What is the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” error?
The “Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical” error in Google Search Console occurs when Google identifies multiple pages with duplicate content. Still, no canonical tag has been specified to indicate which version should be considered the primary one.
When multiple pages have similar or identical content, a canonical tag tells search engines which URL is the “master” version.
Without a user-selected preferred URL, Google may struggle to determine which page to index and rank, potentially leading to issues such as:
- Indexing duplicate pages: Google might index several copies of the same or very similar content, which can dilute each page’s SEO value.
- Ranking confusion: When no preferred URL is present, Google may not know which page to prioritize in search results, potentially lowering the visibility of both pages.
This error typically arises when websites have duplicate content across different pages, like product listings with slight variations, session parameters in URLs, or paginated content without proper canonicalization. Website owners must set a user-selected preferred URL to ensure search engines properly index and rank the intended page.
Launch Sitechecker’s GSC Dashboard to boost your Search Console reporting!
Expand GSC Data Limits
Bypass Google’s 1,000-row cap and unlock up to 36 months of Search Console history in a single dashboard.
Common causes of the error
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Missing or incorrect canonical tags | If a page lacks a canonical tag or the tag points to the wrong URL, Google cannot determine its preferred version. |
| Duplicate content | Pages with similar or identical content, such as product variations or filter pages, may trigger this error if not adequately canonicalized. |
| Conflicting directives | If a page has both a “noindex” tag and a canonical tag, Google may be confused about whether the page should be indexed or if the canonical version should be prioritized. |
| CMS or platform issues | Some content management systems (CMS), like WordPress or Blogger, may automatically generate duplicate pages or fail to set canonical tags correctly, leading to this error. |
| URL parameters and session IDs | Pages with URL parameters (e.g., tracking codes or session IDs) might be treated as duplicates without proper canonicalization, as Google sees them as different URLs. |
| Internal linking issues | Incorrect internal linking or using multiple URLs to reference the same content can confuse Google and cause duplicate content without the preferred URL. |
Step-by-step guide to fix the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” error
Depending on your goals, you can use canonicalization or redirects to fix the “Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical” error.
Use canonicalization when you have multiple similar pages (like product variations or filter options) and want Google to index the main version.
Use redirects when you no longer need the duplicate pages. Directing all versions to one primary page simplifies your site and consolidates link equity.
Cannolicals method
1. Add or correct the canonical tag
If a canonical tag is missing or incorrect, add or update it in the page’s HTML code:
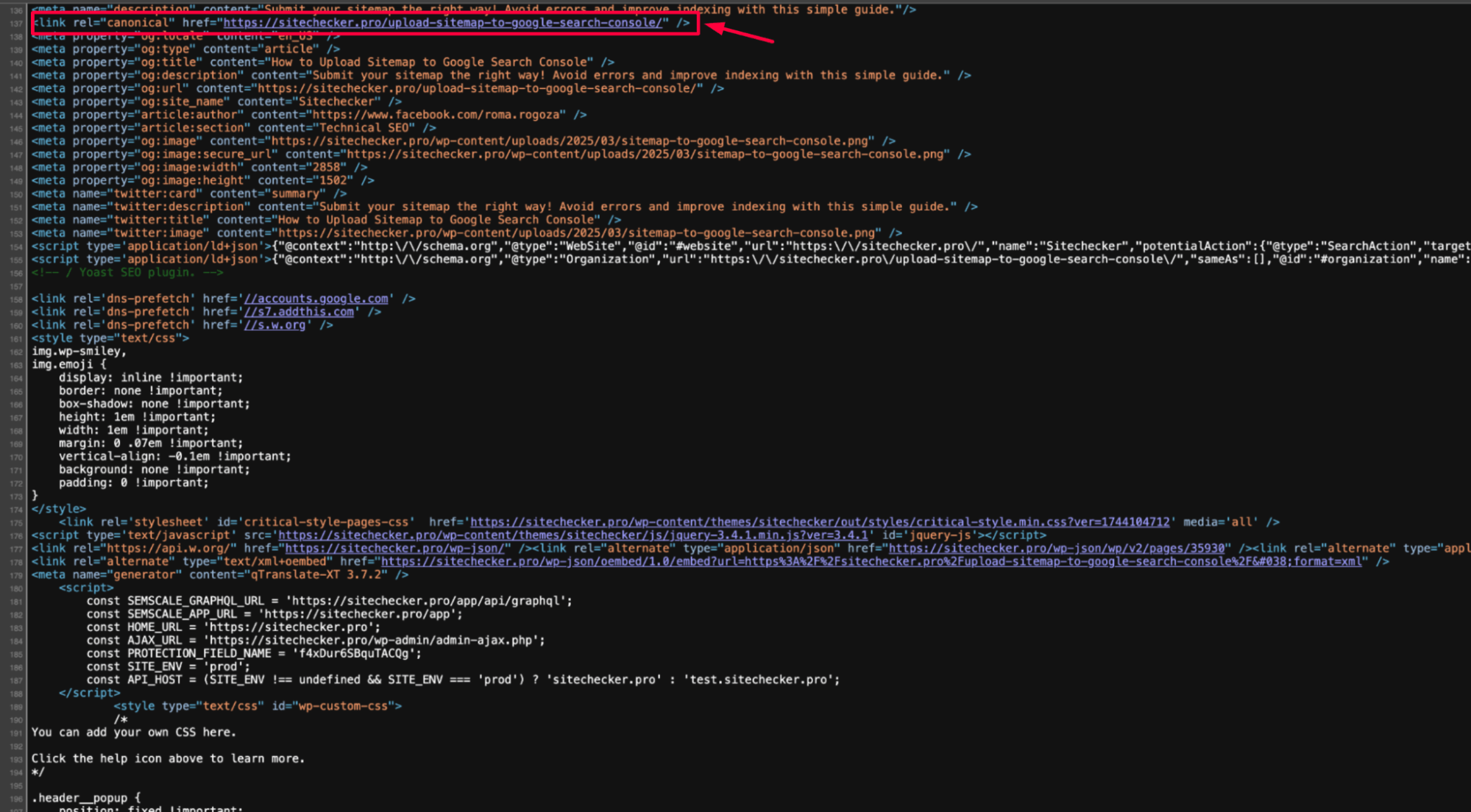
Ensure the preferred URL points to the intended version of the page you want Google to index.
If you are using a CMS, such as WordPress or Shopify, you can update the preferred URL through the platform’s settings or plugins:
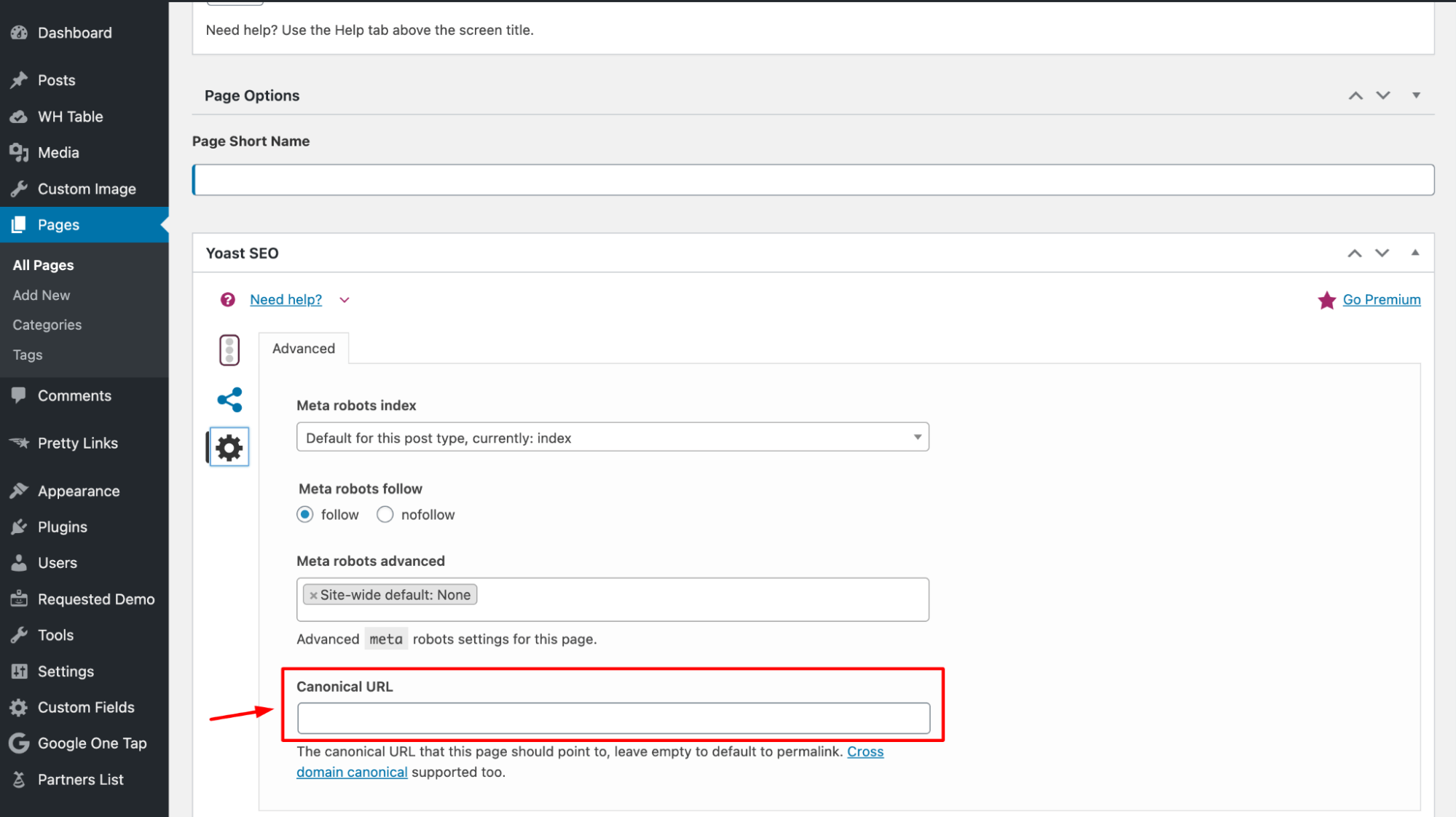
2. Use the canonical tag checker
To check and manage canonical URLs easily, use the Canonical URL Tool by Sitechecker for quick verification and corrections.
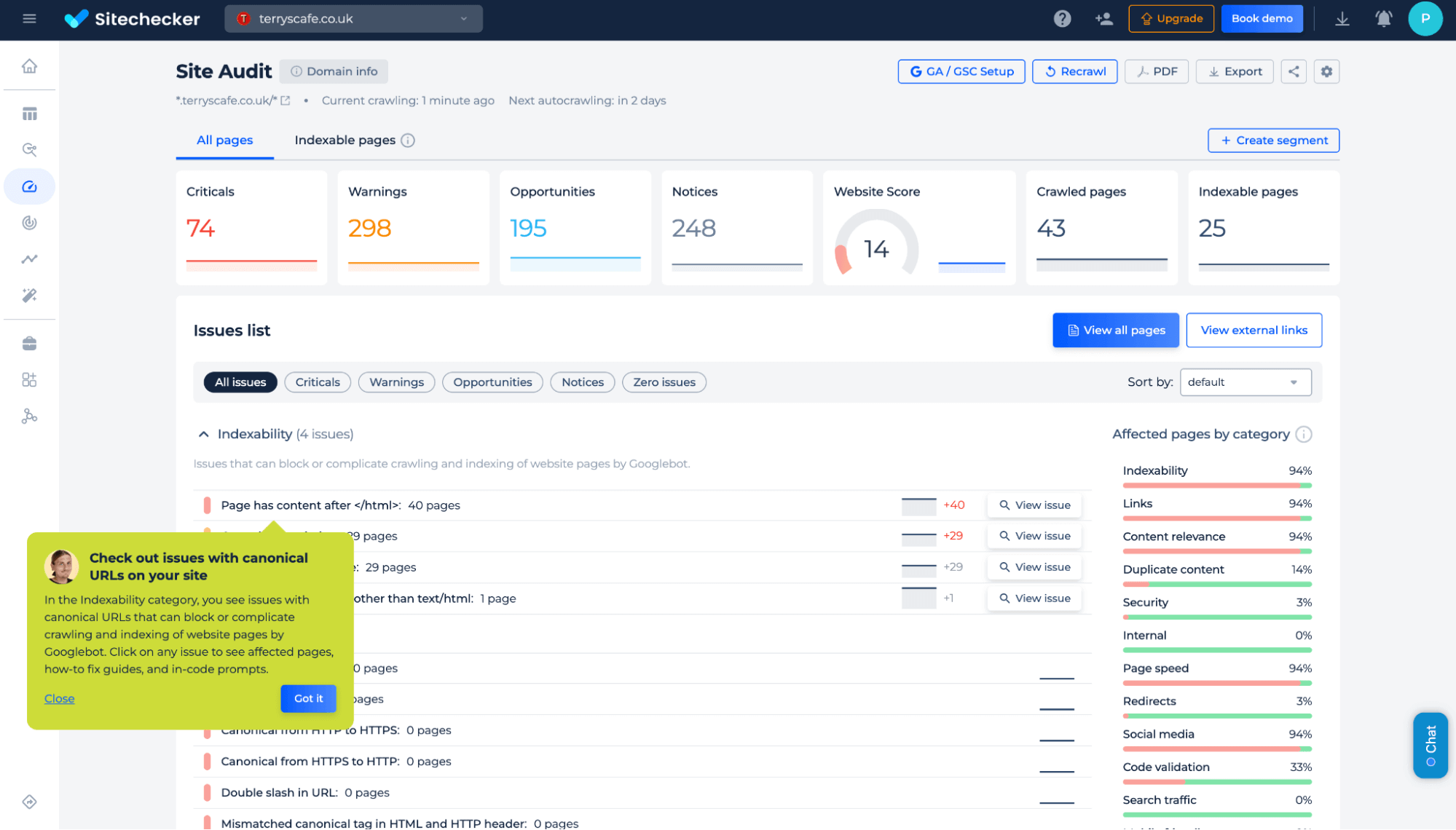
Check your site for this error and get a quick fix with our tool!
After fixing the canonical mismatch, you can verify the changes in Sitechecker without visiting GSC. Sitechecker pulls data directly from your Google Search Console, allowing you to check if the canonical issue has been resolved without navigating to the console itself. This simplifies the process and saves time:
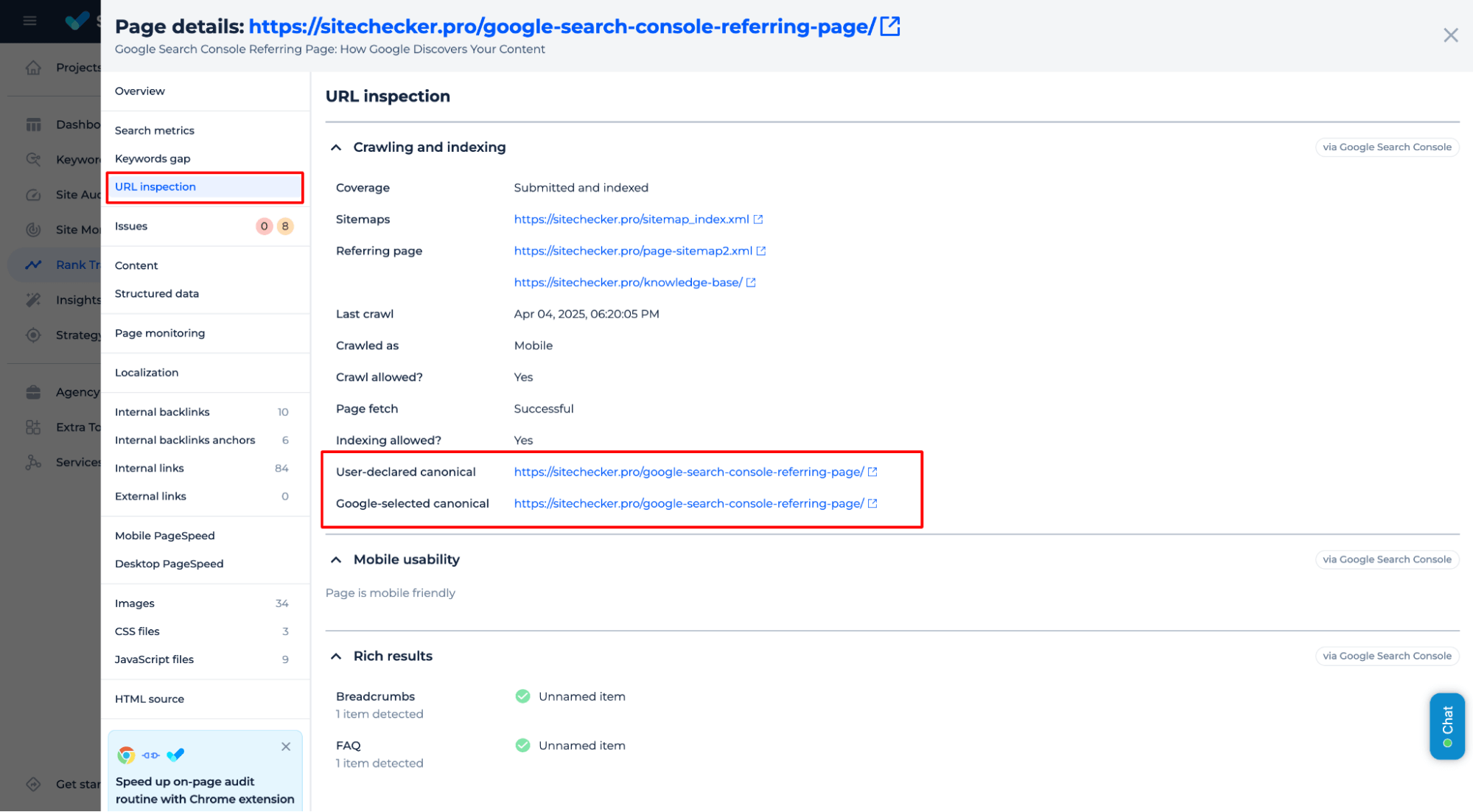
3. Request reindexing (if necessary)
Once you’ve confirmed the canonical tag is set correctly, you can request Google to reindex the page.
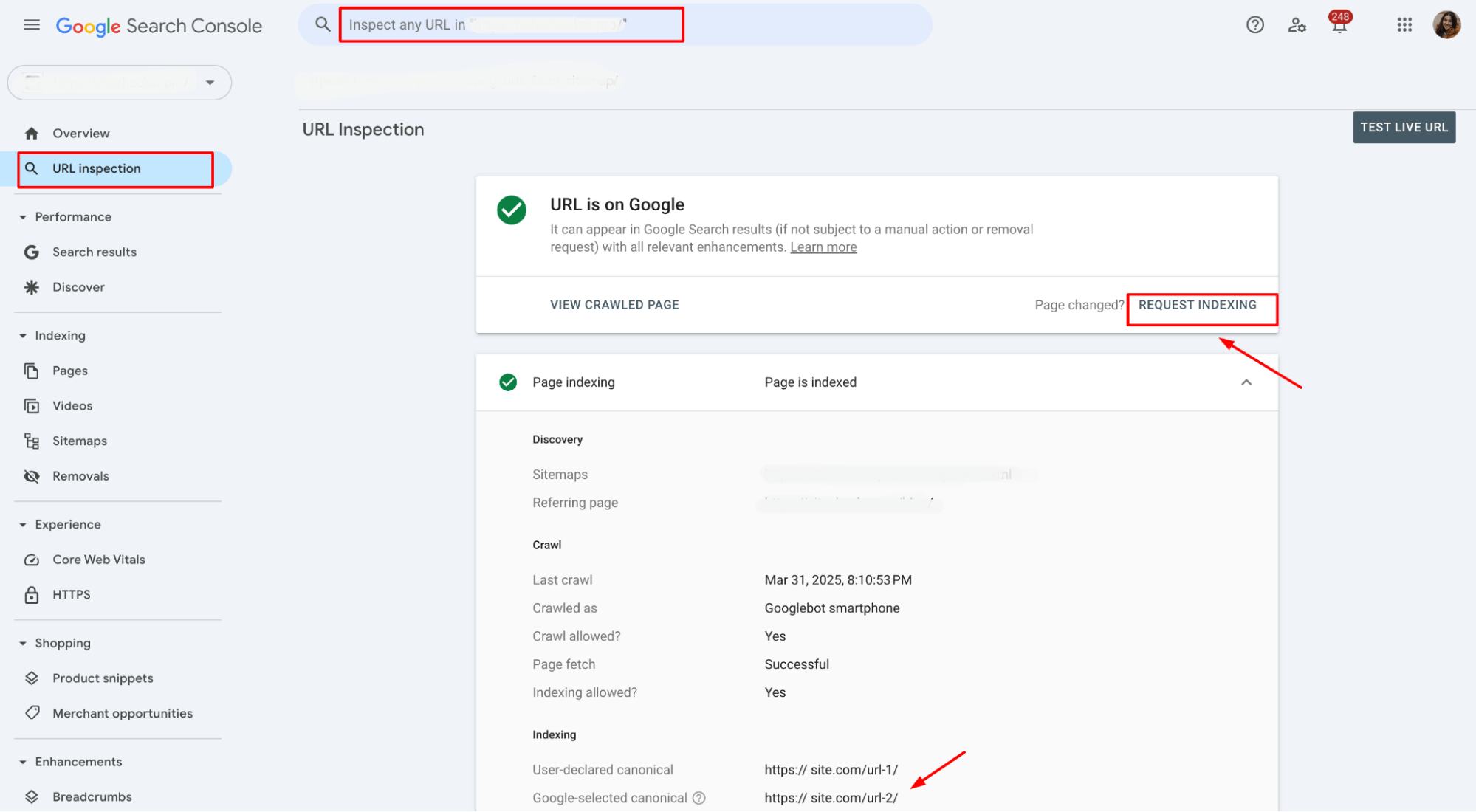
In Google Search Console, click Request Indexing to prompt Google to recrawl the page with the updated preferred URL.
4. Validate and fix in Google Search Console
After you’ve updated the canonical tag, go back to Google Search Console and use the “Validate Fix” option for the affected pages.
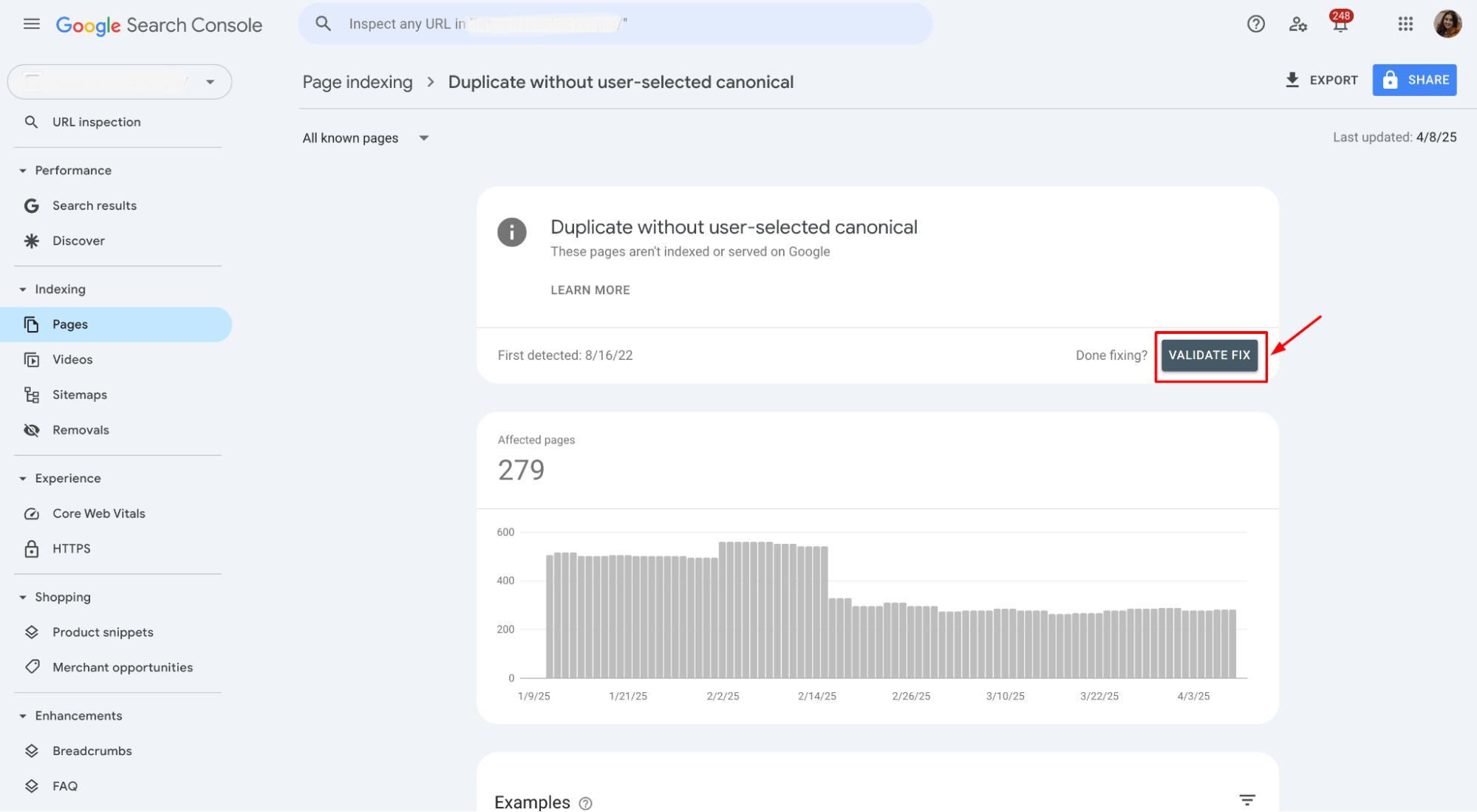
The validation process in GSC may take a few days to complete. Once you click “Validate Fix,” Google will recheck the affected pages. Once the fix is confirmed, the error will be marked as resolved in the Pages report.
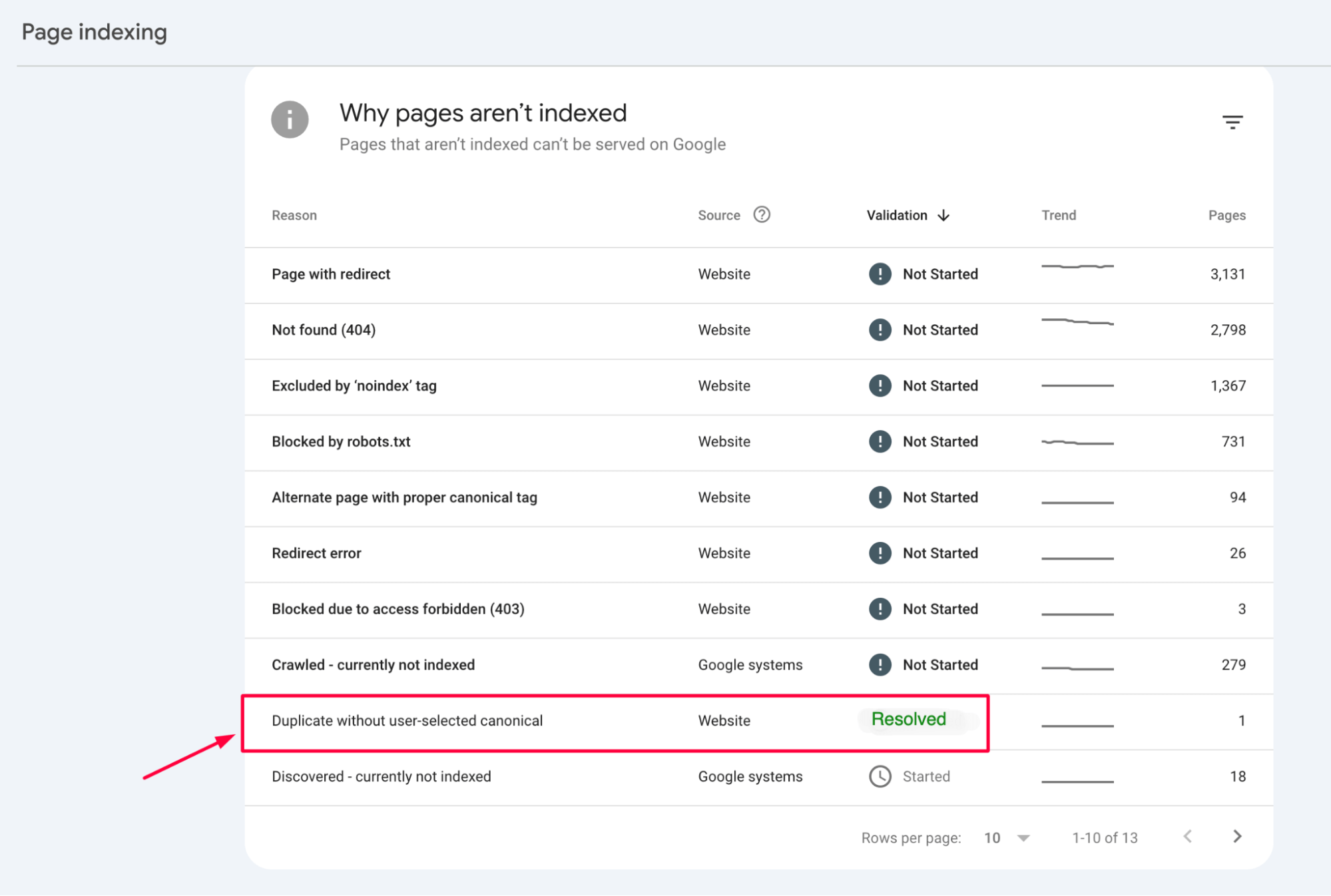
Redirect to fix the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” error
In some cases, instead of just updating the canonical tag, using a redirect is the best solution to fix the “Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical” error. Here’s when a redirect can be particularly helpful:
When to use redirects for canonical errors
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Duplicate pages with no unique content | If you have duplicate pages that essentially serve the same purpose, using a 301 redirect to the main page is better. This will direct both users and search engines to the correct version, ensuring link equity is properly consolidated. |
| Multiple URLs for the same content | Sometimes, the same content can be accessible through several URLs, such as with different URL parameters. In these cases, redirecting to the main page (the one you want indexed) prevents Google from indexing duplicate pages. |
| Product variations or filter pages | If you have product variations or category filters that lead to duplicate content but don’t need individual pages for every variant, use redirects to the main product page to keep things clean and manage SEO more effectively. |
| Session IDs and tracking parameters | URLs with tracking parameters or session IDs often lead to duplicate content. Redirecting those URLs to the main, parameter-free version helps ensure Google indexes the correct page. |
| 404 or redirected content | If you have outdated pages that are no longer relevant, set up a 301 redirect to the most relevant page to direct users and search engines to an active page and avoid SEO penalties. |
How to set up redirects
To implement a redirect, a 301 redirect (permanent redirect) is generally the most effective solution for this issue. This can be done in a few ways:
If you’re using a content management system (CMS) like WordPress, plugins are available that make setting up redirects easy:
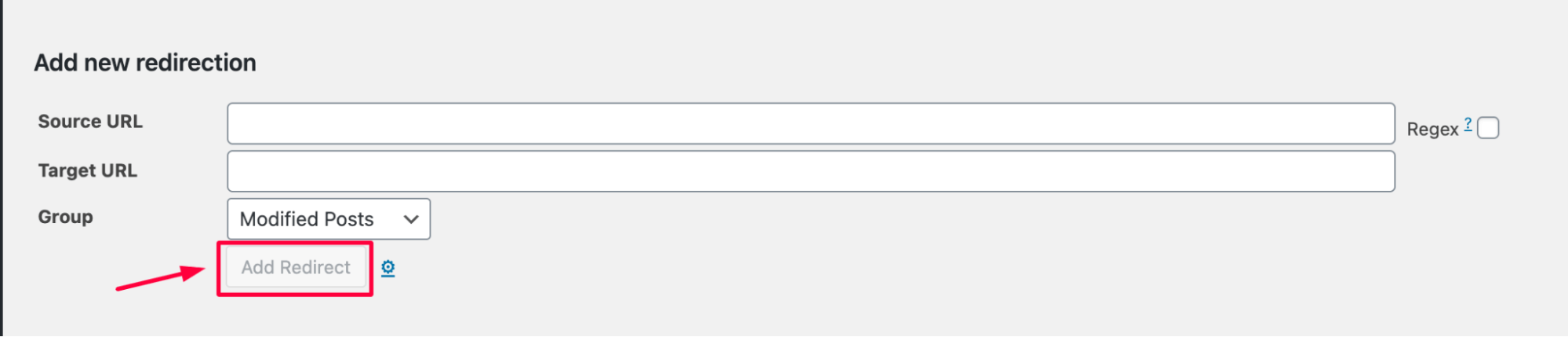
In the context of the “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” error, here’s how you can set up the redirect:
✅ Source URL: Enter the URL of the duplicate page you want to redirect. This is the page that Google has flagged as having duplicate content but no canonical tag.
✅ Target URL: Enter the URL of the preferred, canonical version of the page that you want Google to index. This is the page that should be treated as the primary one.
Alternatively, you can manually add the redirects to your server configuration files (e.g., .htaccess for Apache or nginx.conf for Nginx).
Test redirections
After setting redirects up, it is essential to check if they are working correctly. Redirect Checker can verify the functionality of your redirects and identify any potential issues. The tool helps ensure the redirects are correctly set up and directs users and search engines to the correct canonical pages.
It’s also important to update your internal links to point directly to the new, preferred version of the page. This helps avoid a redirect chain, which can confuse Googlebot. Updating the internal links ensures that Googlebot can easily find the correct page without following multiple redirects.
You can use Sitechecker’s tools to check for internal linking issues and update your links more efficiently and streamlined
How to identify the error in Google Search Console
To identify the “Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical” error in Google Search Console, follow these steps:
1. Log in to your account and navigate to the property (website) you’re managing.
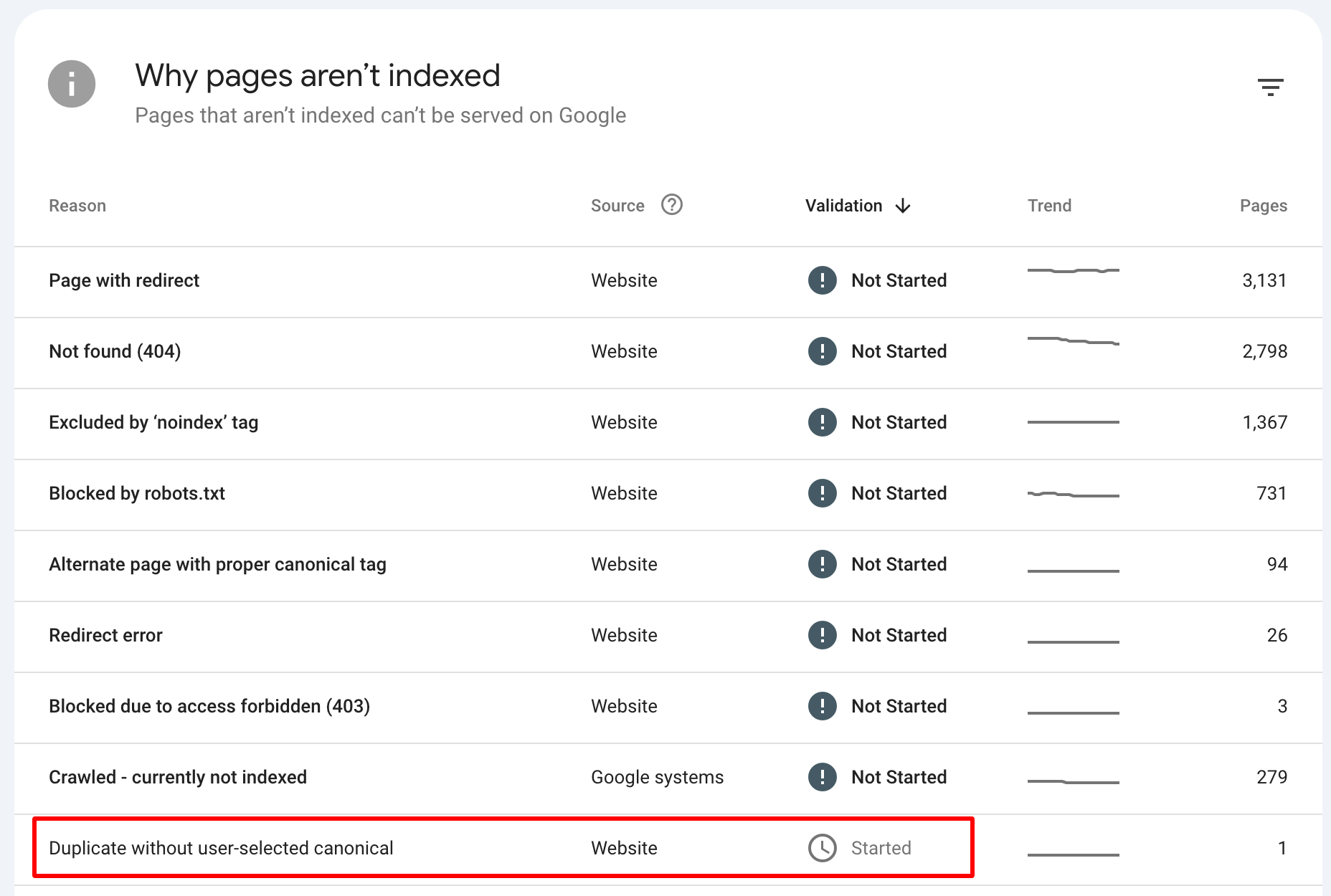
2. In the left-hand menu, click on Indexing and then Pages. This section shows the pages that Google does not index:
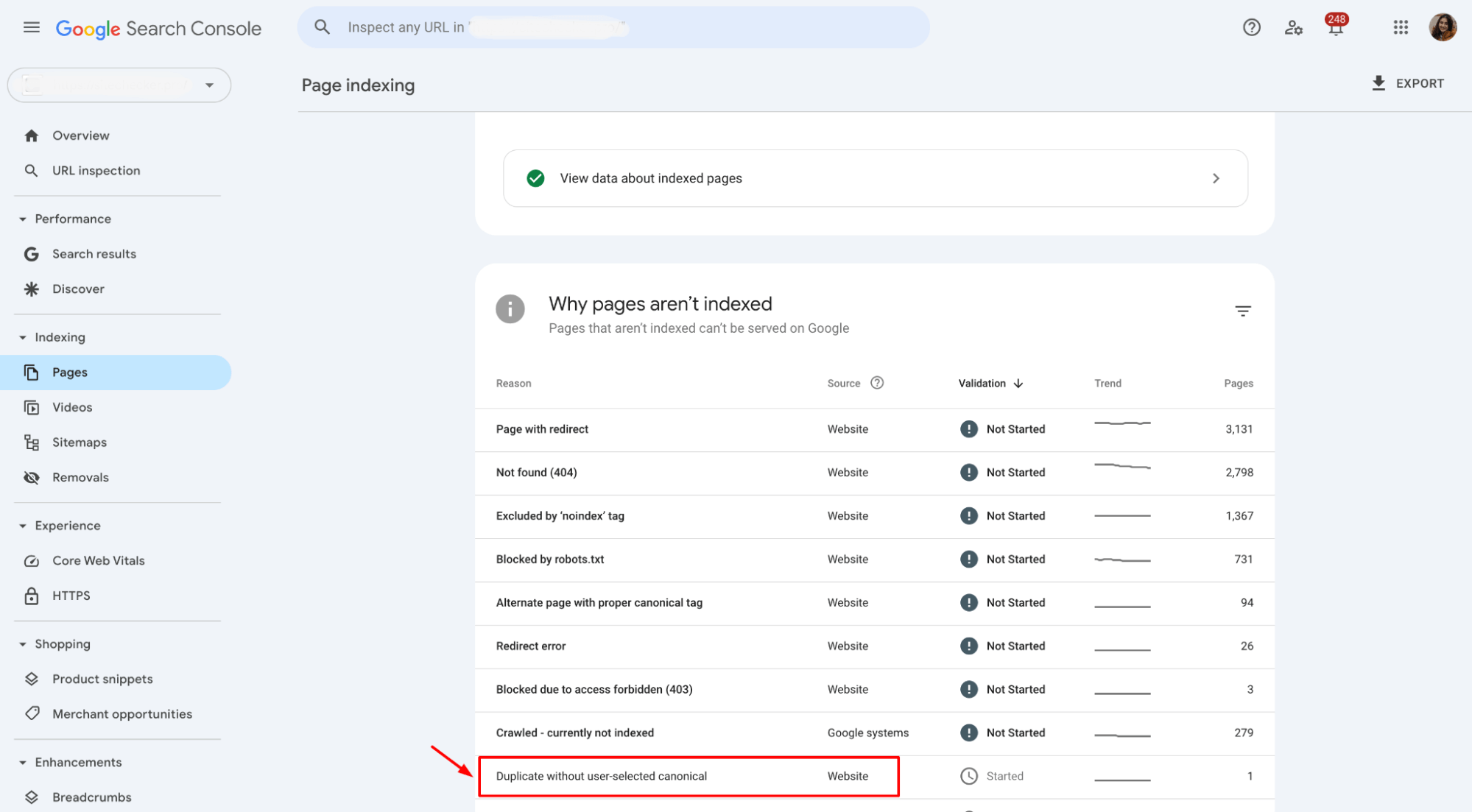
3. Under the Reason column, the error is “Duplicate without user-selected canonical.” This indicates the pages with duplicate content but no canonical tag selected.
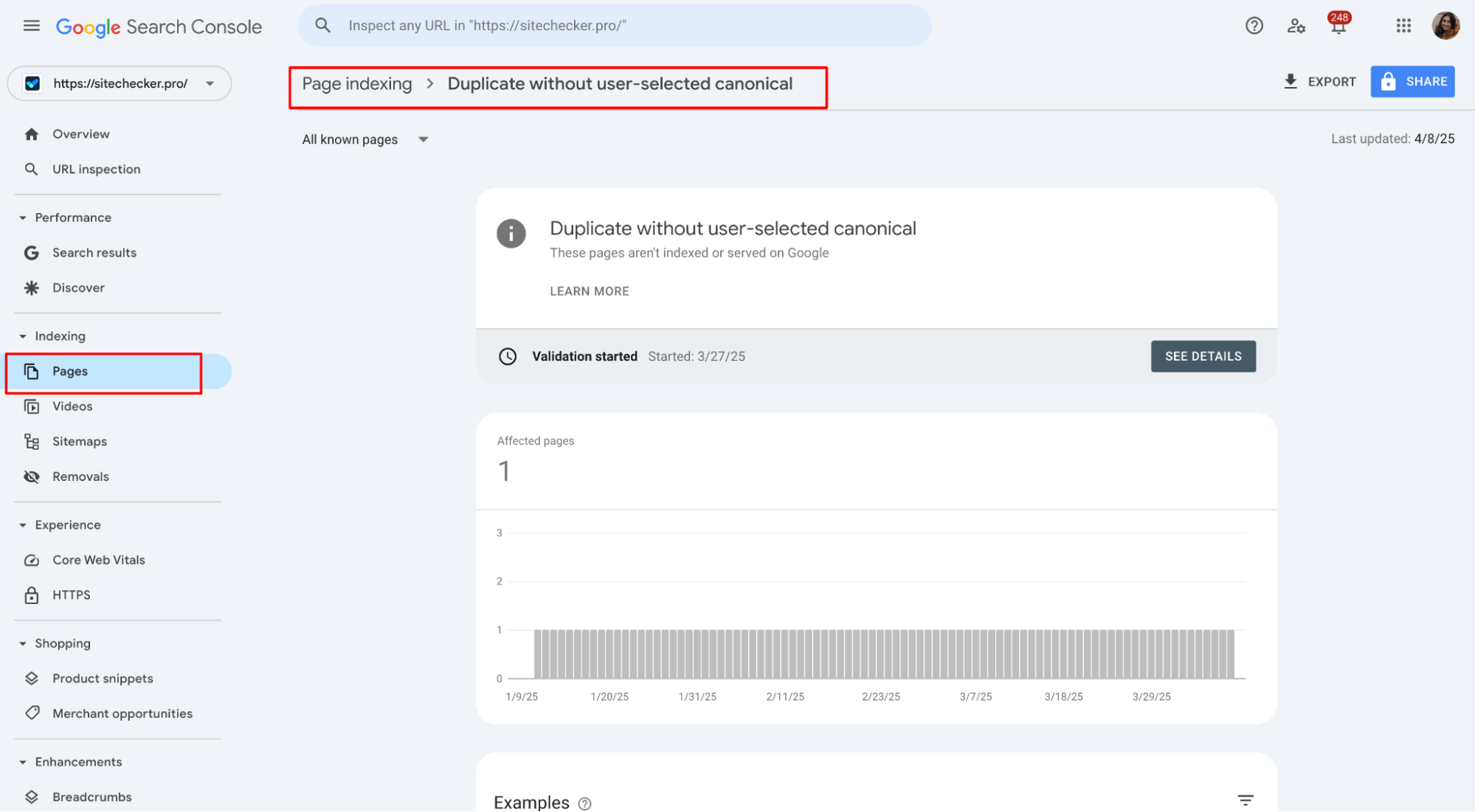
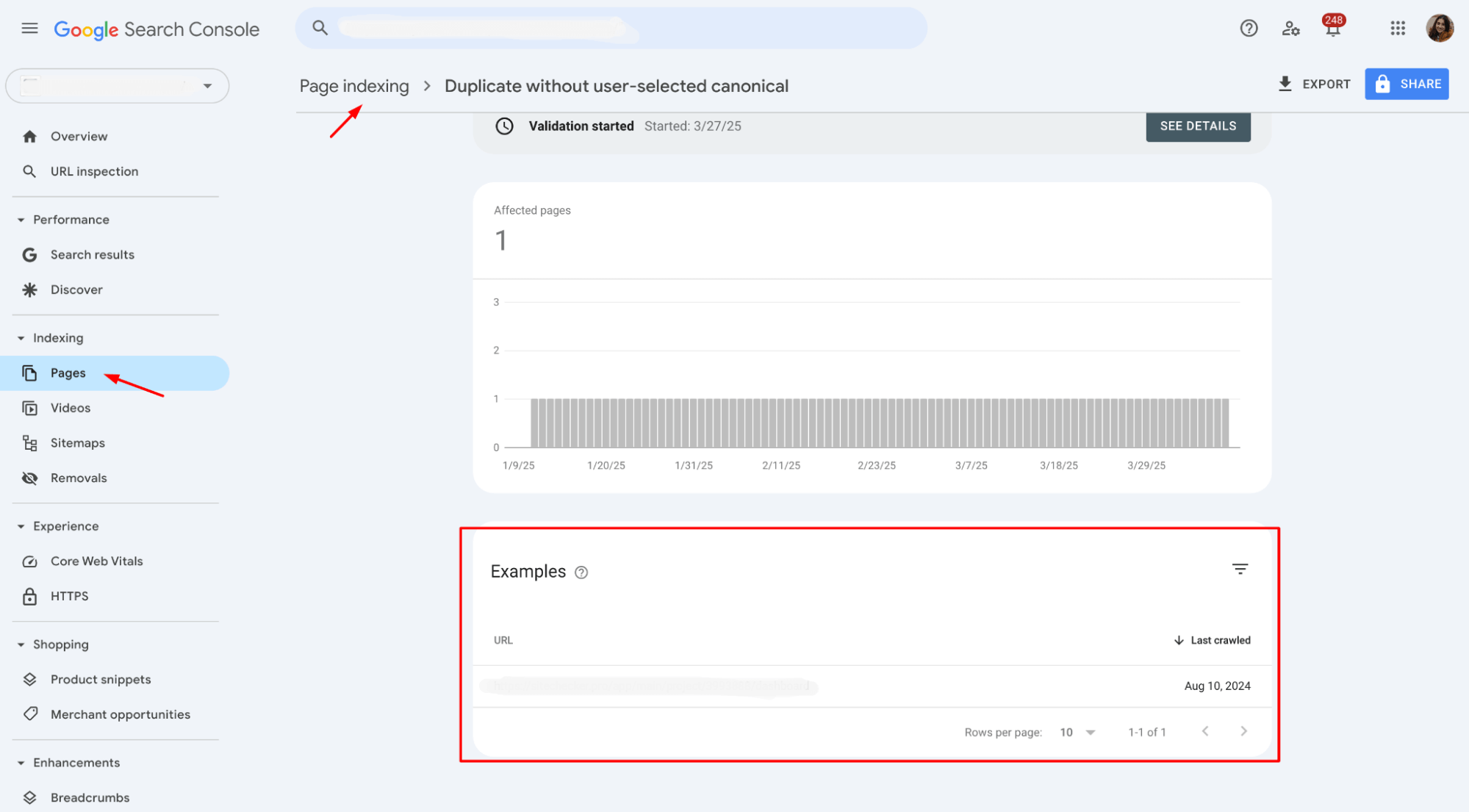
4. You’ll see a list of the affected URLs when you click on this error. These are the pages flagged for duplicate content without a proper preferred URL.
The URL Inspection Tool provides more details on specific pages. Enter the URL of an affected page to check if a canonical tag is set and if it points to the correct version.
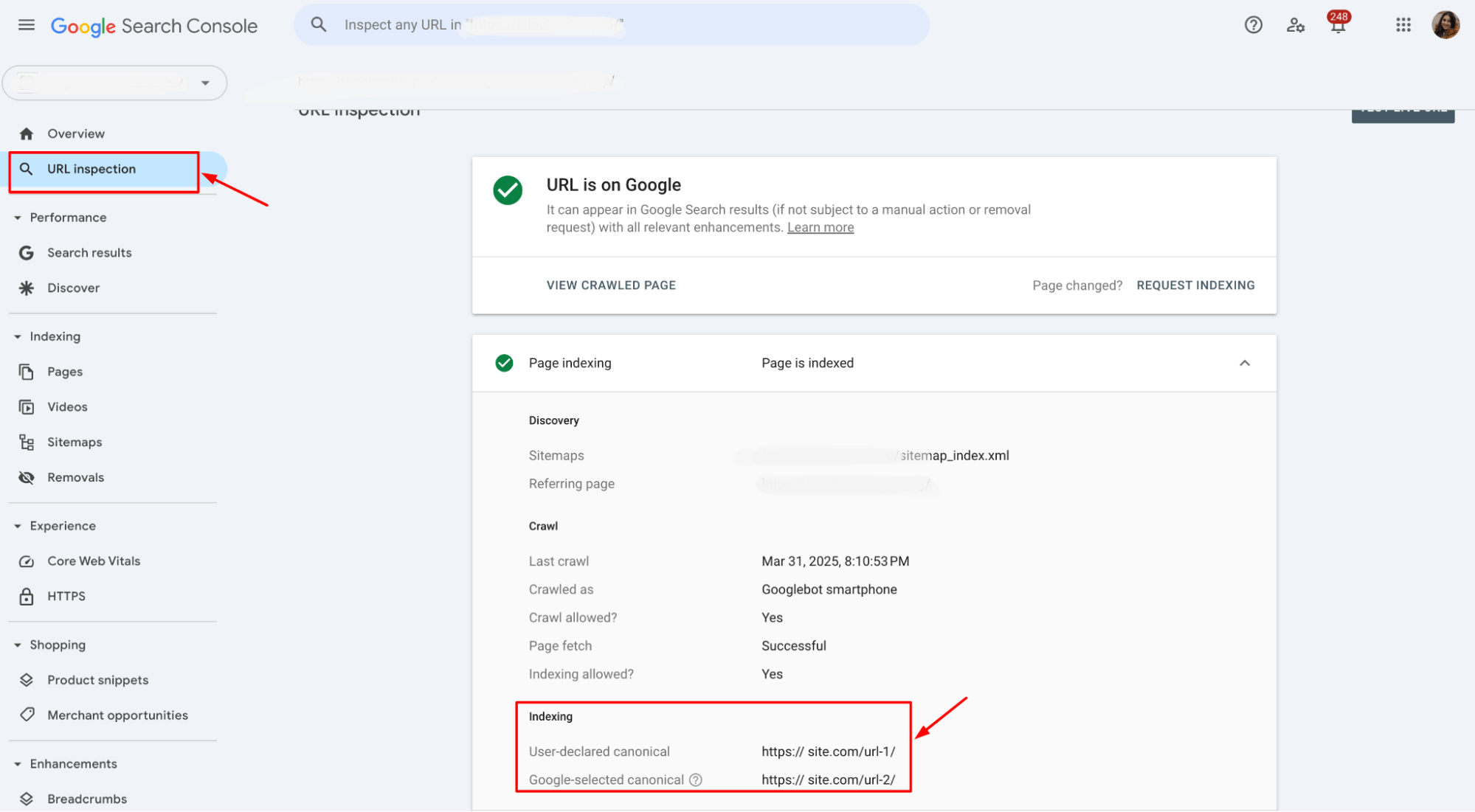
Once you’ve identified the pages affected by this error, you can take the necessary steps to fix it, such as adding or correcting the preferred URL on the affected pages.
You can also easily check the canonical tag with a single click using the Sitechecker Chrome extension:
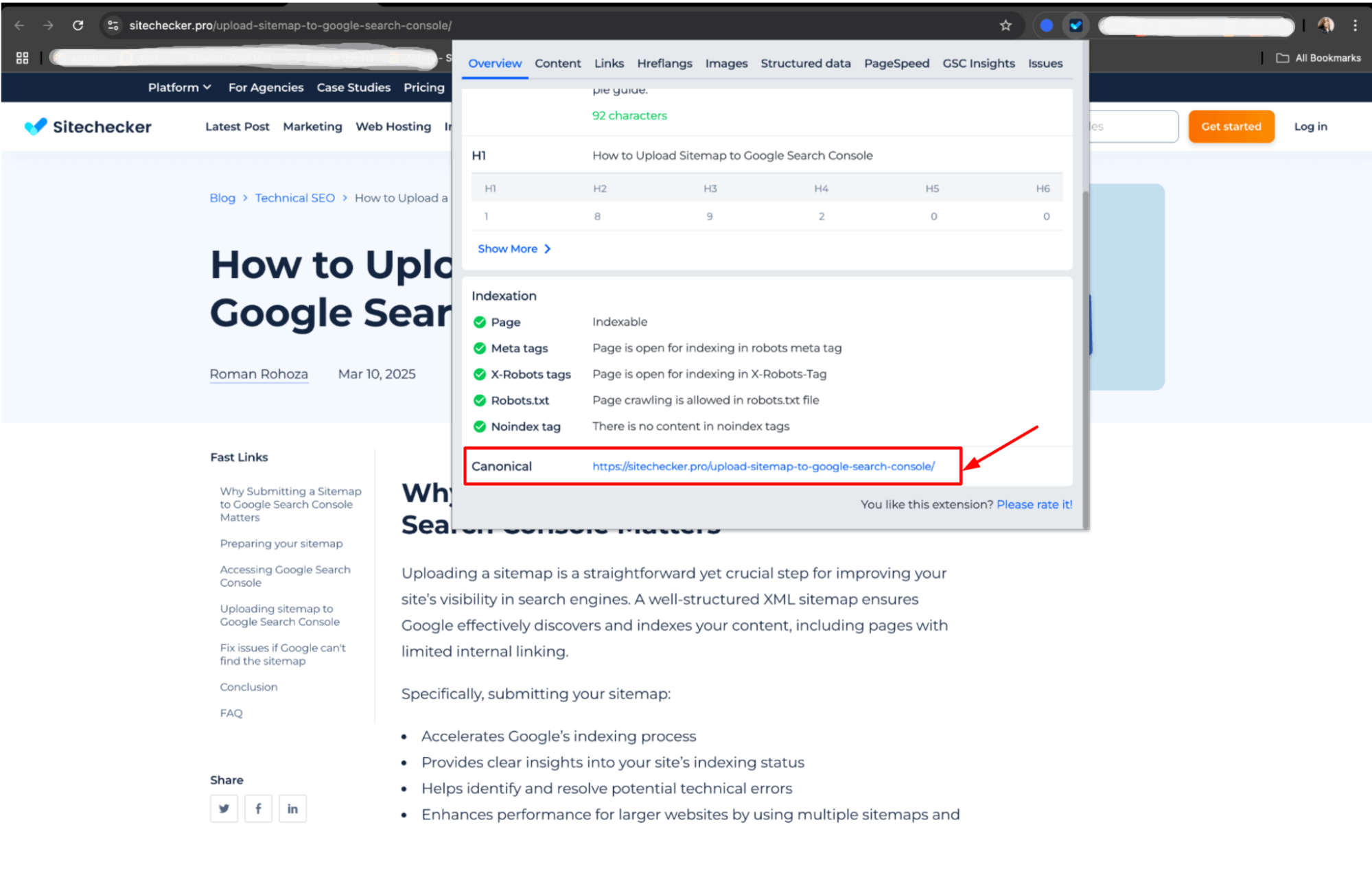
If the canonical tag points to a different URL, you should update the page to set the correct preferred URL that points to the intended version. This can be done by editing the page’s HTML code or through your CMS, ensuring the canonical URL matches the preferred version of the content.
After updating, you can recheck the page using the URL Inspection Tool to confirm the change.
Final idea
The “Duplicate without user-selected canonical” error occurs when Google detects multiple pages with duplicate content but no preferred URL to indicate the primary version. This can lead to indexing issues, diluted SEO value, and ranking confusion. To fix the problem, website owners should identify affected pages in Google Search Console, add or correct the canonical tag, and use tools like Sitechecker for easy verification.
After updating, the fix should be validated in Google Search Console, and once confirmed, the error will be marked as resolved.