Image redirection is a crucial yet often overlooked part of maintaining website integrity, especially during site migrations, redesigns, or URL changes. Implementing proper image redirects ensures that pictures remain accessible, preserving user experience and valuable SEO benefits. Without forwardings, broken image links can lead to poor user interactions and lost traffic from picture searches, making it essential for website managers to understand and apply these techniques effectively.
Overview of Image Redirection
Image redirection is the process of rerouting a picture URL to a new location when the original path changes. This might involve a simple URL update or a more complex process if migrating to a new domain or subdomain. Image forwardings work similarly to webpage redirects (like 301 or 302), helping ensure that users and search engines can still locate these resources, which is critical for maintaining SEO rankings and avoiding broken links.
Common Scenarios for Image Redirection
There are several instances where image redirection becomes necessary. One of the most common is domain or subdomain migration, where pictures hosted on an old domain need to be forwarded to a new one to preserve SEO. Other scenarios include directory restructuring, where folder paths are updated, redesigns or CMS changes, and file renaming for better organization. In each of these cases, image redirection helps maintain accessibility and improves the website’s overall functionality by ensuring all pictures remain intact and load properly.
How to Check for Redirected Images
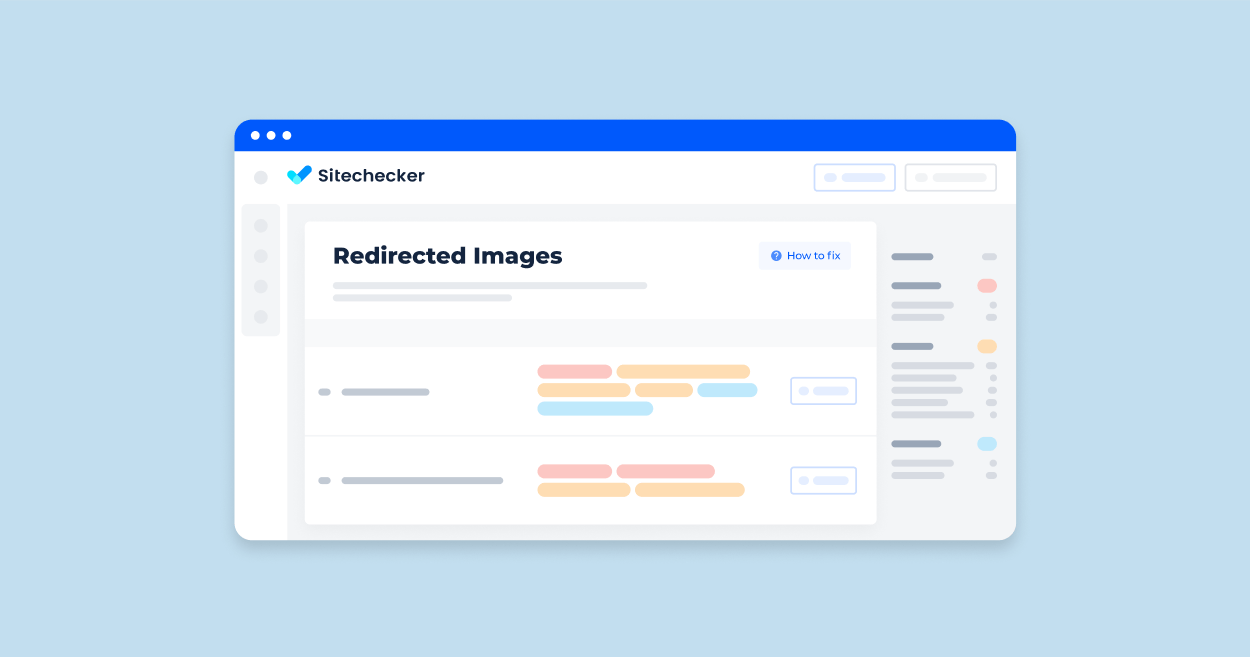
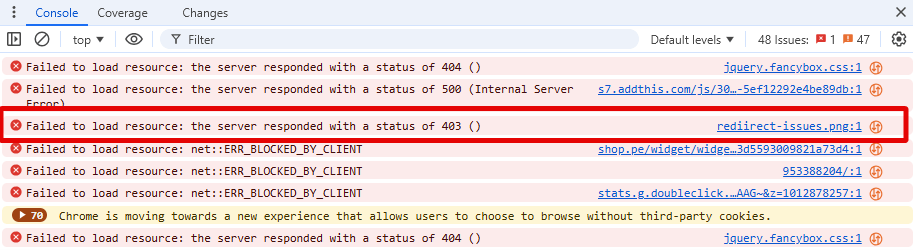
Checking for redirected pictures ages on a website involves identifying images that are being readdressed to another URL rather than being served directly. Here are the steps you can follow to check it:
The Sitechecker SEO tool, in the “Redirects” section under Site Audit, highlights various types of redirect issues that can impact a website’s user experience and search engine crawling efficiency. This tool is designed to help users swiftly identify problematic readdresses, such as chains, broken internal link re-routes, and improper HTTPS to HTTP forwards, among others.
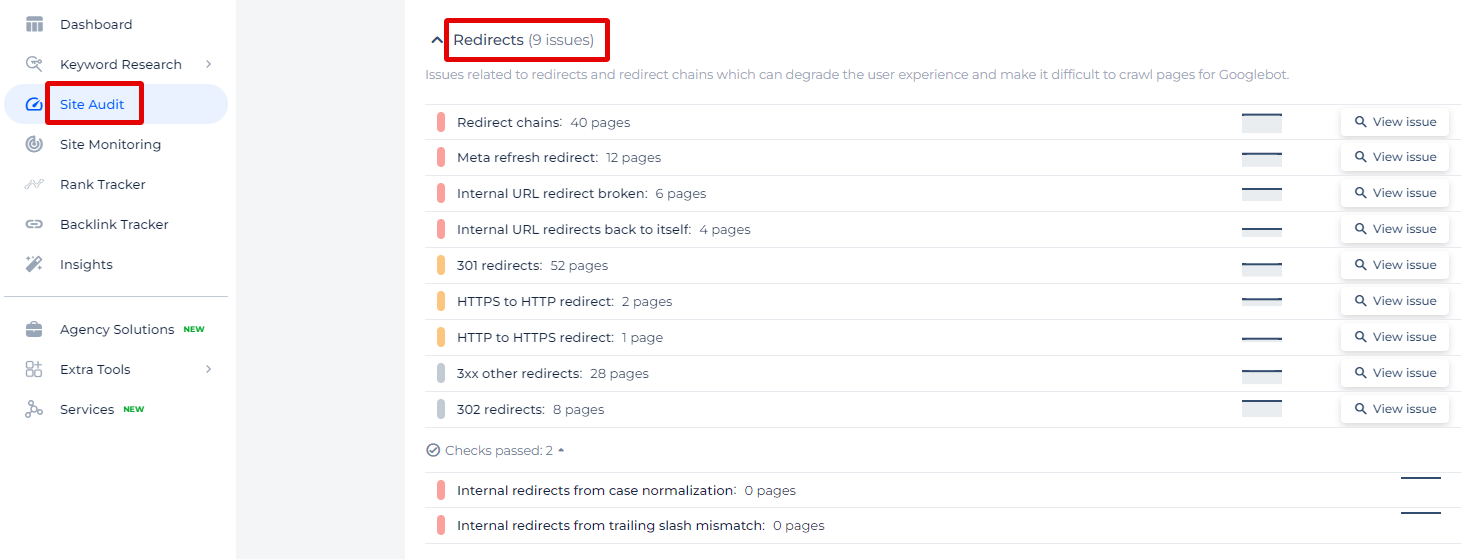
By clicking on “View issue,” users can access a detailed list of pages affected by these specific redirect problems.
Why Redirect Images?
Redirecting images is a valuable practice that supports both search engine optimization (SEO) and user experience. Ensuring that all pictures are properly forwarded can help retain traffic from search engines and avoid broken links that detract from a seamless browsing experience. Here, we’ll discuss why picture redirection matters in these areas.
SEO Benefits of Image Redirection
Image redirection plays a significant role in SEO by helping retain image search traffic and preventing lost rankings. When pictures are moved without a rerouting, search engines treat them as missing, which can lead to lost link equity and a drop in organic visibility.
By implementing 301 redirects, websites can ensure that the SEO value from the original pictures is transferred to the new URLs, maintaining rankings and visibility in image search results.
User Experience Considerations
Image redirection enhances user experience by preventing broken pictures that can disrupt a page’s visual flow and functionality. Broken images or slow-loading ones due to forwarding chains can frustrate visitors, leading to increased bounce rates and lower engagement.
Ensuring images are properly redirected helps pages load smoothly and creates a more consistent and professional user experience, ultimately improving overall site performance and visitor satisfaction.
Types of Image Redirects
When setting up image reroutes, it’s essential to understand the differences between various types, as each serves a distinct purpose. Selecting the correct redirect type can influence both the user experience and search engine indexing of your pictures.
301 vs. 302 Redirects
A 301 redirect is a permanent forwarding, transferring the full SEO value from the original image URL to the new URL. This type is ideal when an image has permanently moved, such as in a domain change or directory restructure.
Conversely, a 302 redirect is temporary, signaling to search engines that the original URL may become active again. This is useful when temporarily moving images, for example, during site testing or A/B picture testing.
Choosing the Right Redirect Type
The choice between a 301 and 302 redirect depends on the intent and expected duration of the move. A 301 redirect should be the default when relocating an image indefinitely, as it preserves SEO value and informs search engines to update the URL. In contrast, a 302 redirect should only be used for temporary moves, as it keeps the original URL active in search indexes without passing full link equity.
This decision is critical to ensuring optimal SEO outcomes and a smooth user experience.
Common Scenarios for Image Redirection
Understanding common scenarios for image redirection can help website owners anticipate when and how to implement forwardings effectively. Each situation requires different techniques to ensure images remain accessible and SEO is maintained.
Domain or Subdomain Migration
When moving a website to a new domain or subdomain, image URLs may change. Forwarding these pictures using 301 redirects helps preserve SEO value and ensures visitors find the images at their new location without issues.
Directory or File Name Changes
Sometimes, directory structures or image file names are updated for better organization. Redirecting pictures from old directories to new paths ensures that any external links or bookmarked images remain functional, avoiding broken links and improving user experience.
Redesigns and CMS Transitions
Redesigning a website or switching to a new CMS often leads to structural changes, impacting image paths. Implementing image redirects during this transition period can prevent disruptions, retain SEO, and ensure a consistent experience for users as the site evolves.
Steps for Implementing Image Redirection
Implementing image redirection depends on your server configuration or CMS. Following the correct steps helps ensure the reroutes work seamlessly and don’t negatively impact SEO or user experience.
Redirects in Apache and Nginx
For Apache servers, image redirects can be configured in the .htaccess file using 301 or 302 directives. In Nginx, use the configuration file to create redirect rules, specifying the original image URL and the new URL. These rules ensure that any request for the old picture path will automatically lead to the new path.
Using CMS Platforms for Image Redirection
Most CMS platforms, such as WordPress and Joomla, offer plugins or built-in settings for setting up redirects. These plugins simplify the process, allowing you to manage image redirects without directly editing server files, which is ideal for non-technical users or quick updates during content transitions.
Recommended Tools and Techniques
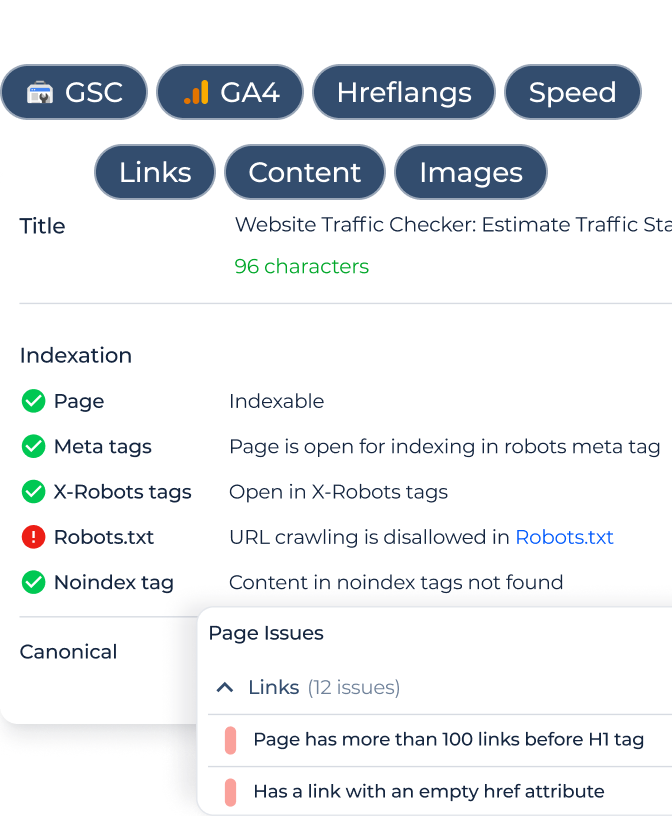
A variety of tools, such as Screaming Frog and Google Search Console, can help identify broken image links and monitor redirect success. Use these tools to audit your forwardings regularly and spot any broken pictures, redirect loops, or unintentional chains that could affect performance or SEO.
Best Practices for Image Redirection
Adhering to best practices for picture forwarding can enhance both SEO and user experience by minimizing issues like redirect loops and broken images. Here are some key guidelines to follow.
301 Redirects for Permanent Changes
Use 301 redirects for any image URL changes intended to be permanent. This type of forwarding transfers the full SEO value from the old URL to the new one, helping maintain search rankings and link equity. Avoid using temporary redirects (302) for long-term changes, as they don’t pass full SEO value.
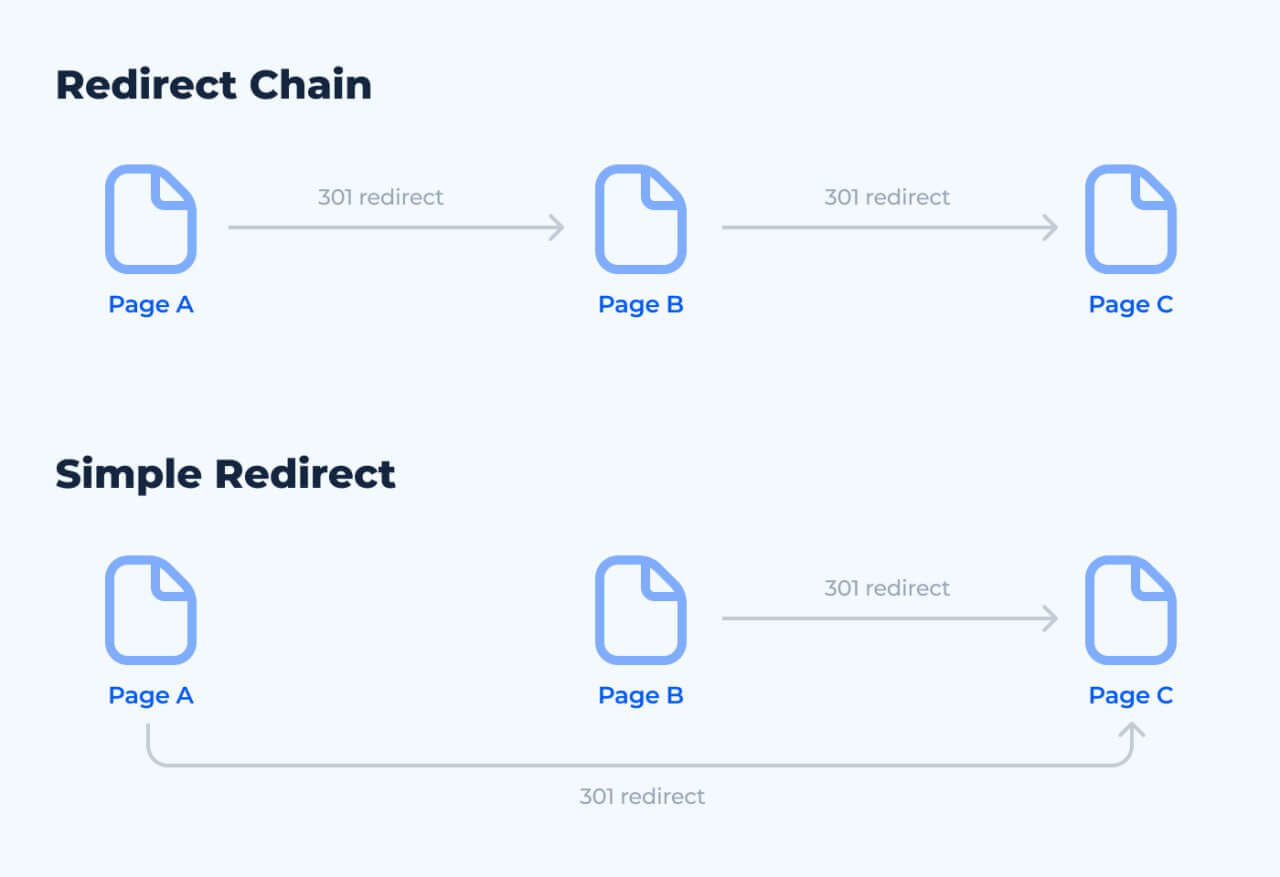
Minimizing Redirect Chains
Redirect chains—where multiple reroutes occur before reaching the final image URL—can slow down page load times and reduce SEO effectiveness. Whenever possible, direct the original URL to the final image location, eliminating any unnecessary steps to improve performance and prevent potential loss of traffic.
Regular Redirect Maintenance
Periodic checks are essential for maintaining a healthy redirect structure. Tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, or other auditing software can help identify broken forwardings, update outdated URLs, and ensure no redirect loops or chains have formed over time. Regular audits improve site health, keeping image links efficient and up-to-date.
Challenges and Pitfalls of Image Redirection
While image redirection offers numerous benefits, there are potential challenges and pitfalls to consider. Addressing these effectively ensures that forwardings serve their intended purpose without unintended drawbacks.
Performance Impacts
Redirects, especially redirect chains, can slow down page load times, as each forwarding adds a request and response cycle. This latency can affect user experience and SEO, so it’s essential to minimize chains and prioritize direct redirects whenever possible.
Common Issues (Redirect Loops, Broken Links)
Redirect loops, where URLs continuously point to one another without reaching an endpoint, can cause loading errors and disrupt the user experience. Similarly, broken links from improper forwarding lead to missing images. Regularly audit redirects to avoid these issues and ensure all URLs resolve correctly.
Monitoring Redirects for Effectiveness
Continuous monitoring of redirects helps identify problems such as broken links, redirect loops, or chains that may impact performance. Use tools like Google Search Console and Screaming Frog to track redirect efficiency, ensure SEO value is maintained, and make adjustments as needed for optimal performance.
Conclusion
Implementing image redirects is essential for maintaining SEO value and a positive user experience during website changes, migrations, and redesigns. By understanding when and how to use 301 and 302 redirects, website owners can prevent broken links, retain search engine visibility, and ensure smooth page performance. Regularly auditing and maintaining redirects helps keep them effective, reducing potential issues like redirect loops and broken links. With these strategies, you can effectively manage image redirects, ensuring your site remains user-friendly and SEO-optimized.