Have you ever opened a website that had too many page elements? There is nothing worse than opening a page, which takes a long time to load, and when it finally does, you can’t make out anything. All the HTML page elements are blocking your view of the whole page itself.
This is one web page design flaw that you need to avoid at all costs. You need to make sure that there is more content on your site than HTML elements. How do you do that? By using a code to text ratio checker.
How Do I Determine the Ratio With the Sitechecker Tool?
The ratio of text to code indicates how successfully your page has been optimized. It is really simple to discover this information: just enter the URL or domain name. The following metrics will be calculated:
- Text size
- Text-to-code ratio
Additionally, the tool provides all the information you will need about each statistic that is measured.
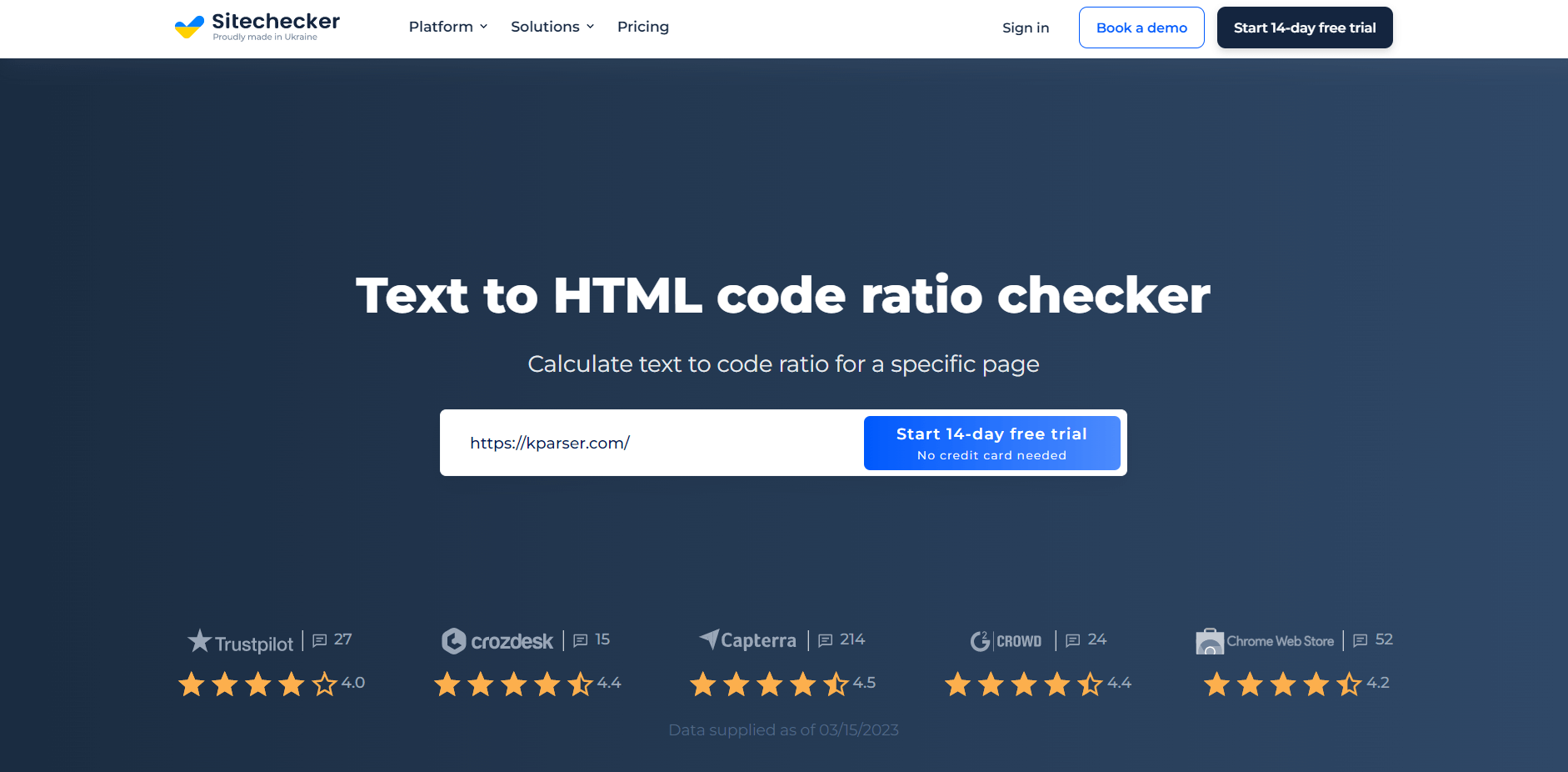
Step 1: Insert your URL and start free trial
We know you’re busy and that time is valuable. That’s why our free trial starts with just an email address or Google account, without the need for any credit card information!
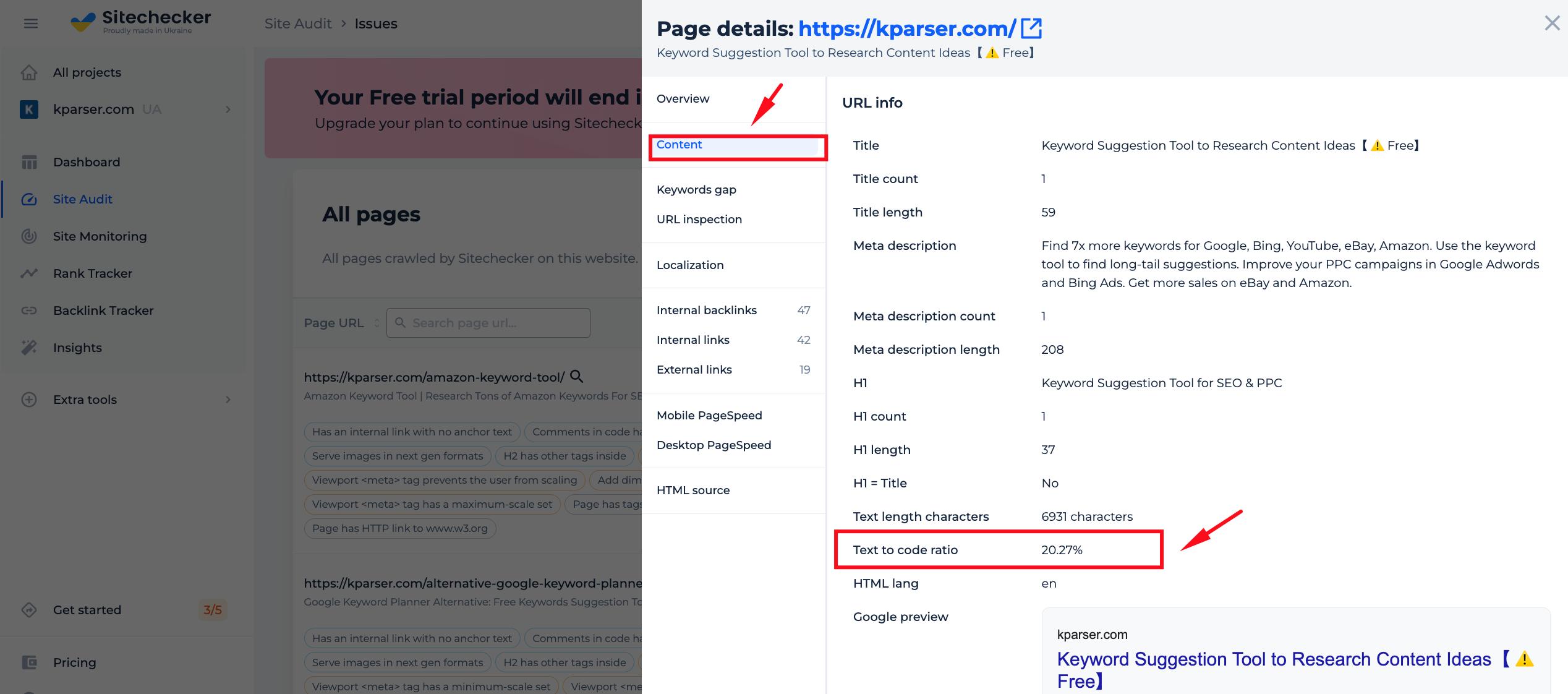
Step 2: Getting the results
After you add a URL to our tool, we will quickly crawl the site and provide you with detailed results, including data on the text-to-code ratio. The audit also includes an overview of all issues present on each webpage in just seconds!
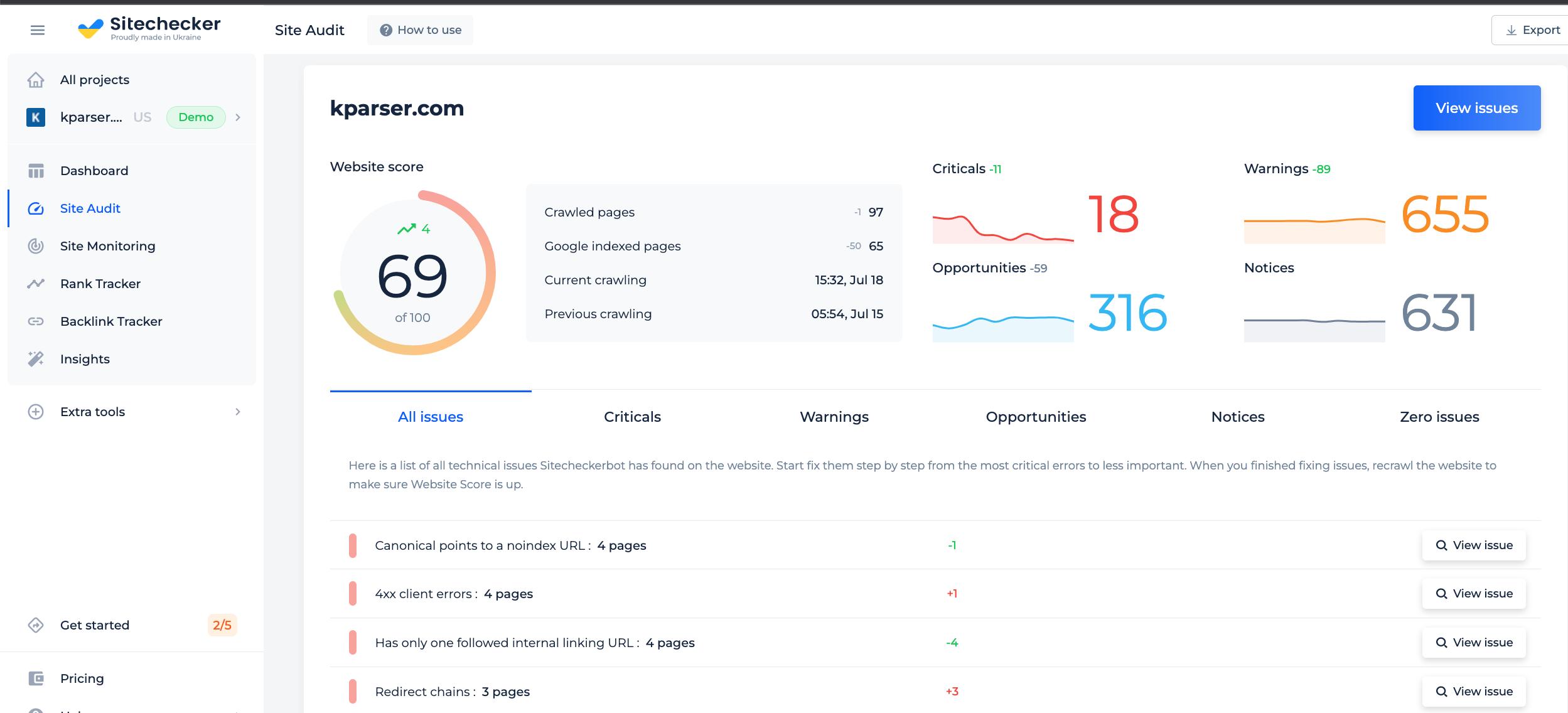
Features of Text to HTML Code Ratio Checker
By creating a trial account, you can run an audit that lists the URLs where problems occur and provides instructions on how to fix them.
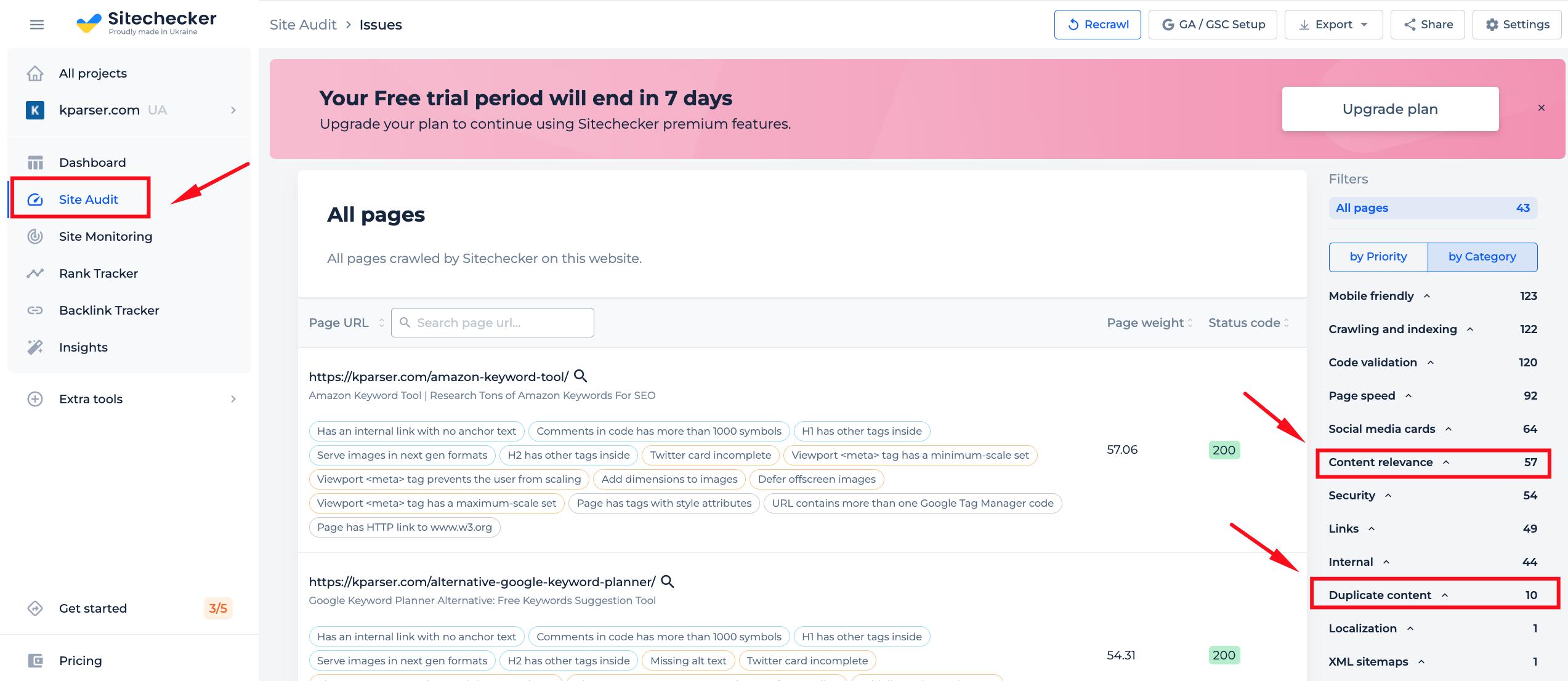
The “Content relevance” and “Duplicate content” sections of the full site audit will help you identify any issues with the content on your site so that they can be quickly fixed. You’ll also receive notifications if these problems arise in the future when new pages are added!
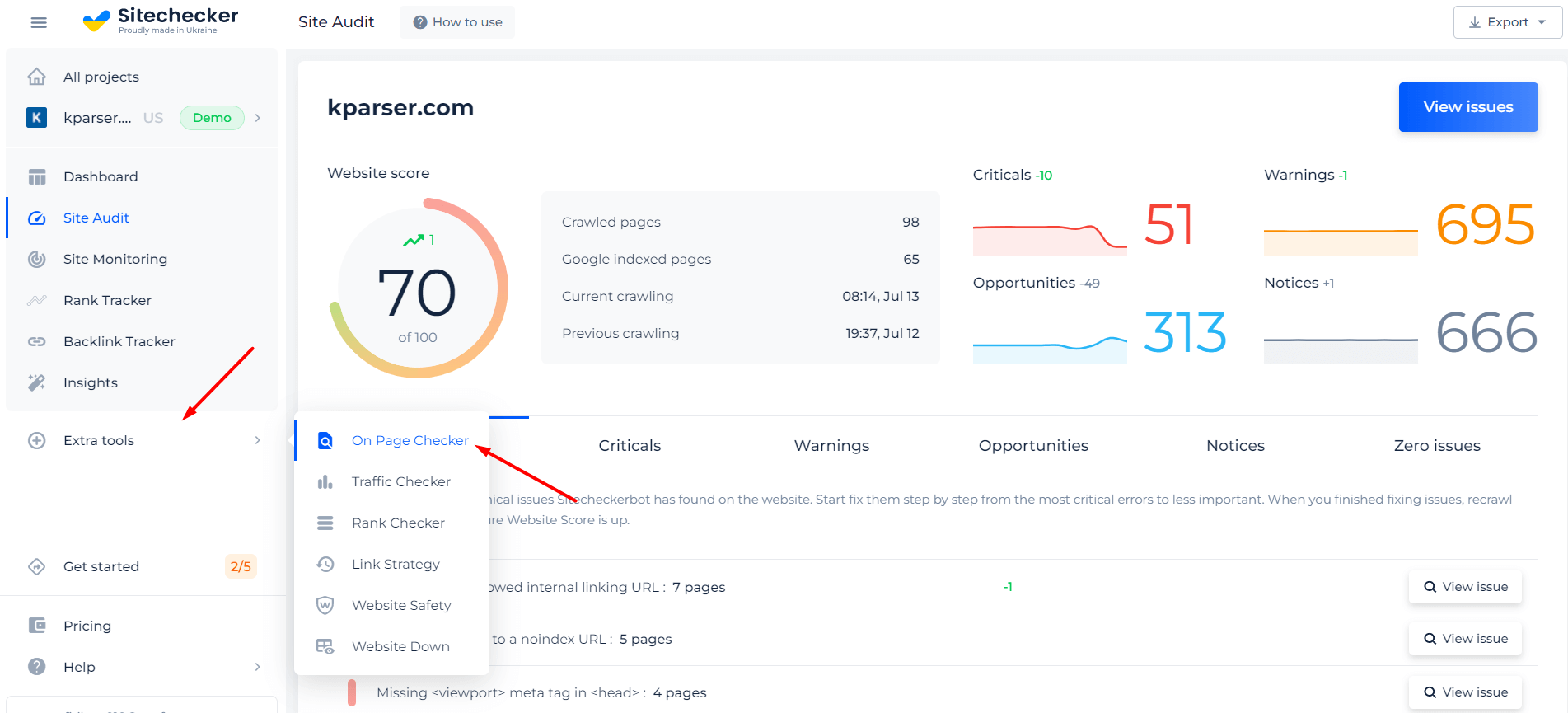
If you’re worried about the text to code ratio on a particular page, our on-page checker tool can help. This will ensure that everything is set up correctly and avoid any potential problems.
Find all pages with text to code ration issues right now!
Make a full audit to find out and fix text to html code ratio issues in order to improve your technical SEO.
What Is the Code to Text Ratio?
The text/HTML ratio tells us just how much text is on a page in comparison to how much code is on the backend. This metric assesses the amount of textual information contained on web pages instead of the amount of HTML code that is necessary to produce the page. The higher the ratio, the better the user experience will be. You want people to actually read what information you have provided, after all.
Is It Important for SEO?
Despite the fact that the Text/Code ratio has a minimal impact on your Google ranking, it is not suggested to “pump” HTML code rather than the actual text on the page. Doing so might have a detrimental impact on your site’s performance. Excessive HTML code can cause a page to load slowly and make it more difficult for search engine robots to perform their tasks.
This is verified from the top brass at Google itself. John Mueller, Google’s Search Advocate and foremost of experts, noted that the text to HTML ratio is not a ranking signal. However, it may be taken as an indication that a webpage contains bloated HTML. When such a site is accessed by consumers, particularly on mobile devices, it can “slow things down.” He also says on the record that, “We don’t use [Text to HTML ratio] for anything,” and that he wouldn’t focus on that metric at all for SEO purposes. Find the whole video here: https://youtu.be/4QL1uuo_NNA?t=1918
What Is the Optimal Text to HTML Ratio?
The ideal text-to-code ratio is 10%, which is the starting point. If your page’s content to code ratio is less than 10%, you should consider optimizing your HTML code, CSS code, and JS code or adding additional content to your website.
But this doesn’t mean you have to stick to a 10% ratio as gospel. It is your site, at the end of the day, and you should do what works for you.
In fact, good text to HTML ratios range from anything between 25% and 70%. You may notice that many top-ranked websites in search results have visible text. This has become increasingly apparent after search engines, such as Google, launched the Panda update, which placed focus on content-driven sites.
How Do I Fix URLs With a Low Ratio?
Despite the fact that this is not a Google ranking factor, it is not advisable to “pump” an HTML code in relation to the helpful content on a page. Doing so may have an indirect negative impact on your website’s rating as a result of the Google algorithm. The loading of a website, as well as the analysis of the page by search robots, may be slowed by redundant HTML code.
As for how to fix it, these are things you can do:
- The website https://validator.w3.org/ allows you to check the HTML code’s validity.
- Delete the code that isn’t needed.
- Large “empty” spaces should be removed from the code.
- Large comments should be removed from the code.
- Remove any concealed text that isn’t visible to the general public.
For more details, please check out https://sitechecker.pro/site-audit-issues/text-to-code-ratio-is-low/
Analyze not only Text to Code Ratio but the entire site!
Conduct a full audit to find out and fix all the site level and page level issues on your website.