What is a Nofollow Link Checker tool?
Nofollow Link Checker is a tool that analyzes a webpage and identifies the rel=”nofollow” attribute of all links and indexing directives. It detects Robots meta and X-Robots-Tag settings, checks for nofollow attributes, shows internal and external dofollow/nofollow links, provides a complete list of anchors, and returns the status codes for each URL.
How the tool can help you
Identification of robots and X-Robots-Tag rules: checks whether the page contains Robots meta or X-Robots-Tag directives, helping you spot noindex, nofollow, or other regulations that may limit crawling or indexing.
Detection of internal and external nofollow links: identifies all dofollow and nofollow attributes across internal and external links, providing complete visibility into how link equity flows through the page.
Complete anchor and link status reporting: provides a structured list of all anchors and verifies the status codes of every URL, allowing you to catch broken links, redirects, and other issues that may impact SEO performance.
Key features of the tool
Unified dashboard: provides a centralized dashboard that offers a comprehensive view of various SEO metrics and website performance indicators.
User-friendly interface: designed with a focus on user experience, ensuring that its interface is intuitive and easy to navigate.
Complete SEO toolset: comes equipped with a full suite of SEO tools. This includes features for keyword research, on-page SEO optimization, site auditing, and more.
How to use the Nofollow Links Checker
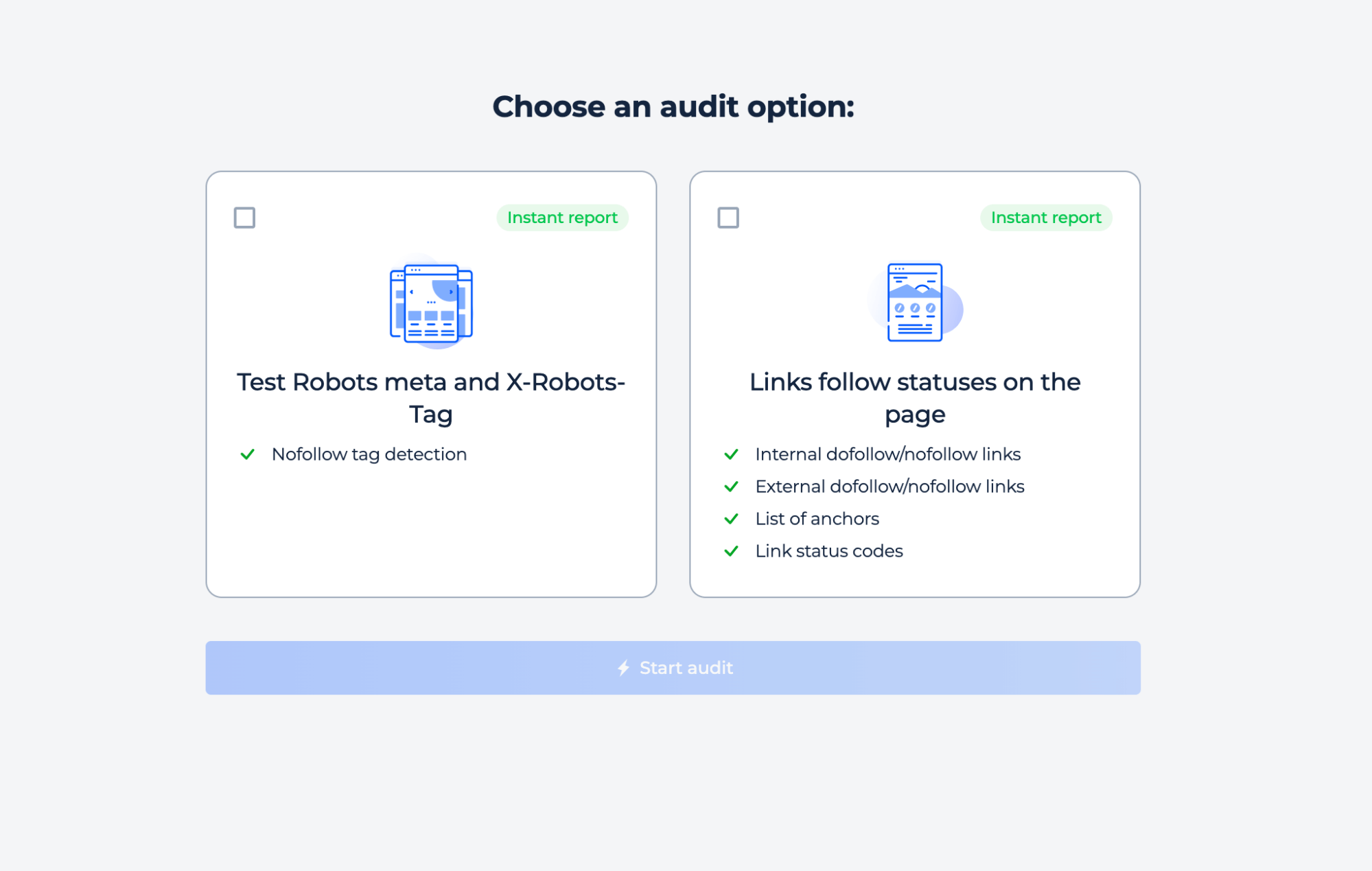
You can test whether the page contains Robots or X-Robots-Tag directives, or analyze all link follow/nofollow statuses on the page. Select the option that best fits your goal, and then begin the audit to receive an instant report.
Check the nofollow attribute in the Robots meta and X-Robots-tag
Step 1: Choose the inspection
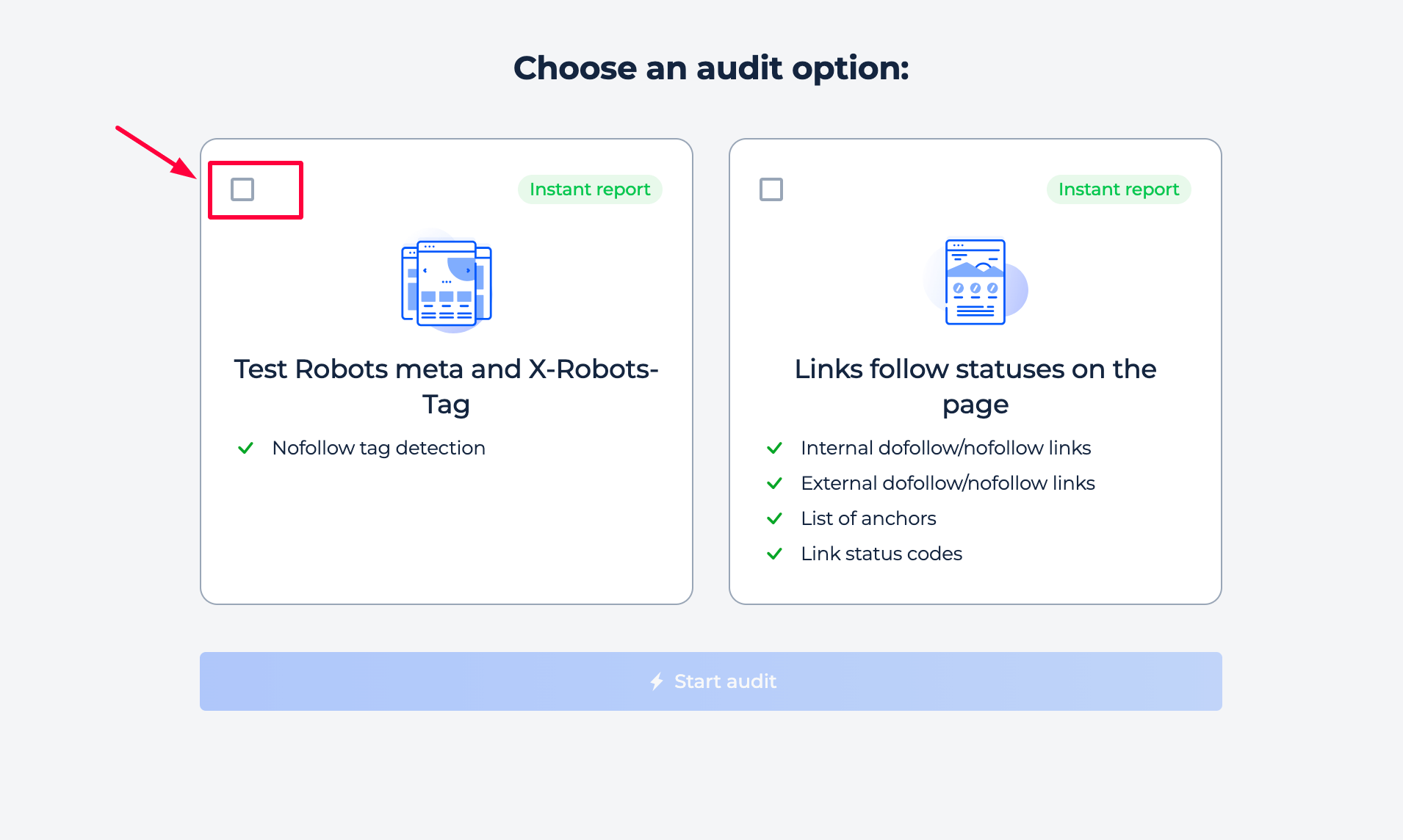
Step 2: Get the results
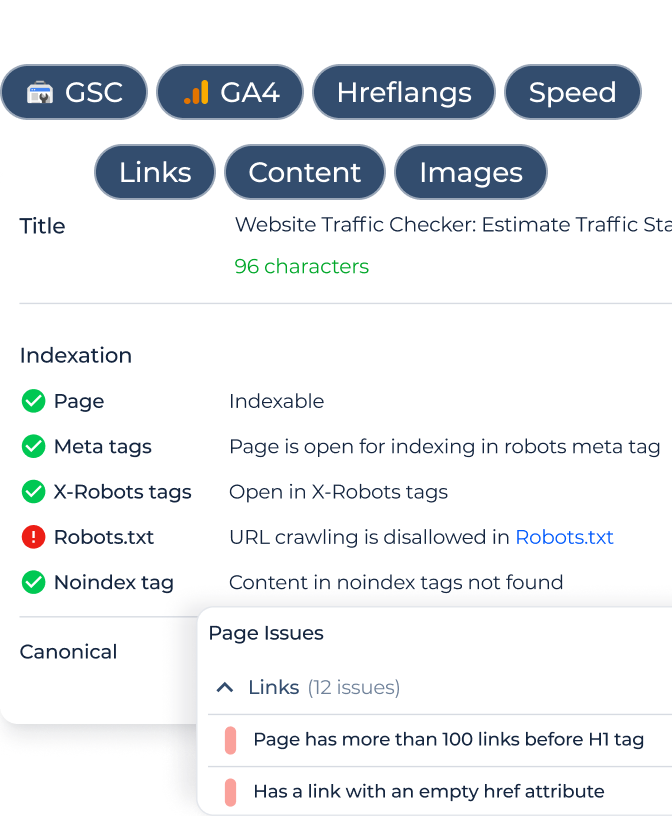
In the results, you can see how the page behaves in terms of indexation based on several signals:
1. Robots meta tag – whether it contains directives like index, noindex, follow, or nofollow.
2. X-Robots-Tag – server-level indexation rules returned in HTTP headers.
3. robots.txt file – whether crawling is allowed or restricted for this URL.
4. Noindex tag – whether any noindex directives appear inside the page content.
This audit helps you quickly understand how search engines are instructed to crawl and index the page.
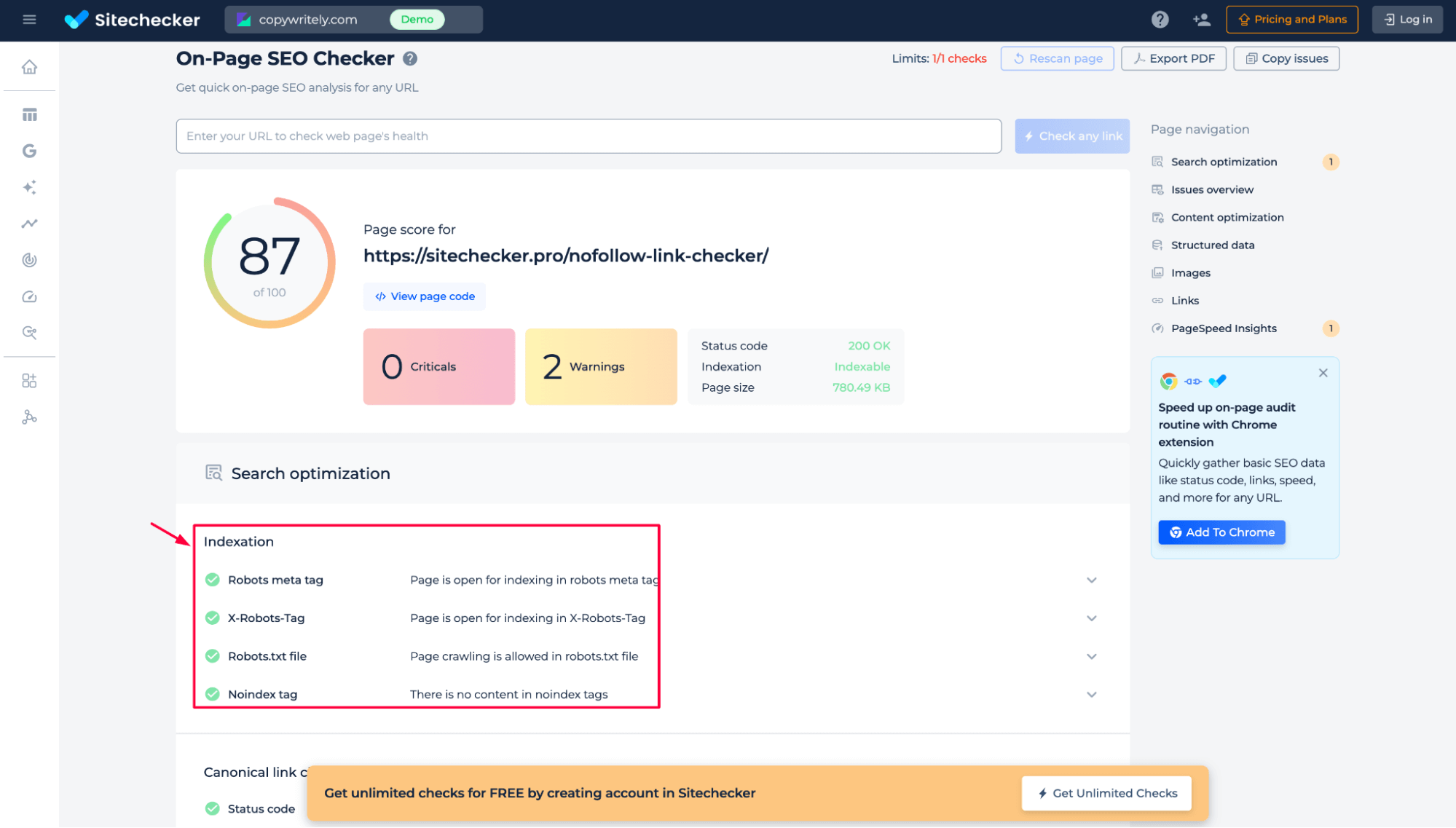
Additional features of the Robots meta and X-Robots-tag check
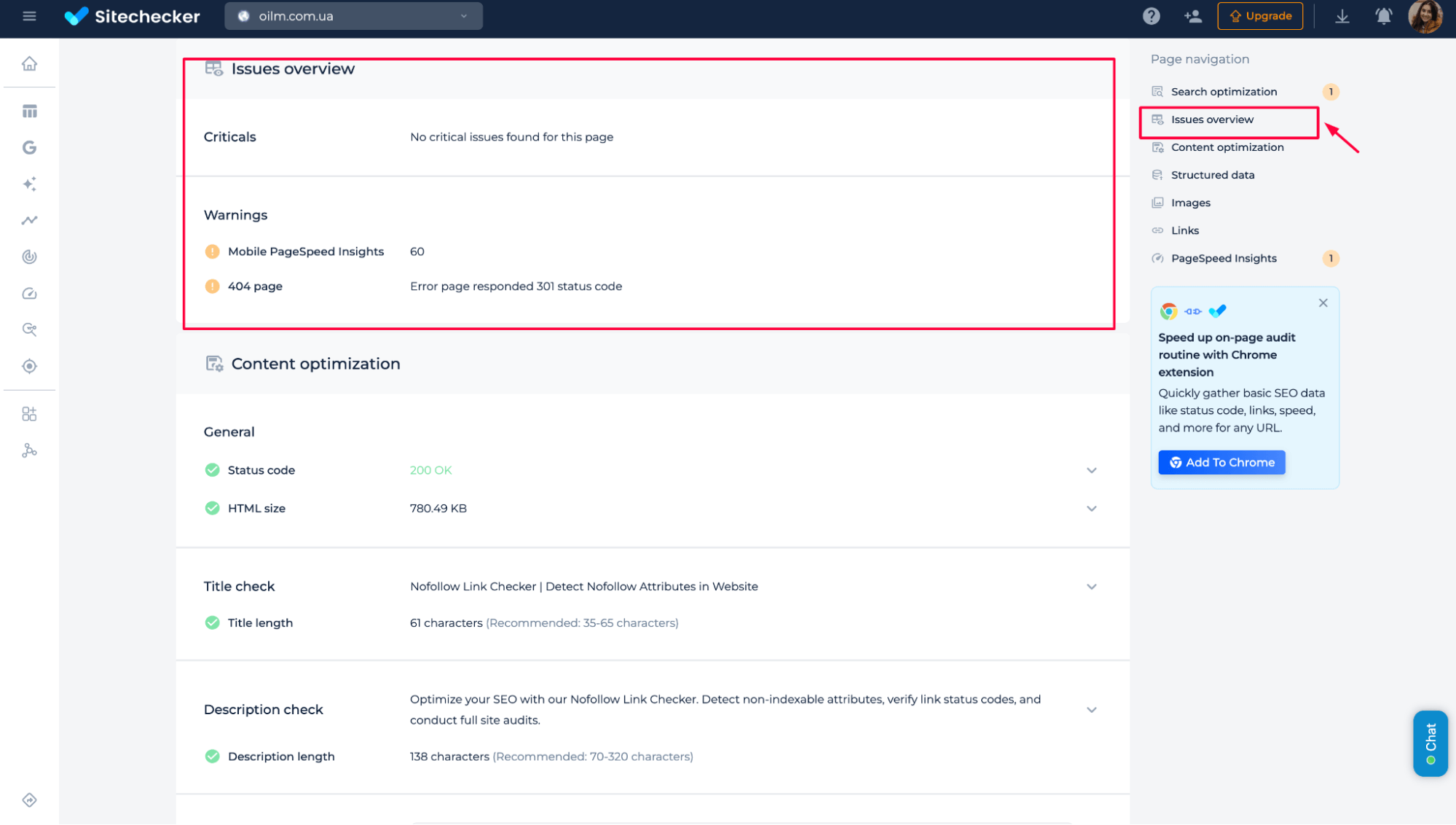
In addition to checking nofollow attributes and indexation rules, the tool also provides a quick overview of other on-page issues. You can identify critical problems, warnings, and technical signals, such as Page Speed issues, 404 errors, status codes, HTML size, and metadata quality.
This allows you to review link attributes and diagnose general SEO problems on the same page in one scan.
Check the links follow statuses on the page
Step 1: Select the “Links follow statuses on the page” option
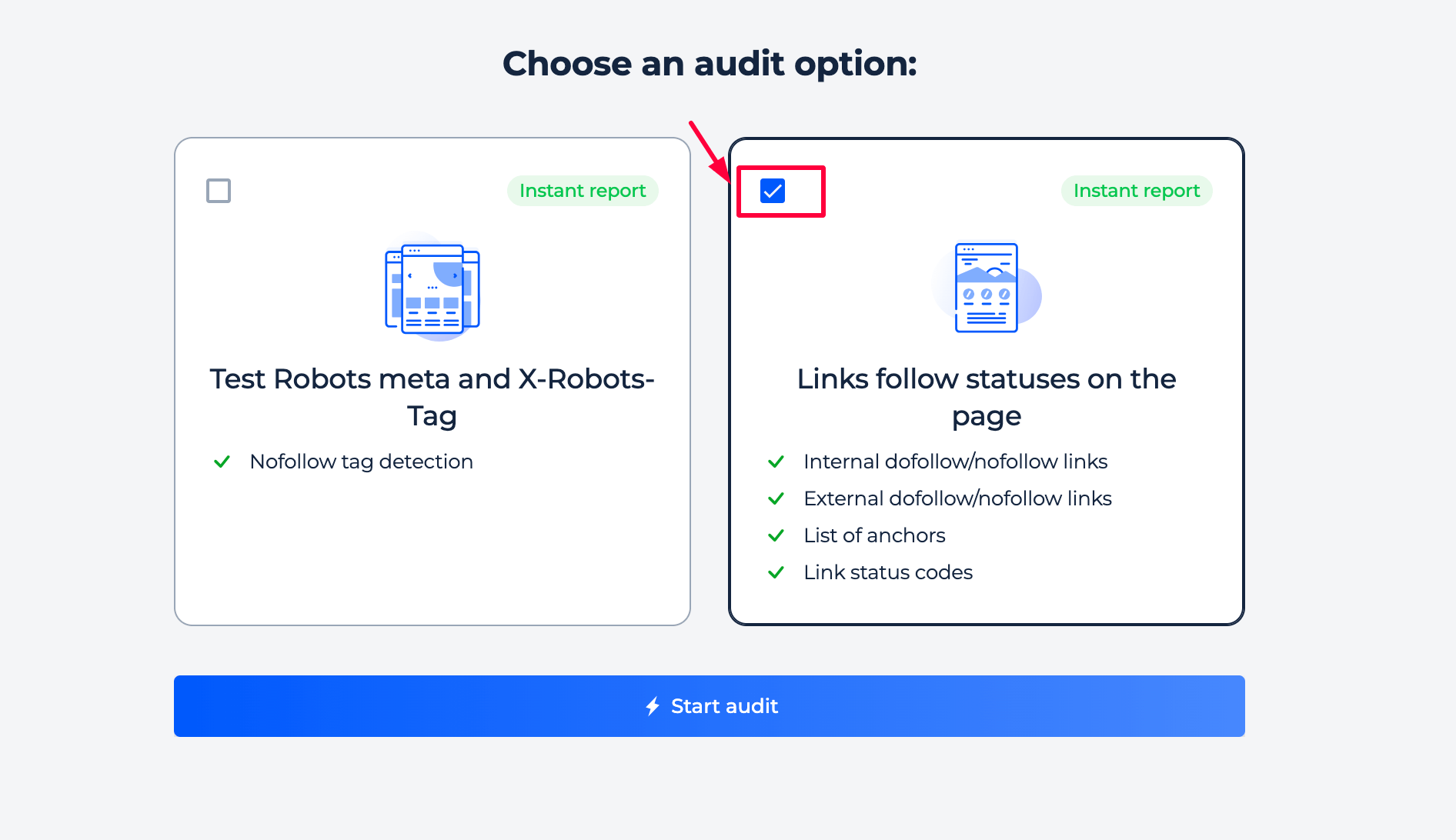
Step 2: Get the results
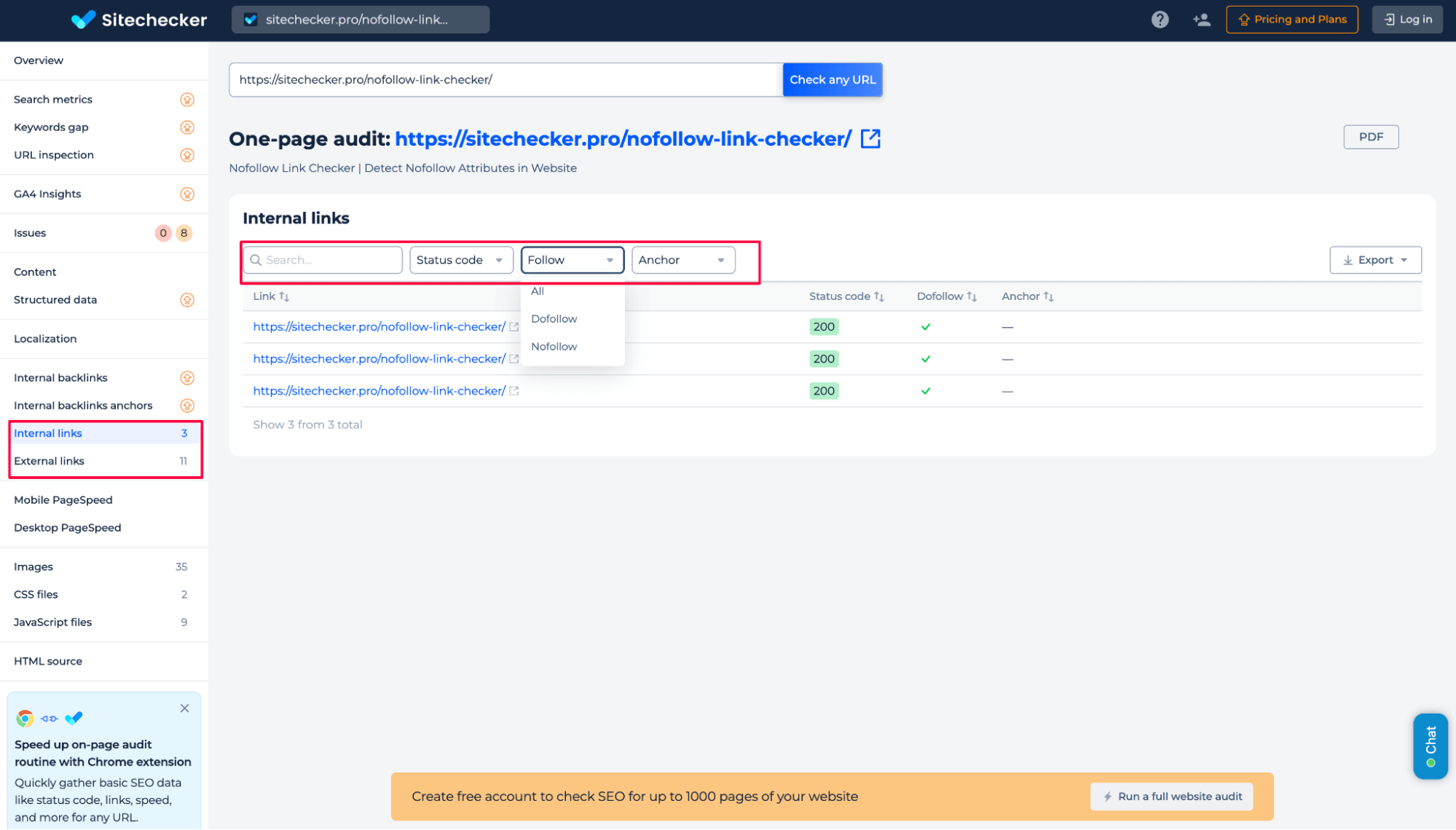
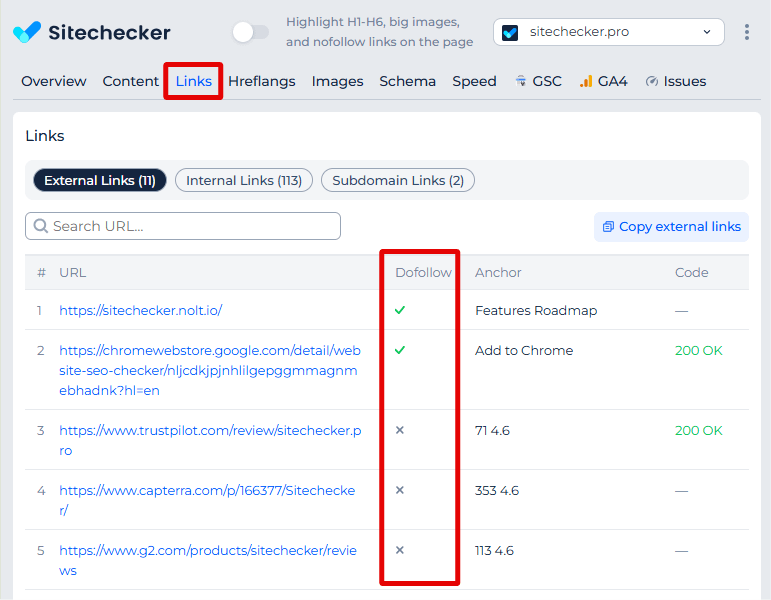
As a result of this audit, you can review all internal and external links found on the page. The report shows every URL the page links to, both inside your site and outside of it. For each link, you can check the HTTP status code, follow/nofollow attribute, and anchor text.
You can filter and sort this data in any way you need, export it for further analysis, or download the full report.
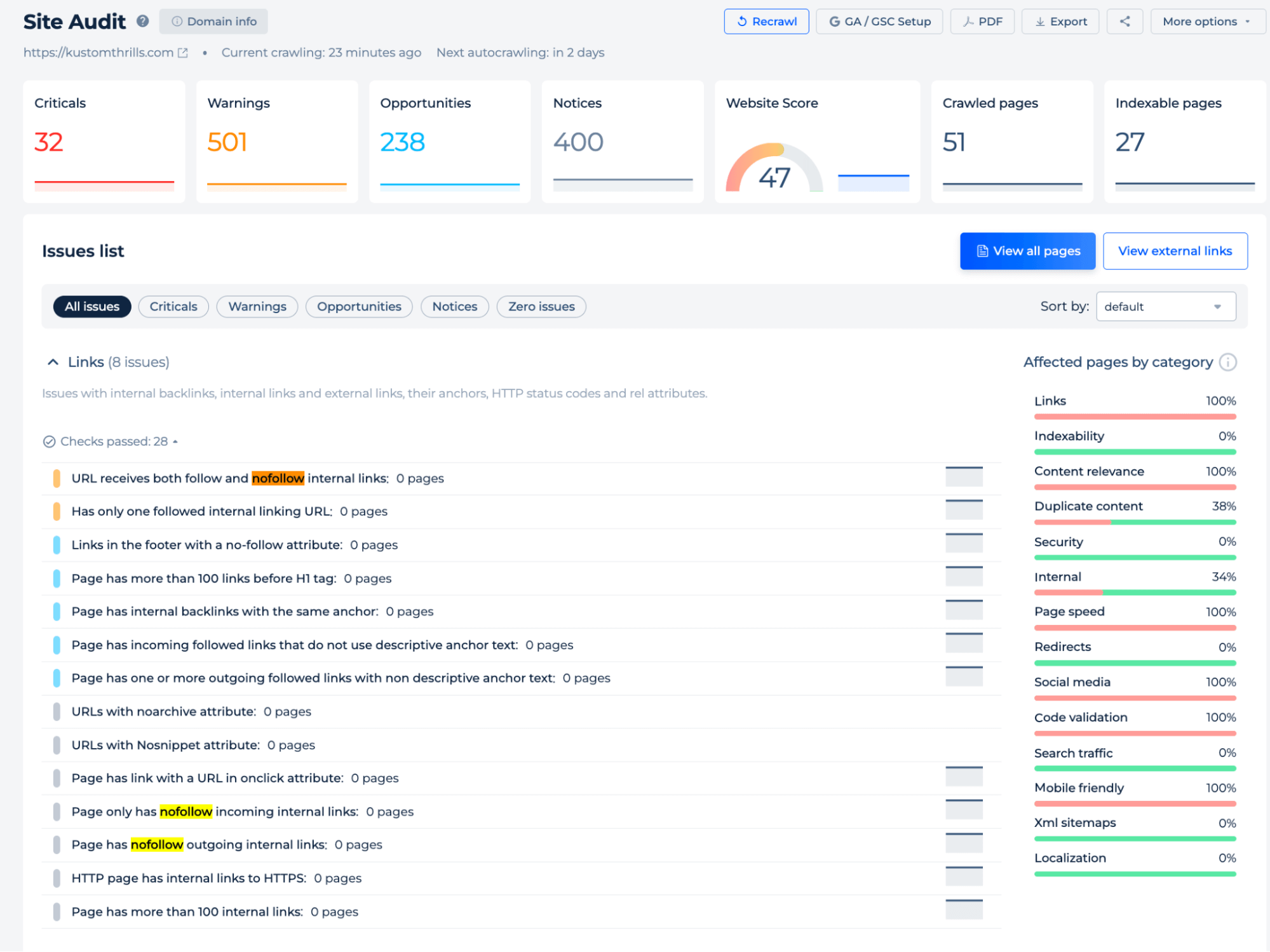
Additional features
On the site-wide level, you can also detect issues related to nofollow links, such as pages that misuse nofollow, have only nofollow internal links, or contain mixed follow/nofollow attributes.
Instant dofollow/nofollow insight in Chrome
The Sitechecker Chrome Extension lets you see the dofollow vs. nofollow status of links on any page without exporting or running a full crawl.
As you browse, it lists all links and clearly flags which ones are nofollow and which are dofollow, so you can quickly spot issues like missing nofollow tags on paid links or excessive nofollows on internal navigation.
It’s a fast way to check link attributes right in your browser without switching tools.
Final idea
Nofollow Link Checker helps you quickly understand how a page handles nofollow attributes, indexation rules, and link behavior. The tool displays robots meta and X-Robots-Tag directives, internal and external follow/nofollow links, anchor texts, and status codes in a single, clear report. You can also detect additional on-page issues and site-wide nofollow problems, ensuring your page is crawled and indexed as intended.