuring a clean, functional, and SEO-friendly site. Adhering to URL encoding standards and using alternative characters for readability can help avoid common issues associated with whitespace in URLs.
URL Encoding Standards
In URLs, whitespace cannot be directly represented, so it must be encoded to prevent errors. The standard encoding for spaces in URLs is %20, a practice widely recognized across browsers and search engines. Here’s why proper encoding is crucial:
Preventing Errors
Unencoded spaces in URLs can cause browsers to misinterpret the URL, resulting in broken links or server errors. By encoding spaces as %20, you ensure that the link is correctly processed across all devices and platforms.
Consistency Across Platforms
Different browsers, servers, and third-party tools may interpret unencoded whitespace differently, leading to unpredictable behavior. Encoding spaces as %20 ensures that your URL is interpreted consistently, regardless of where or how it is accessed.
Professional Appearance
Proper encoding not only prevents technical issues but also gives URLs a cleaner, more professional look. URLs with unencoded spaces can appear messy and unprofessional, which may deter users from clicking on them.
Encoding spaces and other special characters in URLs is essential for seamless navigation and optimal user experience. Following the %20 encoding standard helps avoid unnecessary issues and ensures compatibility with a wide range of tools and devices.
Alternative Characters for Readability
Instead of using spaces in URLs, a best practice is to replace whitespace with hyphens (-). Hyphens are preferred over underscores (_) for several reasons:
SEO Benefits
Search engines, including Google, recognize hyphens as word separators, making it easier for them to parse and index URLs. In contrast, underscores are often ignored, which can make URLs appear as one long, unbroken string. For example, example.com/white-space is more readable and SEO-friendly than example.com/white_space.
Improved Readability
Hyphens improve the readability of URLs, making them more user-friendly. A URL with hyphens between words is easier to understand at a glance and more likely to attract clicks from users, especially on search engine results pages.
Avoiding Encoding Issues
By using hyphens instead of spaces or other special characters, you reduce the need for encoding, resulting in cleaner URLs. Links without encoded characters are visually simpler and convey professionalism and credibility to users.
Using hyphens in place of spaces not only enhances SEO but also creates a more polished and approachable URL structure. Following this best practice can help your site’s URLs appear cleaner and more appealing, both to users and search engines.
Preventing Whitespace in URLs
Taking proactive steps to prevent whitespace in URLs can save time and effort in fixing broken links or addressing SEO issues later on. Establishing consistent naming conventions and configuring content management systems (CMS) and scripts can help keep URLs clean and functional.
Proper Filename Conventions
One of the simplest ways to avoid whitespace in URLs is to establish filename conventions that prevent spaces:
Use Hyphens Instead of Spaces
When naming files that will be uploaded to the web, replace spaces with hyphens (-). For example, instead of naming a file My Document.pdf, use My-Document.pdf. Hyphens are universally recognized as word separators and reduce the risk of encoding issues.
Avoid Special Characters
Beyond spaces, avoid special characters like ampersands (&), question marks (?), or percent symbols (%) in filenames. These characters can lead to encoding errors and may be misinterpreted by servers and browsers. Stick to alphanumeric characters, hyphens, and underscores where possible.
Consistency Across Teams
If multiple team members are responsible for uploading content, establish and share these filename conventions to ensure consistency across the site. This practice will reduce the risk of whitespace or other problematic characters slipping into URLs.
By setting up and following a few simple naming conventions, you can avoid the most common issues caused by whitespace in URLs, ensuring that links function properly and appear clean to users.
CMS and Script Configurations
Many content management systems and custom scripts offer settings to automatically handle or prevent whitespace in URLs. Configuring these options can save time and prevent errors, especially when managing large volumes of content.
Enable URL Slug Settings
Most CMS platforms, such as WordPress, allow you to customize URL slugs and replace spaces automatically. Enable or adjust these settings to use hyphens by default, so that URLs are generated cleanly without whitespace.
Use URL Sanitization Plugins or Modules
Many CMS platforms offer plugins or modules specifically designed to sanitize URLs by removing spaces and special characters. For instance, WordPress has plugins like Yoast SEO that can automatically handle URL formatting. Implementing these plugins ensures that your permalinks remain clean and SEO-friendly.
Custom Script Validation
If your site uses custom scripts for generating URLs, consider adding validation functions to handle whitespace automatically. By using functions that replace whitespace with hyphens or remove it entirely, you can prevent URL issues before they arise. This approach is especially useful if URLs are generated based on user input, where spaces are common.
Configuring your CMS or scripts to prevent whitespace helps maintain clean URLs site-wide. Whether through built-in settings or custom validation functions, automating whitespace handling ensures a more reliable user experience and reduces the need for manual URL management.
Addressing Existing URLs with Whitespace
If your website already has URLs containing whitespace, it’s important to address them to ensure optimal functionality and maintain SEO integrity. Setting up redirects and regularly monitoring your site can help manage any issues arising from whitespace in URLs.
Implementing Redirects
One of the best ways to handle existing URLs with whitespace is to set up 301 redirects. A 301 redirect is a permanent redirection from an old URL to a new, correctly formatted URL. Here’s how to implement 301 redirects to manage whitespace effectively:
Identify URLs with Whitespace
For checking whitespaces in actual URLs, you can simply observe if there are characters in the path. Whitespace can be represented by + and %20 (not 20%.)
To make this process easier use Sitecheckeюr. It can scan your website and detect all pages with whitespaces in the URL.
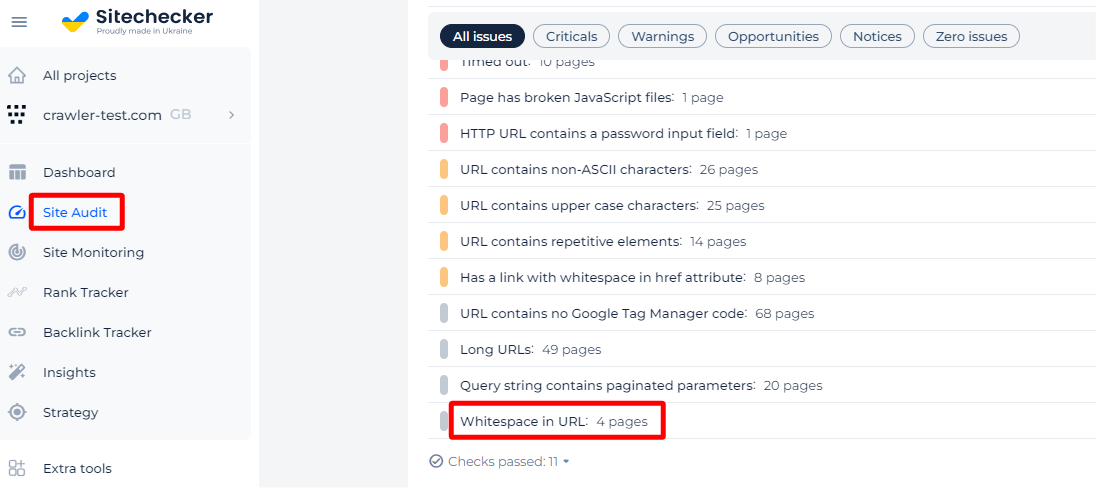
You will be presented with all impacted pages just by clicking the issue.
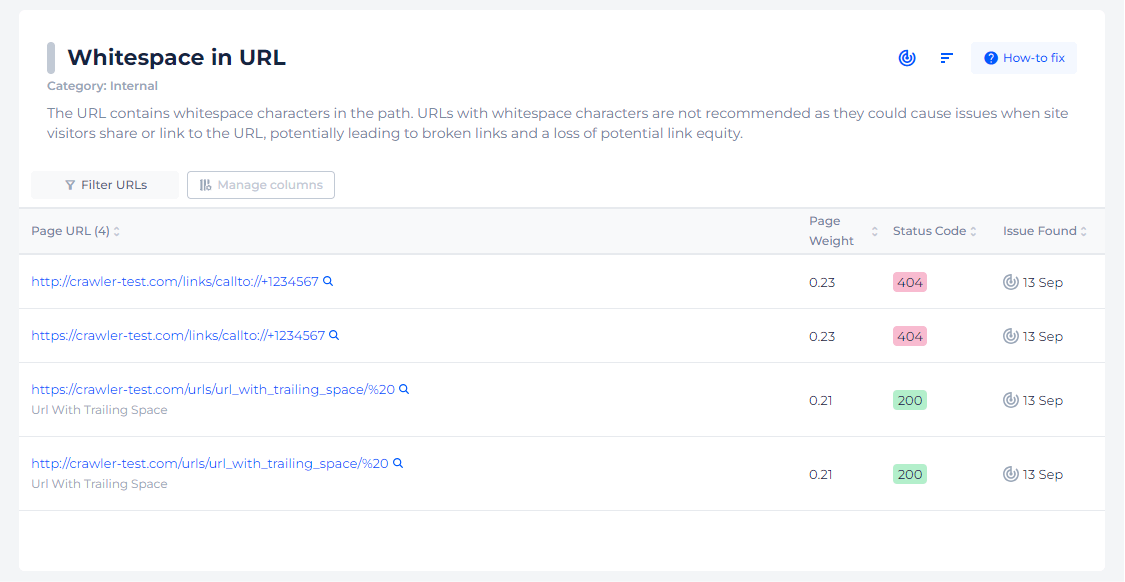
Set Up 301 Redirects
Using your server configuration or CMS, redirect URLs with whitespace to their corrected versions. This process varies depending on your server:
For Apache Servers: Use the .htaccess file to add redirect rules. For example:
Redirect 301 "/old%20url" "/new-url"For Nginx Servers: Add redirect rules to the configuration file:
rewrite ^/old%20url$ /new-url permanent;CMS Redirect Plugins
Many CMS platforms, like WordPress, offer plugins that simplify the process of setting up 301 redirects. Plugins like Redirection or Yoast SEO allow you to manage redirects directly from the dashboard.
Test Redirects
After setting up redirects, test them to ensure they work as expected. Use tools like Redirect Checker to verify that the redirect points to the intended URL and responds with a 301 status code.
Implementing 301 redirects ensures that visitors and search engines are directed to the corrected URL, preserving link equity and preventing broken links. It also helps consolidate SEO signals, which can positively impact rankings.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Once you’ve addressed existing URLs with whitespace, ongoing monitoring and maintenance are essential to keep URLs clean and functional:
Conduct Regular Audits
Periodically audit your site to detect any new URLs with whitespace or other formatting issues. SEO tools and site audit services can automate this process, making it easier to spot problematic URLs early.
Track Redirects
Keep an eye on your 301 redirects to ensure they’re still necessary and functional. Over time, as pages are updated or removed, some redirects may become obsolete or lead to outdated content. Regularly review and update your redirects to keep your site structure optimized.
Train Content Managers and Editors
Educate anyone involved in content creation or uploading files about best practices for URL management. By promoting filename conventions and enforcing CMS settings, you can prevent future issues with whitespace in URLs.