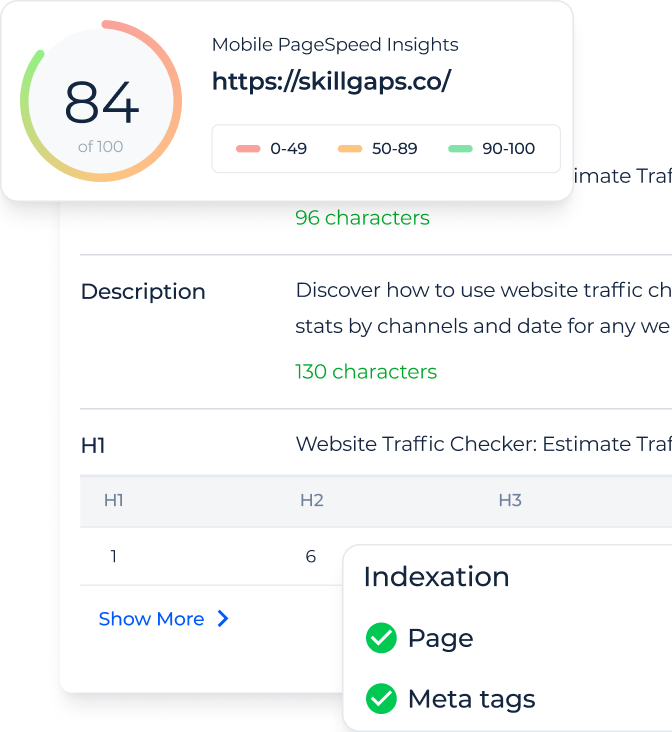
What is the Canonical Tester?
The Canonical URL Checker by Sitechecker verifies and analyzes preferred versions of webpages to prevent duplicate content issues and ensure correct indexing by search engines. It offers a site-wide audit to detect missing or incorrect canonical tags and a quick single-page check for instant tag validation.
How the tool can assist you
Preferred URL Verification: checks if a page has a correctly implemented preferred version of a webpage to prevent duplicate content issues.
Issue Detection: scans all pages to identify missing, incorrect, or conflicting tags for proper indexing.
Canonical Tag Monitoring: tracks preferred URL tags across the site to detect changes, errors, or inconsistencies that could affect SEO.
Key features of the tool
Unified Dashboard: provides a centralized view of all SEO insights, website health, and optimization recommendations.
User-Friendly Interface: simplifies SEO analysis with an intuitive design, making it easy to monitor and fix issues without technical expertise.
Complete SEO Toolset: offers a comprehensive suite of tools, site audits, keyword tracking for full website optimization.
How to Use the Tool
To use the Canonical URL Tester, select an audit option based on your needs. Choose “Check canonicals on all pages” for a full website audit or “Check canonicals on the page” for an instant single-page check. Once selected, click “Start audit” to analyze canonical tags and ensure proper indexing.
Test Canonicals for All Pages
Step 1: Choose the first selector options

Step 2: Get results
Identify missing, incorrect, or conflicting preferred URL tags that affect indexing. Get detailed issue reports, affected pages, and actionable recommendations to ensure proper search engine recognition and prevent duplicate content problems.
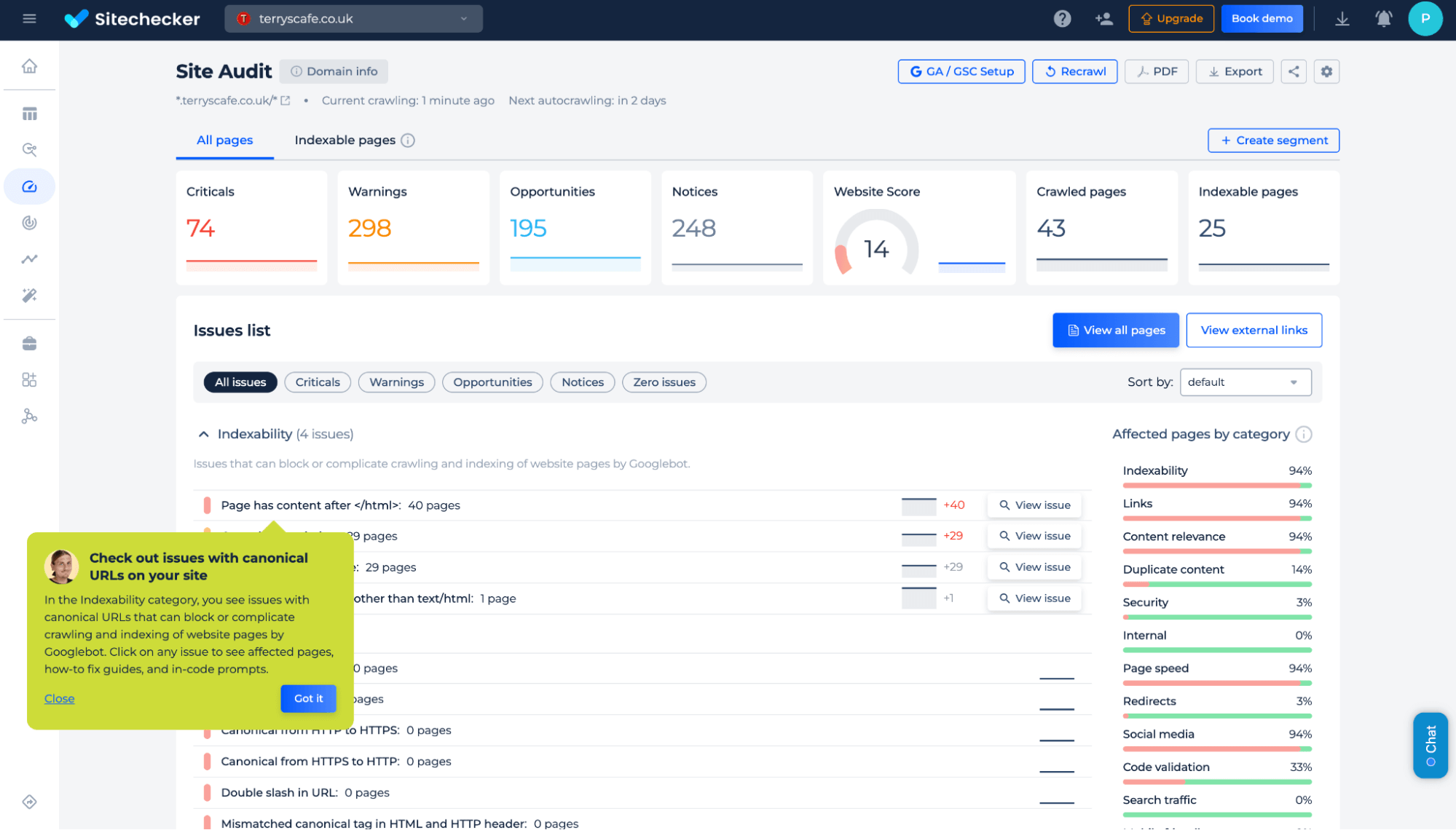
Additional features of the tool
Gain a full-site audit with detailed reports on preferred URL tag issues, indexability, duplicate content, and technical SEO factors. Identify critical errors, warnings, and optimization opportunities to enhance search engine visibility and website performance.
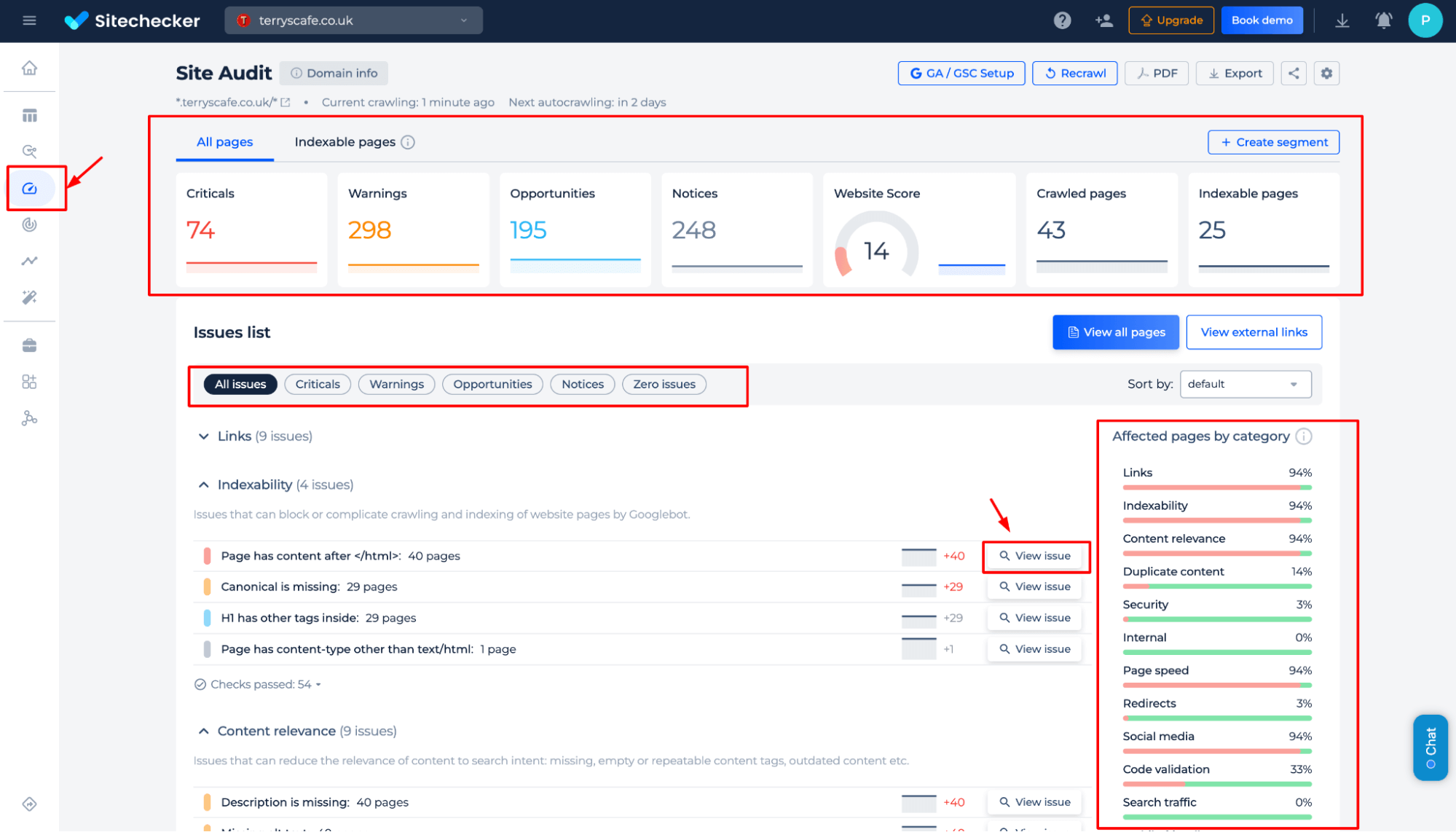
Test the Canonical Tag on the Page
Step 1: Choose a page audit option and start the check
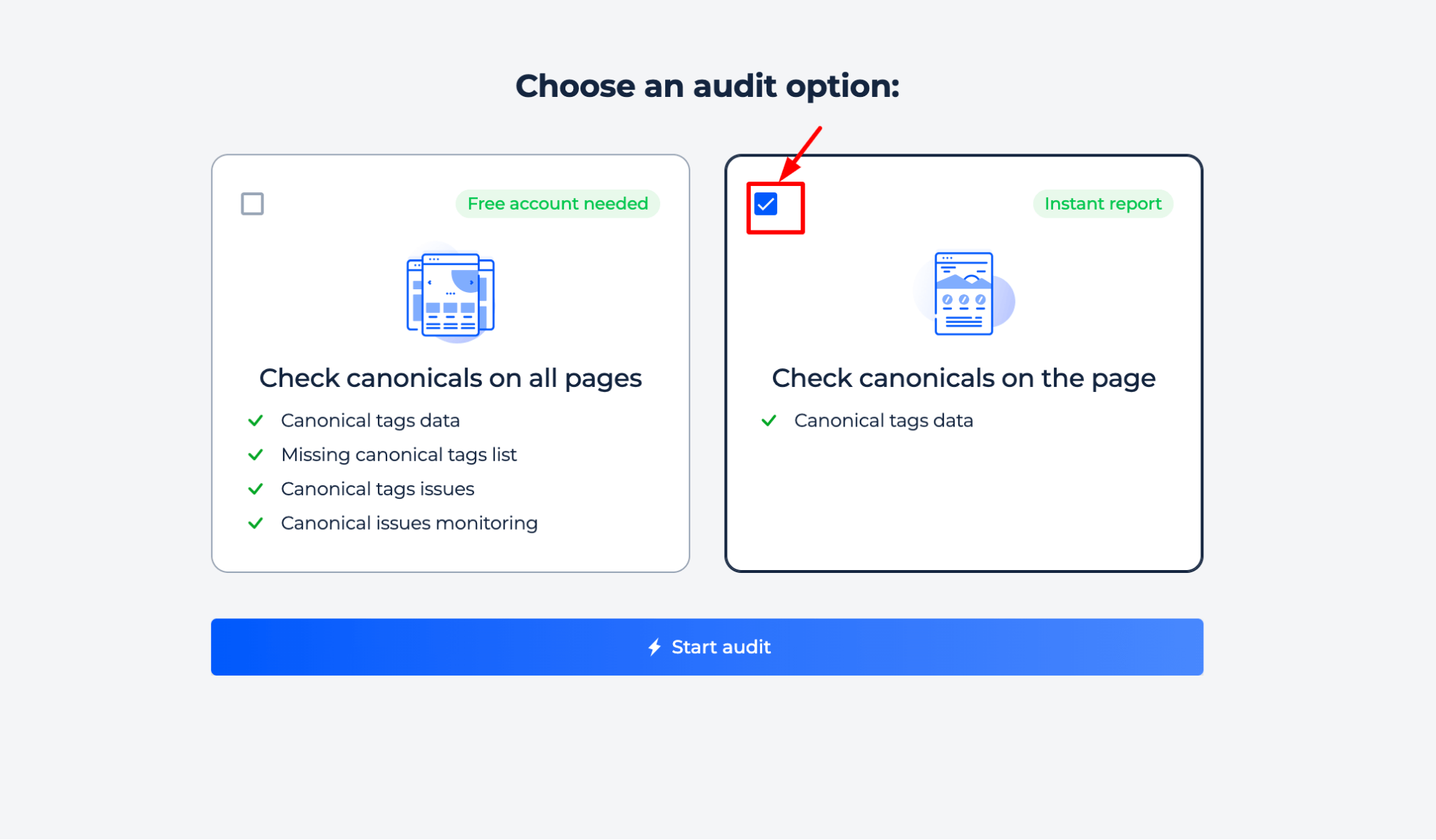
Step 2: Get the results
Instantly verify if a webpage has a properly implemented preferred version of a webpage, check its status code, and ensure correct indexing to prevent duplicate content issues.
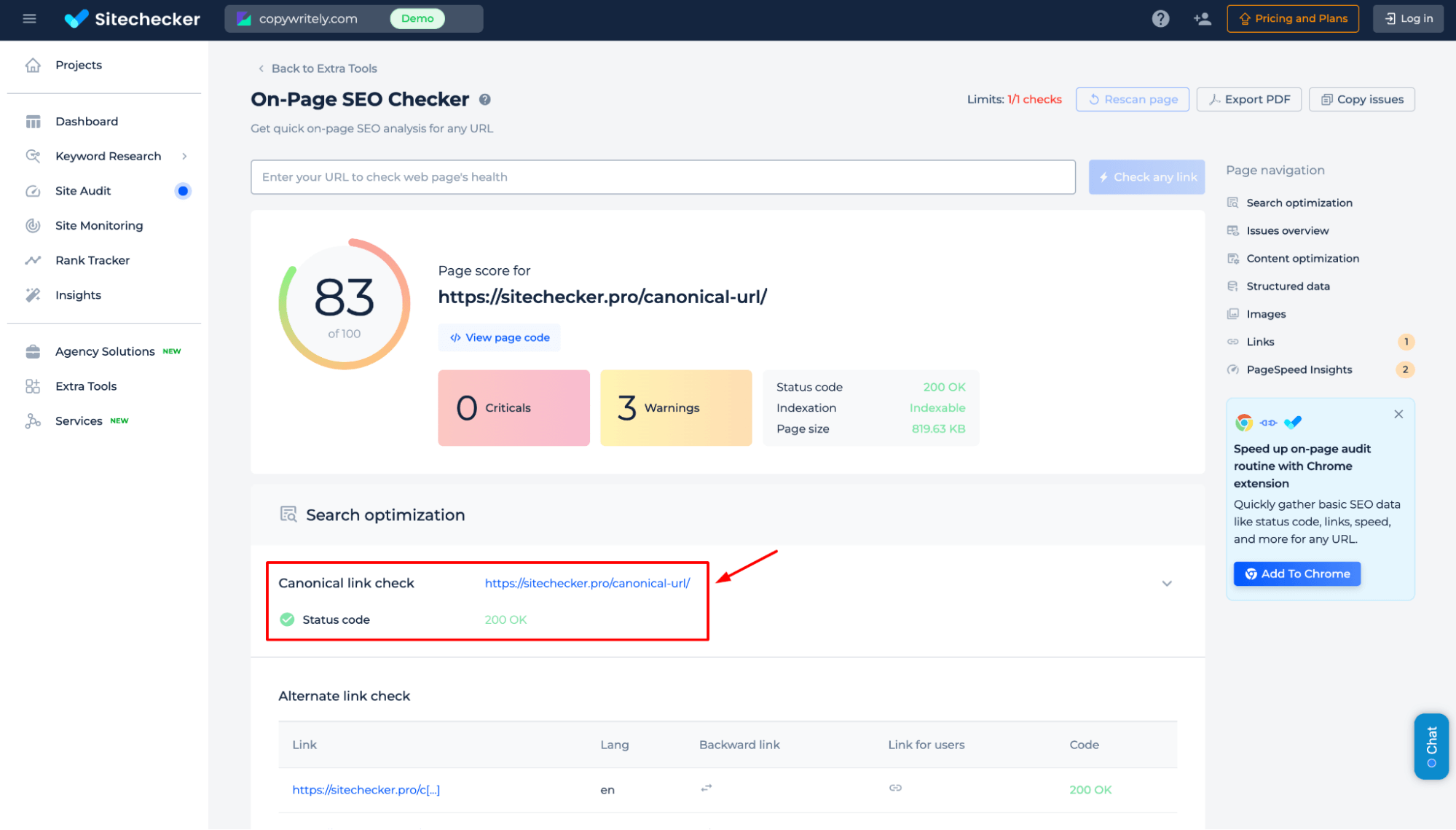
Maximize the tool’s capabilities in the Site Audit section. Explore the demo to uncover critical SEO issues, boost website performance, and simplify technical optimization of your website.
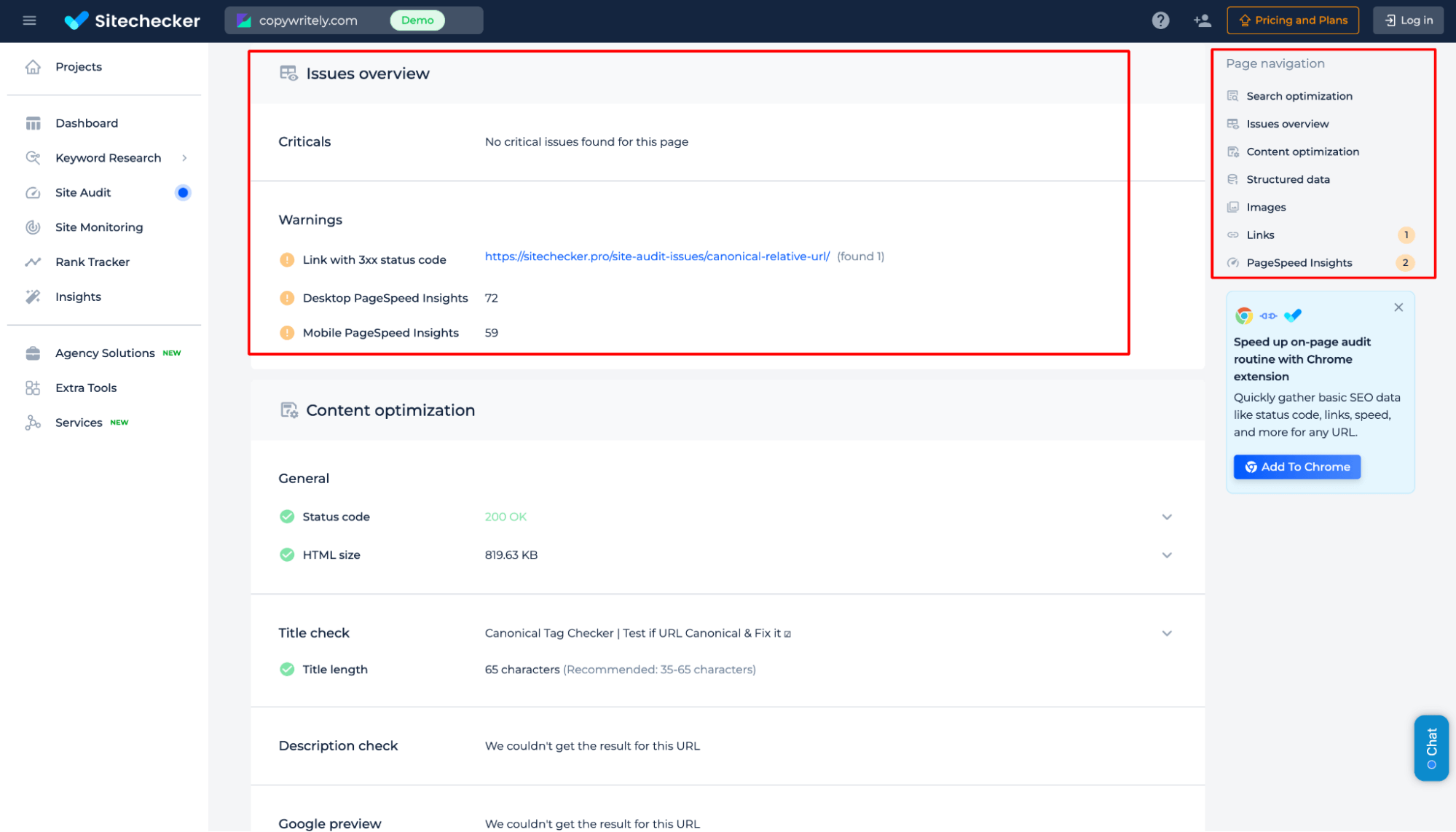
Additional features of the canonical tag test
Beyond the preferred version of a webpage validation, get a detailed overview of critical and warning issues, PageSpeed performance, indexability, and content optimization. Identify technical SEO problems and receive actionable recommendations to enhance your webpage’s search visibility.
If a missing canonical URL is detected, we provide a detailed, comprehensive guide on fixing the issue. You can also watch the video version of the guide here.
Final Idea
The Canonical Tag Checker helps ensure correct indexing by verifying, detecting, and monitoring canonical tags across your website. It offers site-wide audits to identify missing or incorrect tags and instant single-page checks for quick validation. With a user-friendly interface, unified dashboard, and a complete SEO toolset, it simplifies SEO analysis and optimization. Users can uncover critical SEO issues, enhance website performance, and prevent duplicate content problems.