As you may know, hreflang lets search engines like Google and Yandex know that your webpage is available in a particular language and for a particular region. Meanwhile, the language or lang attributes on the HTML tag let your browser know the language of the current document or webpage.
Read more on the Google Devs guide here on how to tell Google about the localized versions of your page.
What Does “Mismatch Hreflang and Lang Attributes” Mean?
As we stated above, this problem signifies that your hreflang and language HTML attributes don’t match or aren’t compatible with each other.
What Triggers This Issue?
When your language codes declared in the HTML lang attribute and in the hreflang annotation for the URL don’t match, you’ll see an issue report on the page. The issue may also get triggered when you have URLs where the hreflang annotations are defined, but they have a missing HTML language tag.
How to Check the Issue?
Check if you have an issue by running a code checker. If there is a problem, it will be shown in the reports on the page URLs for mismatched hreflang and HTML lang attributes. If no report about the mismatch of hreflang and lang attributes comes up, you’re safe from the problem.
However, this doesn’t mean that you’re free of other hreflang issues. If you encountered other types of hreflang errors, feel free to check our other guides.
In the Sitechecker SEO tool under the ‘Localization’ category, we’re highlighting a key issue that could impact your website’s international SEO effectiveness: ‘Mismatched hreflang and HTML lang attributes.’ This specific check is crucial as it ensures that your multilingual or multi-regional pages are correctly identified by search engines, facilitating accurate language or regional targeting.
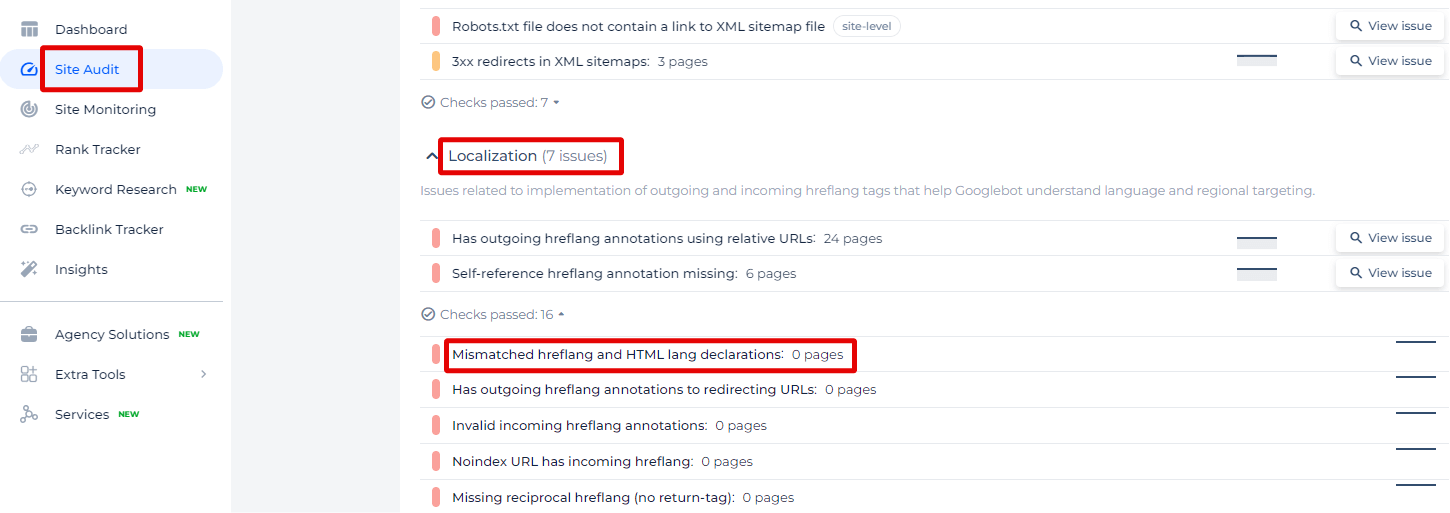
By clicking ‘View issue,’ users are not only presented with the total number of pages affected but also detailed insights into each page. This includes page-specific URLs, their respective status codes, and the discrepancy between the hreflang attribute (which signals to search engines the language and geographical targeting of a webpage) and the HTML lang attribute (which defines the language of the page content).
Harmonize Your Hreflang and Lang Tags!
Discover and correct misalignments between hreflang and lang tags to boost international visibility.
Why is This Important?
Although Google doesn’t always necessarily use the HTML lang attribute today, other search engines and browsers do. Bing is an example of a search engine that still uses the HTML lang attribute. Some programs, such as screen readers, also need to understand the language of the page. They need both the hreflang and lang attributes to match to be able to deliver the page to your visitors.
This issue can also affect your SEO and how visitors find you on the affected search engines.
How to Fix the Issue?
Fixing the mismatch between language-targeting tags and web page markup lang attributes involves ensuring that both attributes consistently specify the same language and region codes on your web pages. Here’s a step-by-step guide to address this issue:
1. Understand the Difference
- html lang attribute: Specifies the language of the content in the HTML document.
- hreflang attribute: Specifies the language and optionally the region of the linked resource, indicating to search engines the language and region of the target URL.
2. Identify the Mismatch
Check your webpage’s source code to identify where the mismatch occurs. Typically, it will look like this:
...
<link rel="alternate" href="https://example.com/fr/" hreflang="fr">
<link rel="alternate" href="https://example.com/de/" hreflang="de">
...
3. Match the lang and hreflang tags
Ensure that the lang attribute in your <html> tag corresponds to the appropriate language-targeting attribute values used in your alternate links.
If your website has different versions for English, French, and German, you need to set the HTML lang attribute for each version to match the markup language values in the alternate links:
For the English version:
<html lang="en">
<head>
<link rel="alternate" href="https://example.com/fr/" hreflang="fr">
<link rel="alternate" href="https://example.com/de/" hreflang="de>
<!-- other head elements -->
</head>
<body>
<!-- content -->
</body>
</html>
For the French version:
<html lang="fr">
<head>
<link rel="alternate" href="https://example.com/en/" hreflang="en">
<link rel="alternate" href="https://example.com/de/" hreflang="de>
<!-- other head elements -->
</head>
<body>
<!-- content -->
</body>
</html>
For the German version:
<html lang="de">
<head>
<link rel="alternate" href="https://example.com/en/" hreflang="en">
<link rel="alternate" href="https://example.com/fr/" hreflang="fr>
<!-- other head elements -->
</head>
<body>
<!-- content -->
</body>
</html>
4. Validate Your Changes
- Manual Check. Manually inspect the web page markup source code of your pages to ensure the lang and language-targeting attributes match as required.
- Tools and Validators. Use tools such as Google’s Search Console, and Sitechecker to verify that the hreflang and html lang attributes are correctly implemented and matched.
5. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Incorrect Language Codes. Ensure that you are using the correct ISO 639-1 language codes (e.g., en for English, fr for French).
- Incorrect Region Codes. If specifying regions, ensure they follow the correct format (e.g., en-US for American English, en-GB for British English).
- Omitting Alternate Links. Ensure every language/region version of your site includes alternate links for all other versions.
By following these steps, you can ensure that the lang attribute and hreflang attributes are correctly matched, improving your site’s SEO and usability for different language audiences.