Why Uploading a Sitemap to Google Search Console Matters
Uploading a sitemap is a straightforward yet crucial step for improving your site’s visibility in search engines. A well-structured XML sitemap ensures Google effectively discovers and indexes your content, including pages with limited internal linking.
Specifically, submitting your sitemap:
Preparing your sitemap
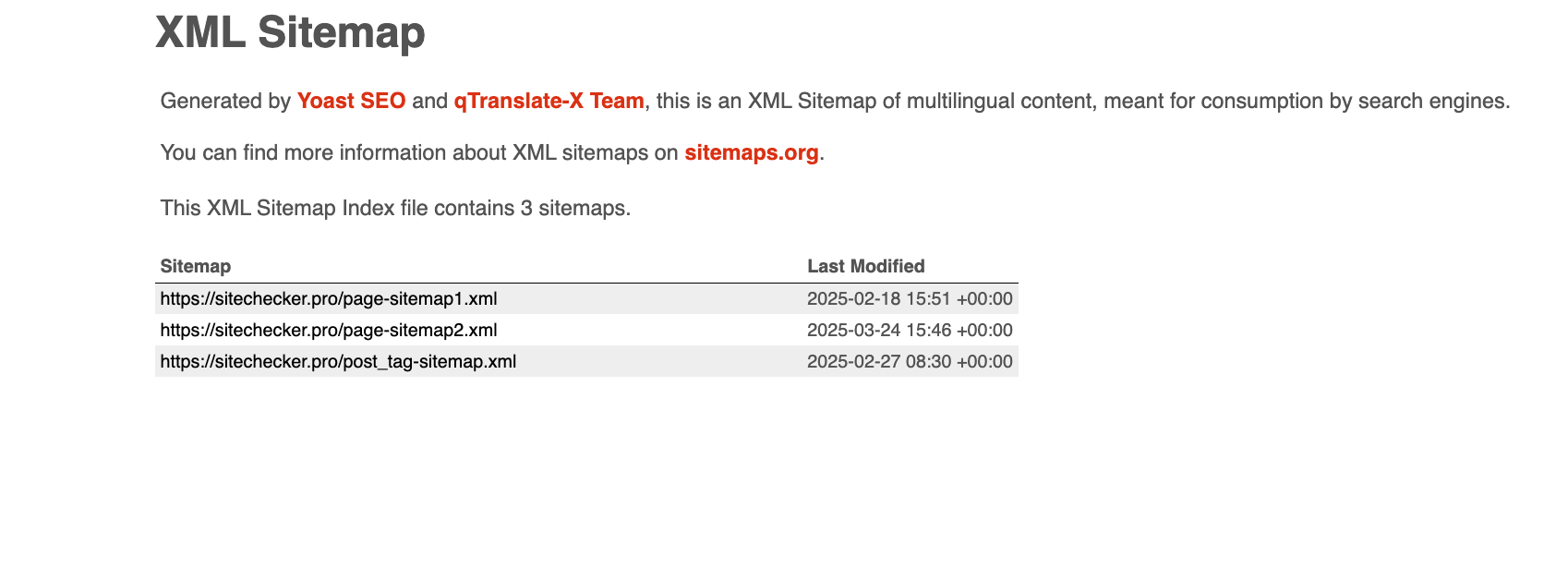
Sitemaps come in different formats, with XML being the most common. Other formats include TXT (a simple URL list), RSS/Atom (for dynamic content), and Google News sitemaps. It is important to create a sitemap index file to organize multiple sitemaps, especially when dealing with large volumes of URLs.
You can generate a page directory automatically using CMS plugins (e.g., Yoast SEO for WordPress) or online tools, or create one manually in XML format. When a sitemap exceeds size limits or contains more URLs than permissible, it is advisable to create a sitemap index file for better organization and tracking of individual sitemaps’ performance in Google’s Search Console.
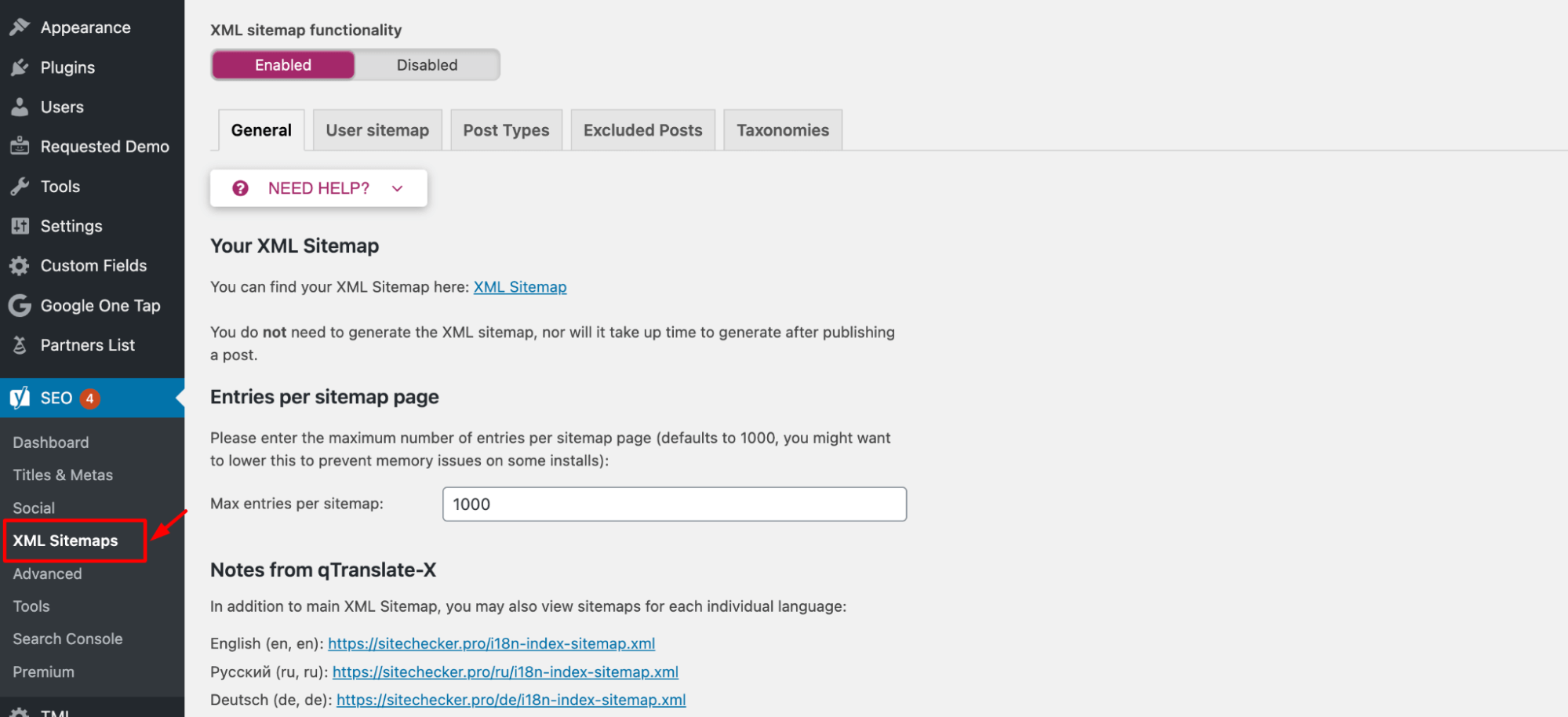
Once created, upload the file to your website’s root directory (e.g., https://example.com/sitemap.xml) to ensure search engines can access it.
Accessing Google Search Console
Before you can submit a website structure map, you need to set up Google Search Console (GSC) for your website. Start by signing in with your Google account at Google Search Console. If your site isn’t connected yet, add it by choosing either the Domain option (covers all subdomains and protocols) or URL-prefix (for a specific version of your site).
Next, you’ll need to verify ownership. The easiest method depends on your setup:
- DNS record – Add a TXT record in your domain’s DNS settings.
- HTML file – Download a verification file from GSC and upload it to your website’s root directory.
- Google Analytics/Tag Manager – If your site is already linked to these tools, GSC can verify it automatically.
Once verification is complete, you’ll have full access to GSC, where you can monitor your site’s indexing and submit your website structure map for Google to crawl.
Launch Sitechecker’s GSC Dashboard to boost your Search Console reporting!
Expand GSC Data Limits
Bypass Google’s 1,000-row cap and unlock up to 36 months of Search Console history in a single dashboard.
Uploading sitemap to Google Search Console
Once your website is verified in Google Search Console, you can submit your website structure map for indexing.
1. Go to the “Sitemaps” section – In the left-hand menu, select “Sitemaps” under Indexing.
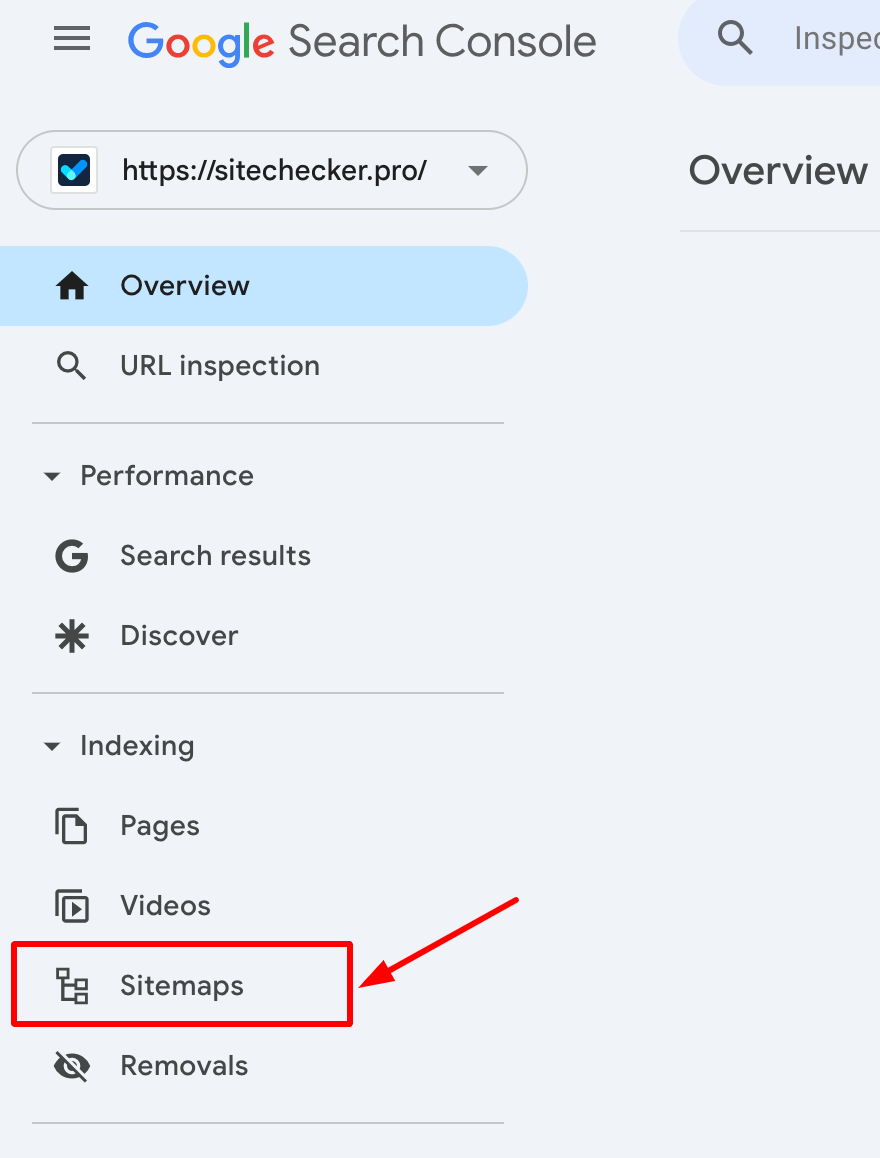
2. Enter your sitemap URL – Type the full path (e.g., https://example.com/sitemap.xml) in the submission field.
3. Submit and confirm – Click “Submit”, and GSC will start processing your file.
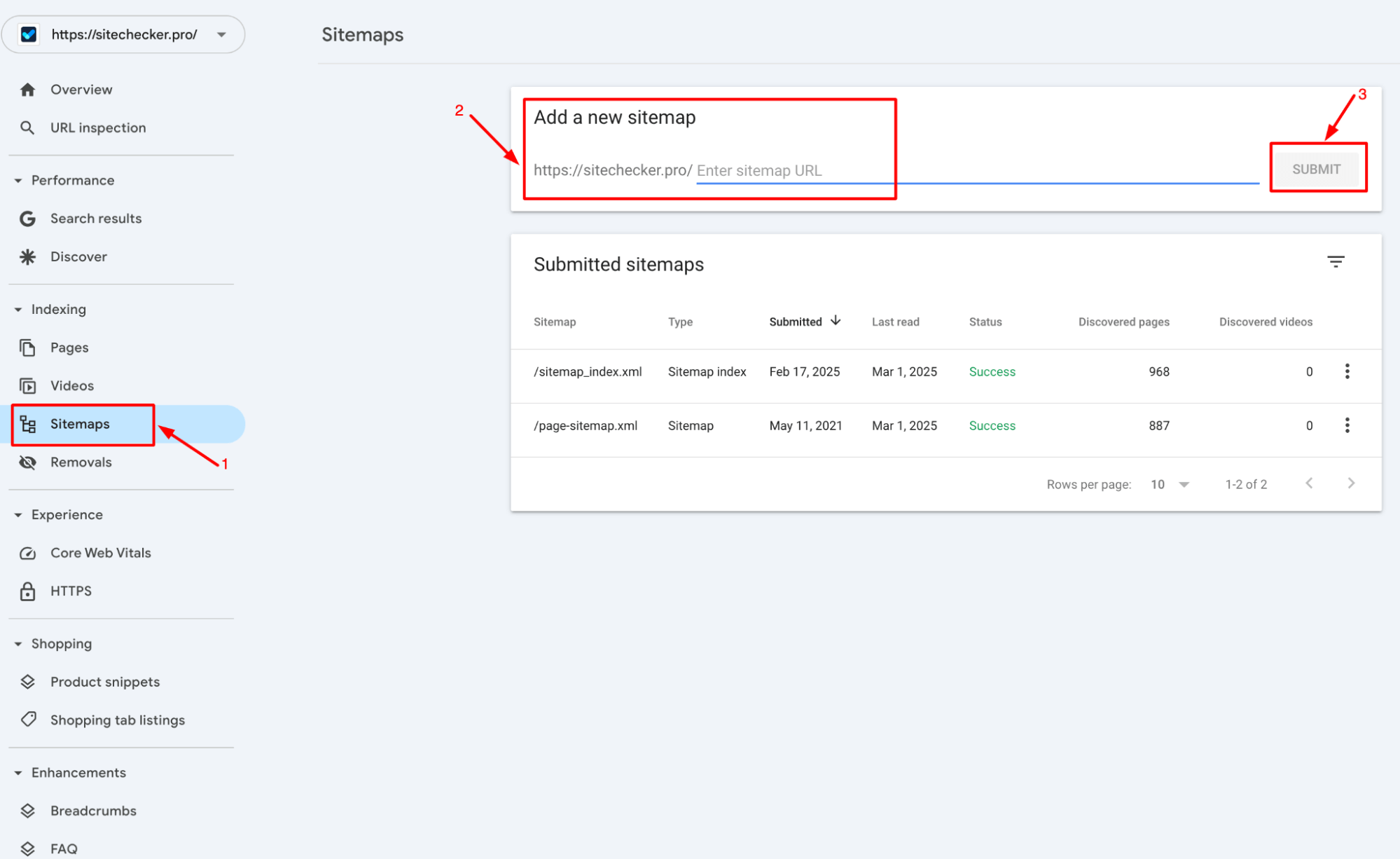
Google will now crawl the website structure map and display its status, helping you track indexing progress and potential errors.
Checking sitemap submission status
Once you’ve submitted your page directory in Google Search Console, it’s important to check its status to make sure everything is working properly. Head to the “Sitemaps” section in GSC, where you’ll see whether Google has successfully processed your website structure map or if there are any issues.
Here’s what the status indicators mean:
✅ Success – Google has processed the website structure map without any problems.
⚠️ Warnings – Some URLs might be inaccessible or have indexing issues, but the page directory was still accepted.
❌ Errors – Google couldn’t process the file, possibly due to an incorrect format, blocked URLs, or other issues that need fixing.
Regularly checking this section helps ensure your site is properly indexed and any potential problems are addressed quickly.
Fix issues if Google can’t find the sitemap
To ensure Google can properly access and process your sitemap, first, verify that the URL is correct and publicly accessible. Next, check your robots.txt file to make sure there are no restrictions blocking search engines from crawling it. Additionally, ensure that the website structure map follows Google’s official guidelines to prevent any formatting or indexing issues. Regularly monitoring its status in Google Search Console will help maintain proper indexing and keep your site’s content updated in search results.
Troubleshooting common issues
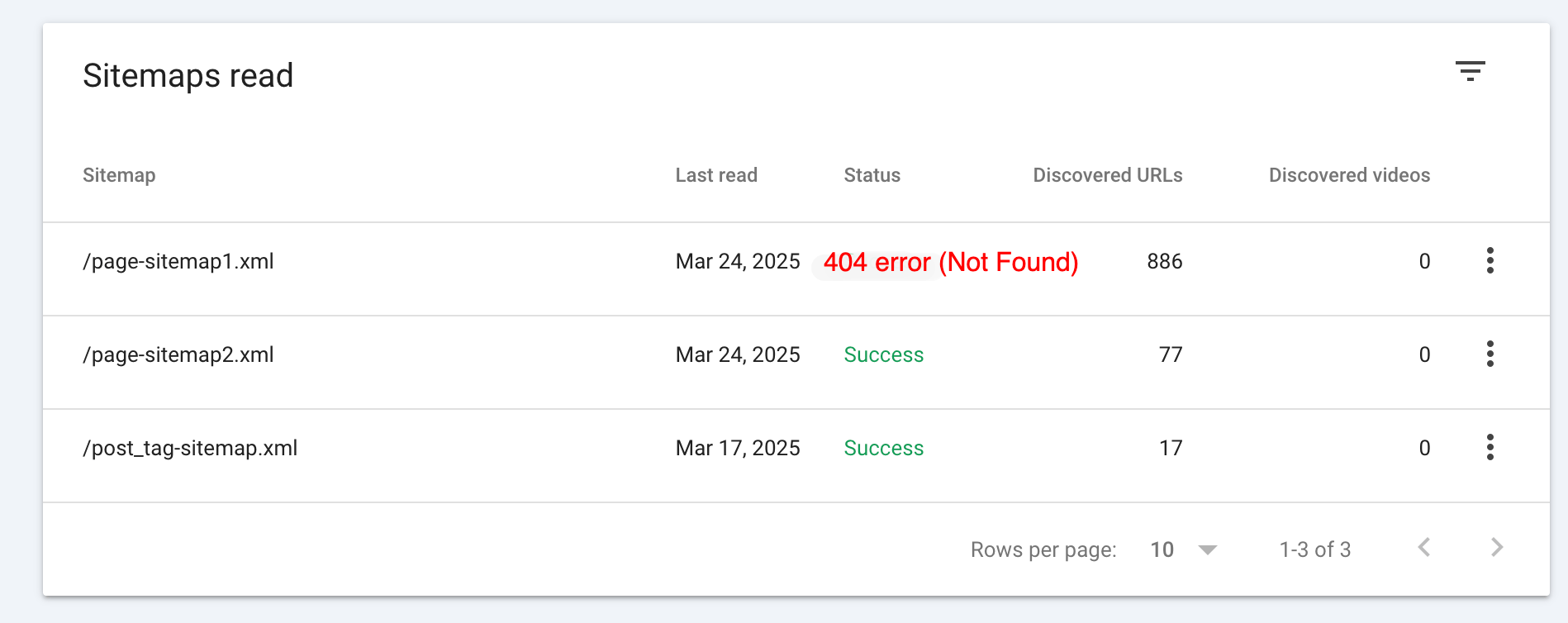
If Google Search Console isn’t processing your sitemap correctly, there are a few common issues to check. First, look for syntax errors in your sitemap.xml. Make sure it follows Google’s official guidelines, validate it with Google’s Sitemap Testing Tool, and double-check for any broken tags, incorrect URLs, or unsupported characters.
Access problems are another common cause. If you get a 404 error (Not Found), confirm that the file is in the correct directory, such as https://example.com/sitemap.xml . A 403 error (Forbidden) might indicate permission issues, so ensure the file is publicly accessible.
Also, check your robots.txt file – if it contains Disallow: /sitemap.xml, Google may be blocked from crawling it.
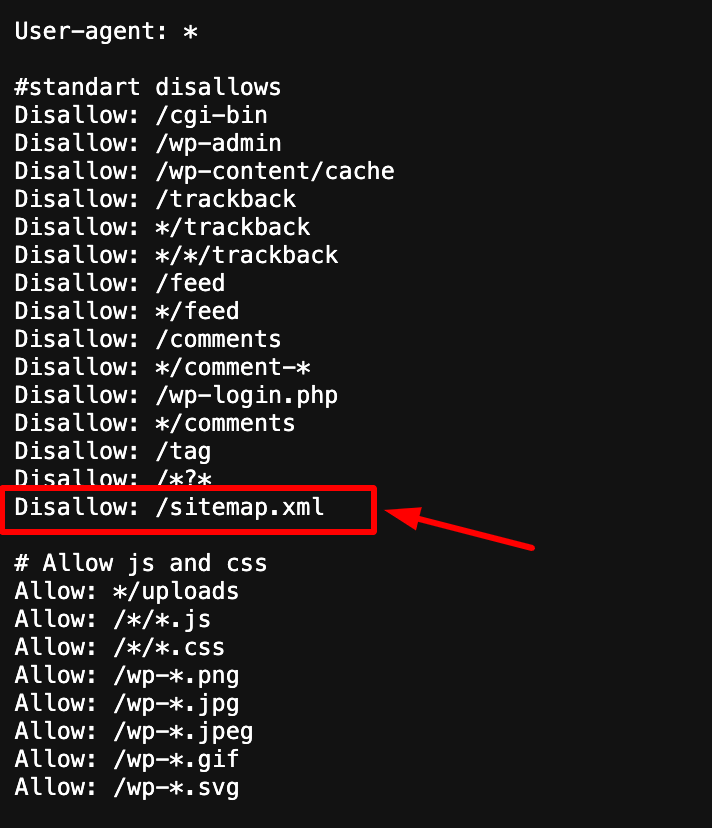
If you’ve recently made changes to your website, such as adding or removing pages, your sitemap needs to be updated. Regenerate and upload the latest version, then resubmit it in Google Search Console. You can also notify Google manually by using this ping URL: https://www.google.com/ping?sitemap=https://example.com/sitemap.xml.
Use Sitechecker to quickly detect and fix sitemap errors, ensuring Google properly crawls your pages. Gain instant insights, resolve issues efficiently, and enhance your website’s search visibility with ease.
Check & Fix Sitemap Issues Instantly!
Submit a clean sitemap to Google Search Console and improve your site's indexing. Start now!
Keeping your sitemap updated
Keeping your sitemap updated ensures that search engines always have the latest version of your website’s structure. Here’s how to automate the process:
1. Automate sitemap updates
Use CMS plugins like Yoast SEO (WordPress) or built-in website structure map features in platforms like Shopify and Wix.
Set up server-side scripts (e.g., a cron job) to regenerate the website structure map automatically when content changes.
Use robots.txt to guide Google
Add a directive in your robots.txt file to inform search engines about your sitemap:
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xmlResubmitting an updated sitemap in Google Search Console
If you’ve made major changes to your site – like adding, removing, or updating pages – it’s a good idea to resubmit your URL map in Google Search Console under the “Sitemaps” section.
You can also notify Google manually by visiting: https://www.google.com/ping?sitemap=https://example.com/sitemap.xml
Keeping your website structure map updated helps Google crawl and index your site more efficiently.
https://www.google.com/ping?sitemap=https://example.com/sitemap.xmlConclusion
Submitting a sitemap to Google Search Console helps search engines efficiently index your website, ensuring all important pages are discoverable. Creating a website structure map can be done automatically with CMS plugins or manually in XML format, then uploaded to your site’s root directory.
Once verified in GSC, you can submit and monitor the status to detect any errors or indexing issues. By automating updates and using robots.txt, you keep Google informed about your latest content for optimal indexing.