Understanding Google recrawling and indexing
Before your page shows up in Google search results, Google first needs to find it crawling and then store it in its database (indexing). Crawling is when Google’s bots scan your website to discover new or updated content. Indexing is when that content gets added to Google’s search library. Without crawling and indexing, your pages stay invisible to searchers.
Launch Sitechecker’s GSC Dashboard to boost your Search Console reporting!
Expand GSC Data Limits
Bypass Google’s 1,000-row cap and unlock up to 36 months of Search Console history in a single dashboard.
Primary method: request recrawl via Google Search Console
The fastest and most straightforward way to ask Google to take another look at your page is through Google Search Console. The process takes just a few clicks if your site is verified there.
Start by opening GSC and heading to the URL Inspection Tool (you’ll find it in the left-hand menu). Paste the full URL of the page you want Google to recrawl into the search bar at the top and hit Enter.
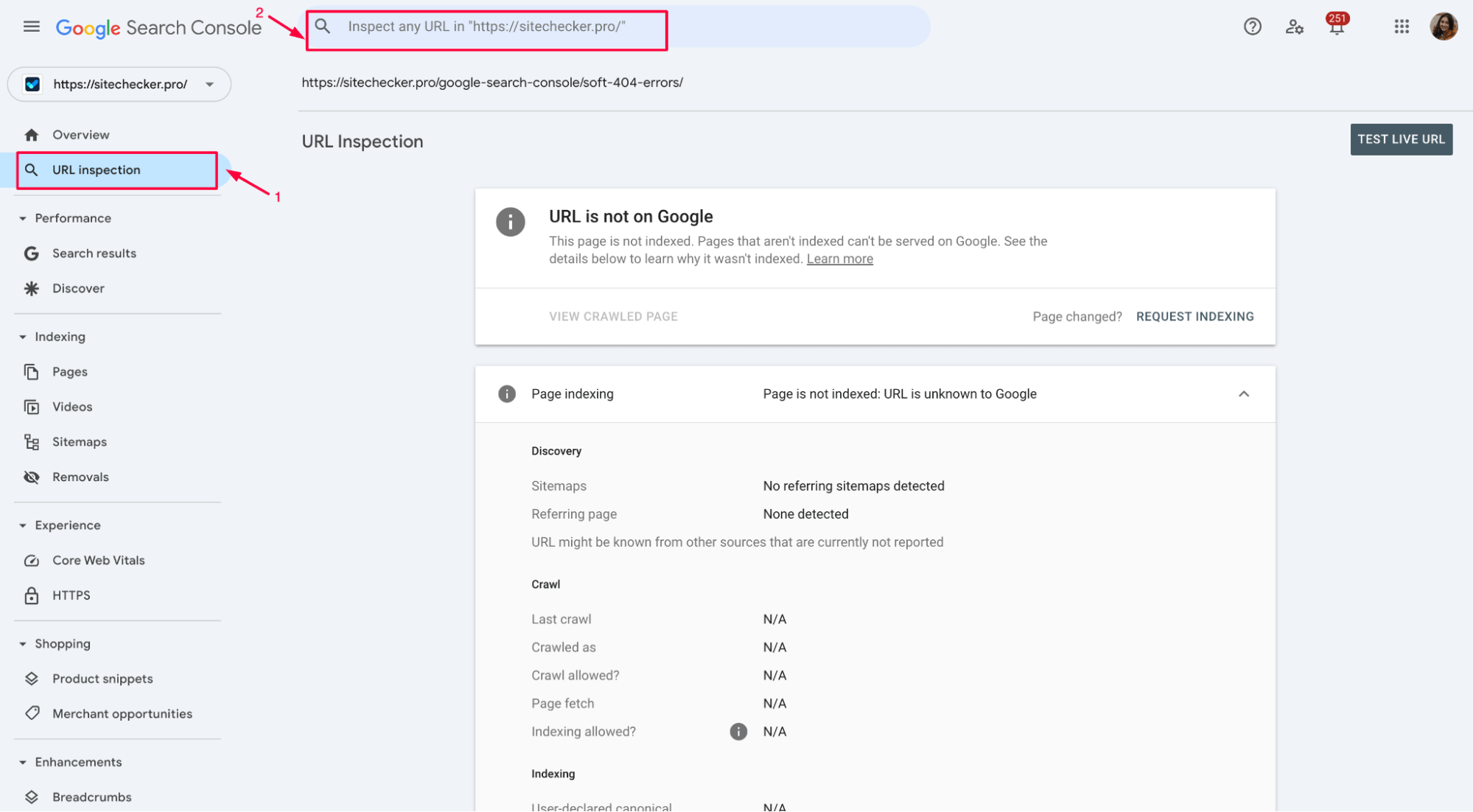
Google will check its index and tell you whether the URL exists.
If the page is indexed but you’ve made updates – or if it’s missing entirely – you can click the Request Indexing button to prompt a recrawl.
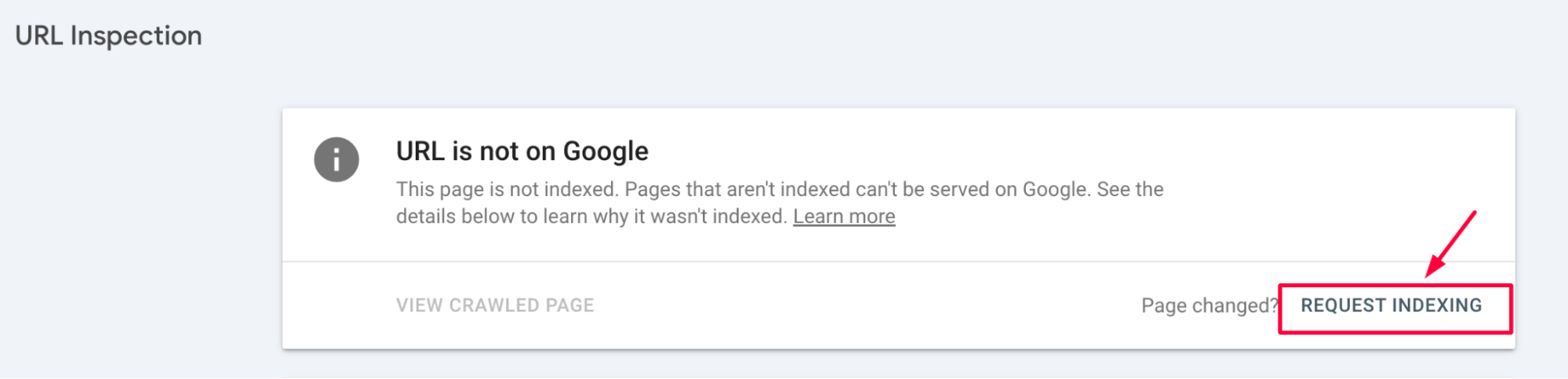
This action adds your URL to Google’s priority queue. It doesn’t guarantee instant indexing, but it usually speeds things up.
Depending on how busy Googlebot is and how your site is structured, you might see results within a few hours or days.
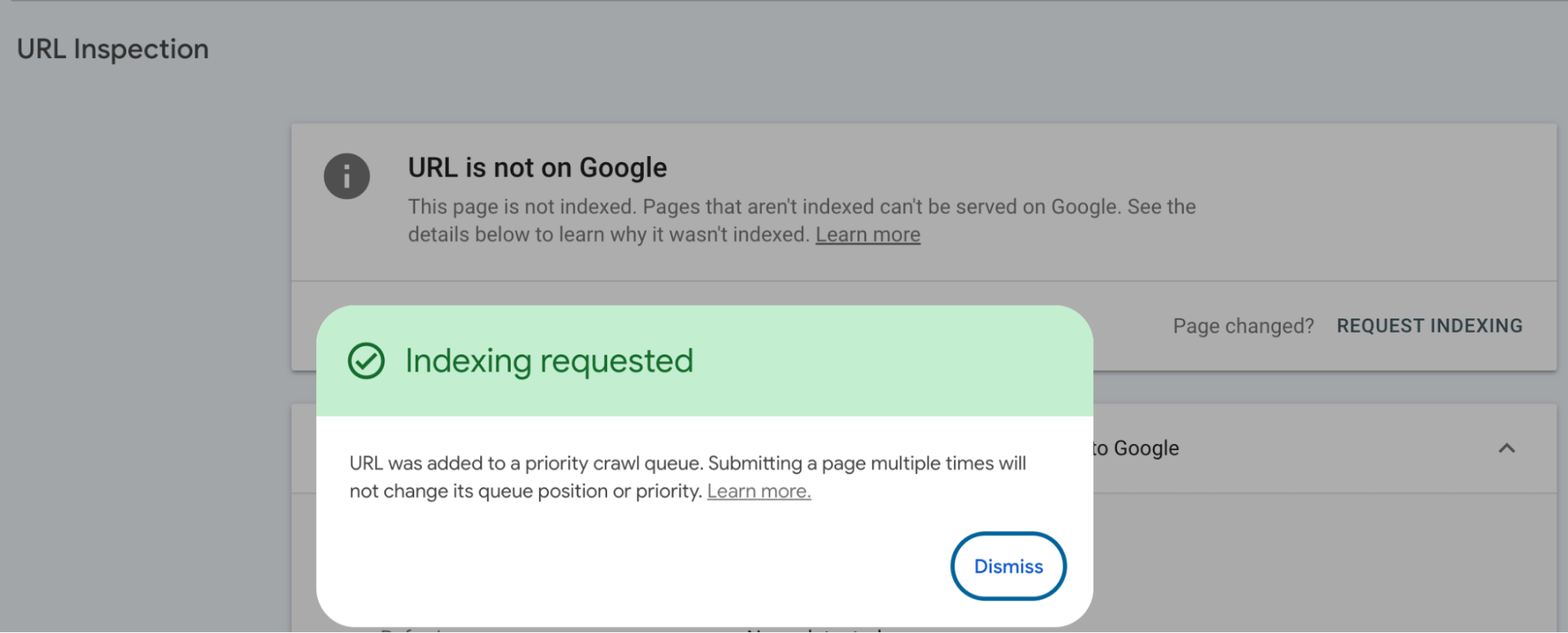
Google limits how often you can request indexing through the Search Console. You might see a message saying you’ve hit your quota if you submit too many URLs quickly. In that case, you’ll need to wait before making new requests.
Sometimes, indexing requests get delayed even when you follow all the steps correctly. Google may temporarily suspend manual indexing features to prevent system overload, especially during major updates or high-demand periods. Technical issues on your site, like server errors or blocked resources, can also slow recrawling.
When and why to request recrawling
You don’t need to request a recrawl for every tiny update. Google will usually find changes on its own. But when you make major updates – like rewriting a page, fixing critical SEO errors, adding new vital pages, or recovering from a site issue – it’s smart to request a recrawl manually.
Requesting recrawling also makes sense if you spot errors in how Google displays your content, like wrong titles, outdated descriptions, or indexing old page versions. In these cases, a fresh crawl can help fix problems faster.
Here’s a quick video that explains how it works:
Alternative ways to encourage Google to recrawl
If the manual request tool isn’t available – or if you want to boost your chances – there are other ways to get Google to notice your changes.
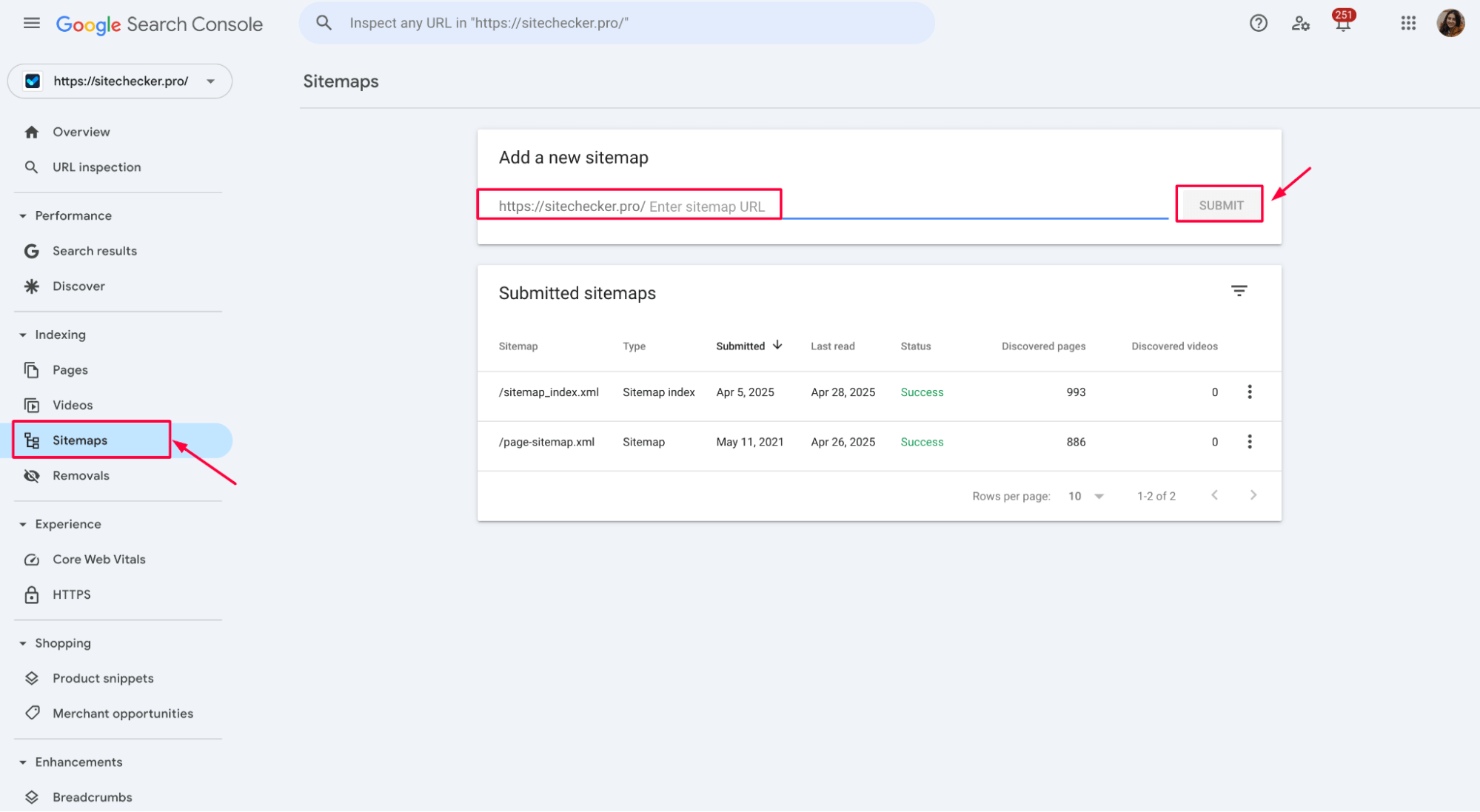
1. Resubmit your sitemap
Upload an updated sitemap in Google Search Console. This signals Google that new or changed content is available:
2. Improve internal linking
Link to your site’s updated or new pages from older, high-traffic pages. Googlebot follows internal links, which helps it discover changes faster.
Use Page Rank Checker to identify top-performing URLs and use them strategically.
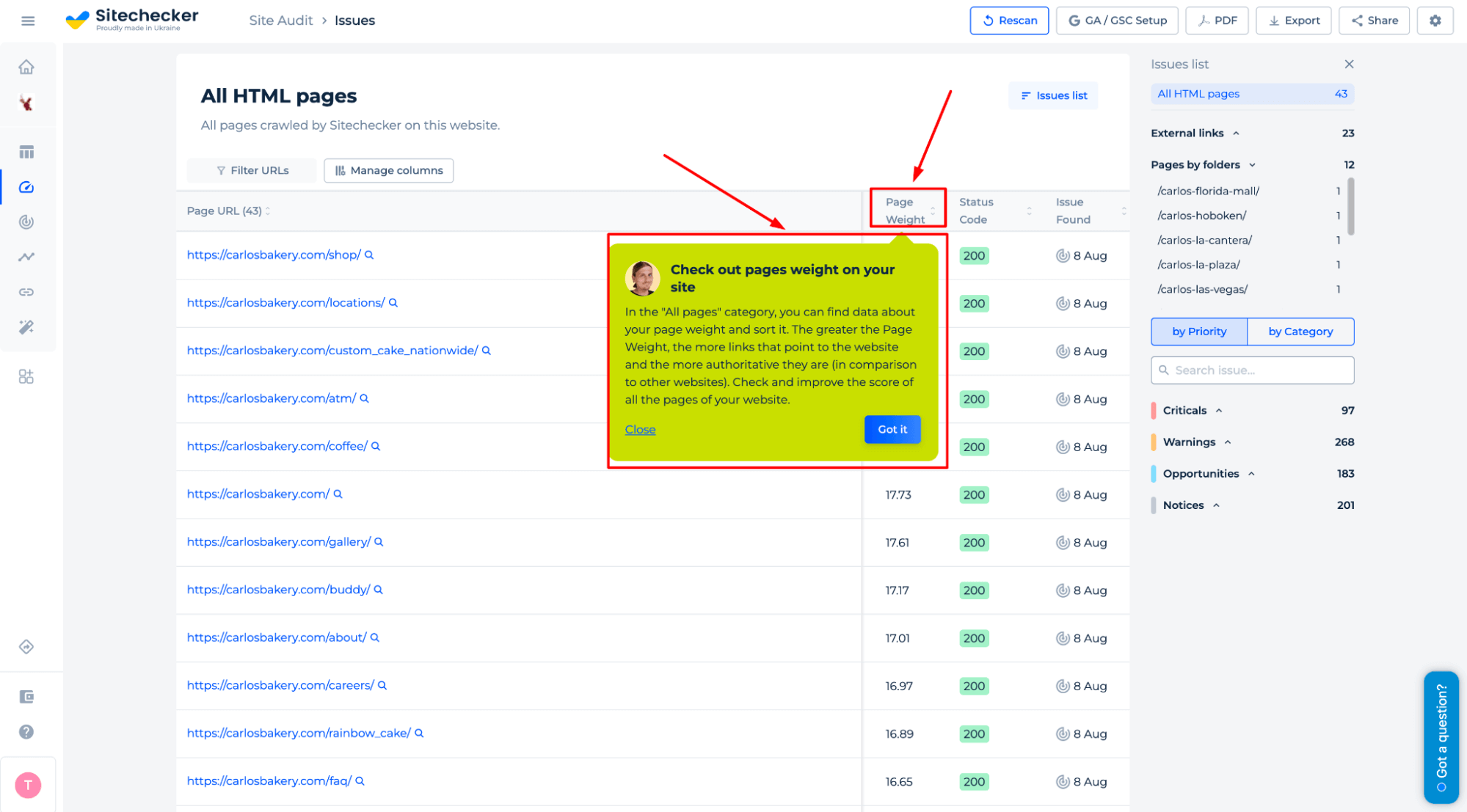
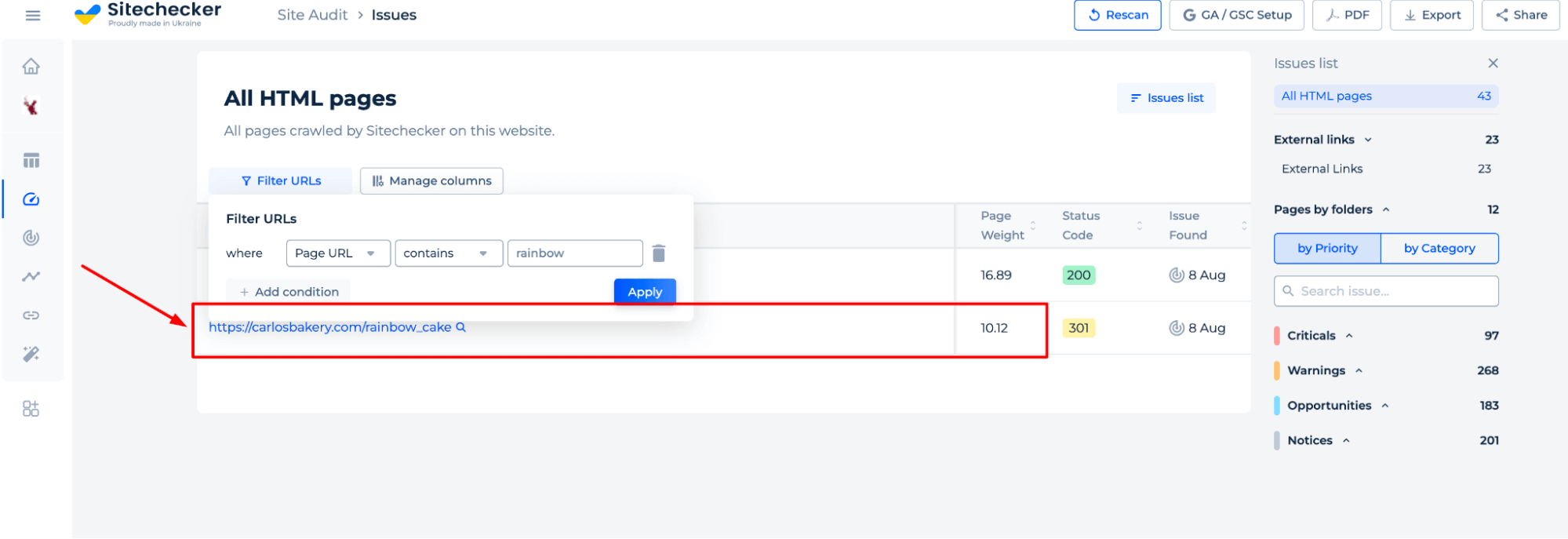
Use the “Page Weight” metric in Sitechecker to find which pages have the most internal authority. You can also filter URLs to spot and strengthen low-performing ones quickly.
3. Build backlinks
Getting a fresh backlink to a newly updated page from another website, especially one already indexed, can nudge Google to crawl the page again.
Here’s a simple example of how a backlink might look in HTML:
<a href="https://yourdomain.com/updated-page">Check out this updated guide on [your topic]</a>
You can place this link in a guest post, a partner blog, or even your existing content on another site you control.
4. Use social media and traffic signals
Sharing updated URLs on social platforms can drive real traffic to your page. More visitors mean more activity, which sometimes triggers a new crawl.
Common problems when requesting recrawling
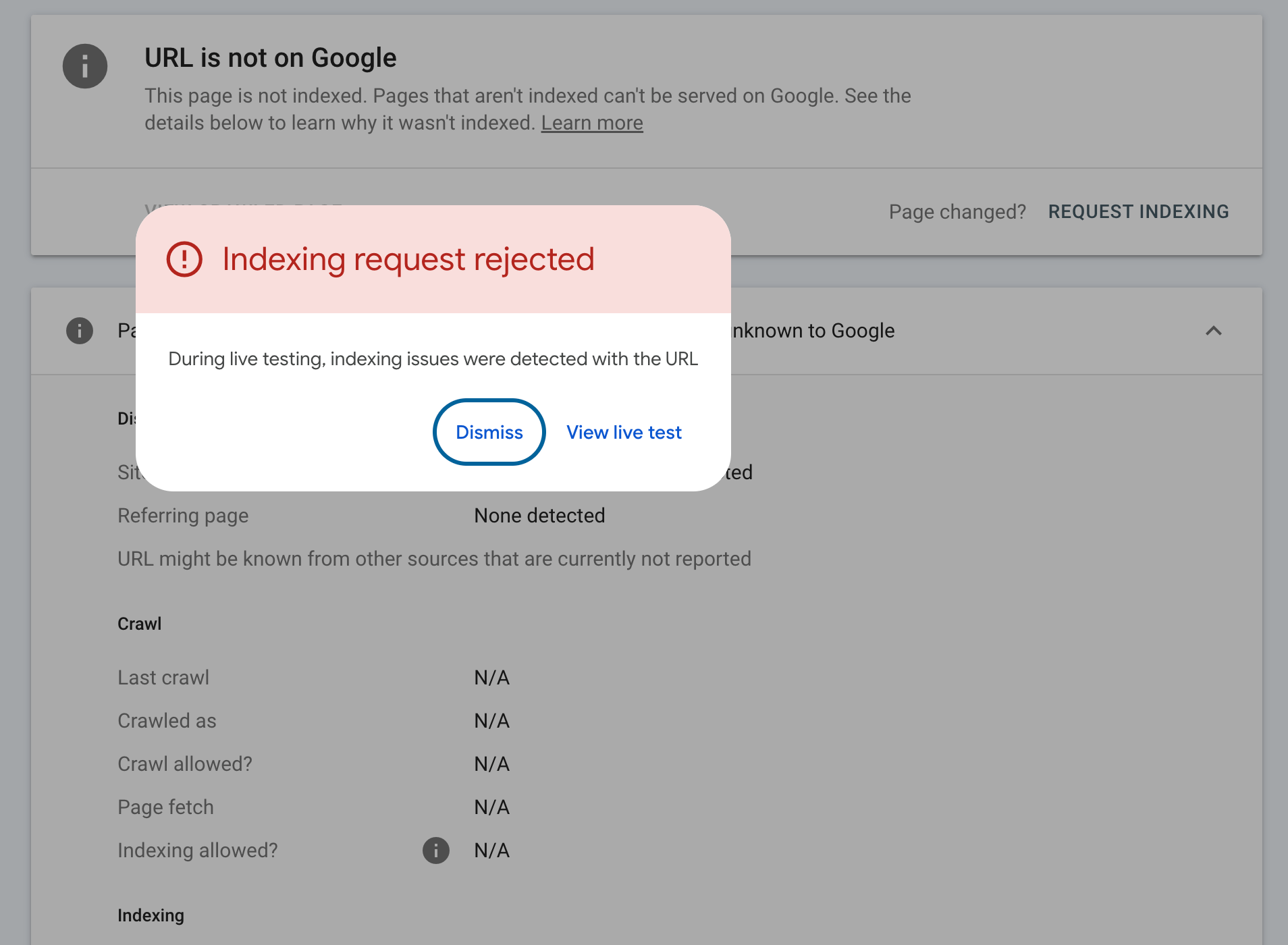
Sometimes, even when you do everything right, Google won’t accept your indexing request. One common error is: “We had problems submitting your indexing request. Please try again later.”
This usually means Google has temporarily disabled manual indexing, often during algorithm updates or system maintenance.
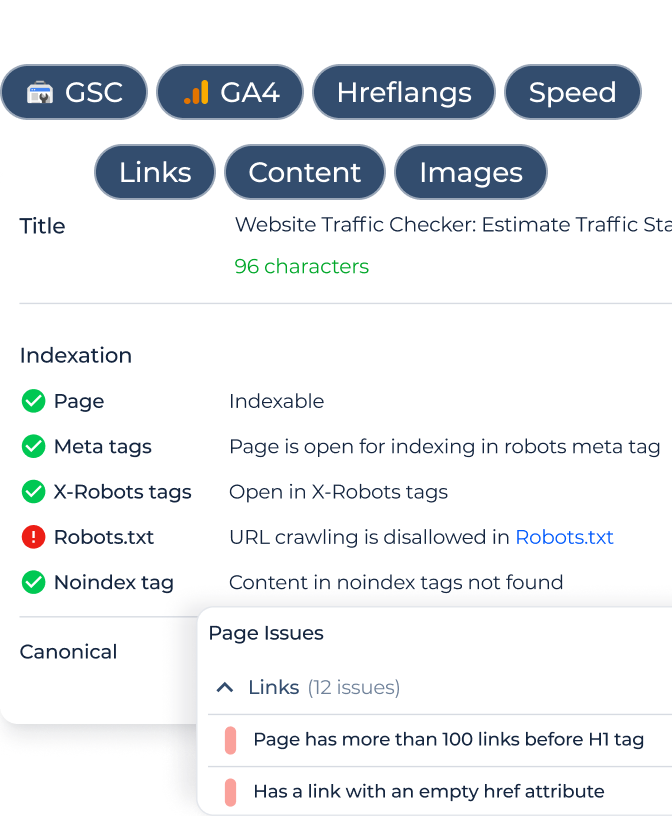
Another issue? Your page might not meet Google’s quality standards. If the content is thin, duplicated, or blocked by noindex, Googlebot may skip it. Use the URL Inspection Tool to check crawl status, coverage issues, and potential blockers.
Also, double-check that your page:
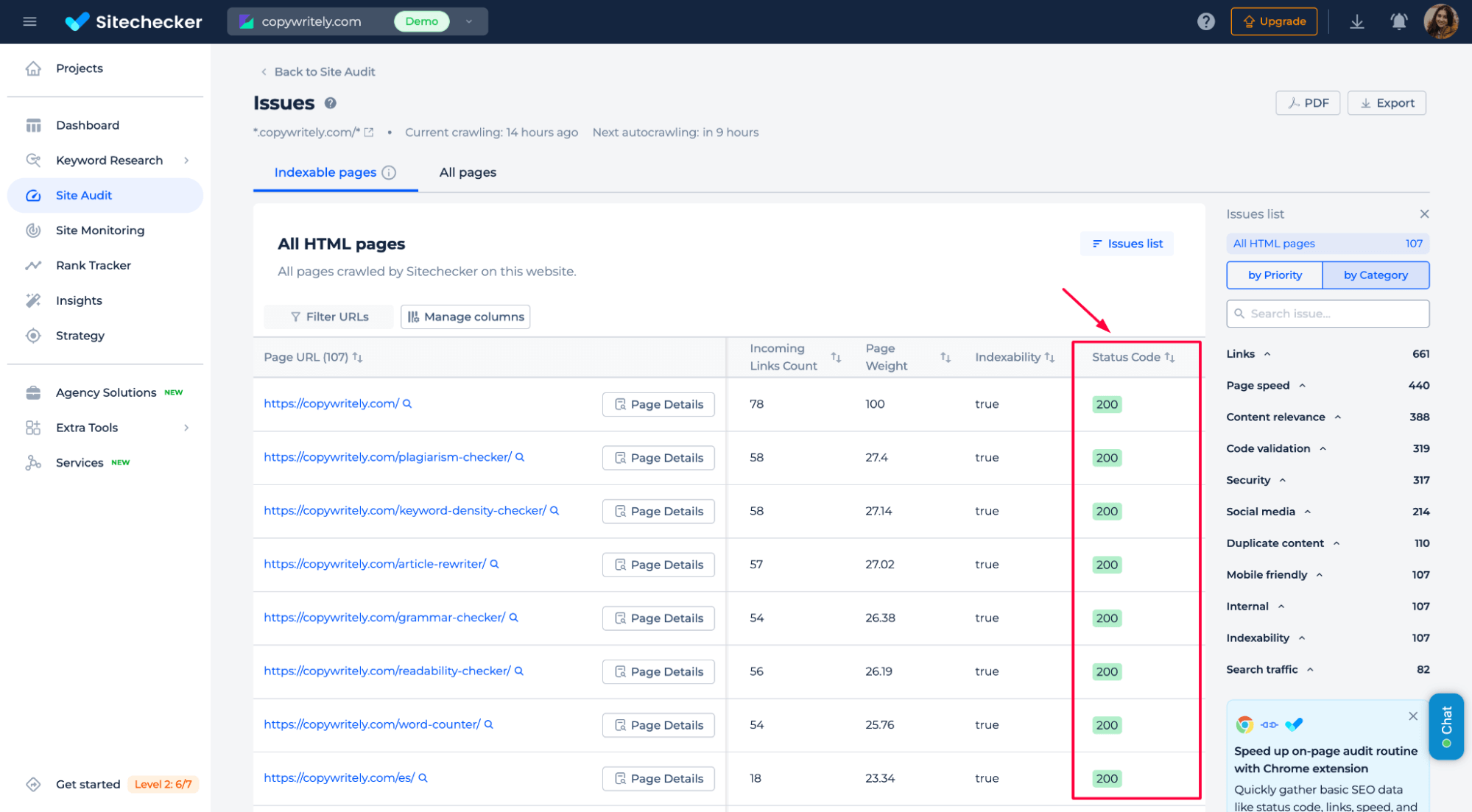
– Returns a valid 200 HTTP status
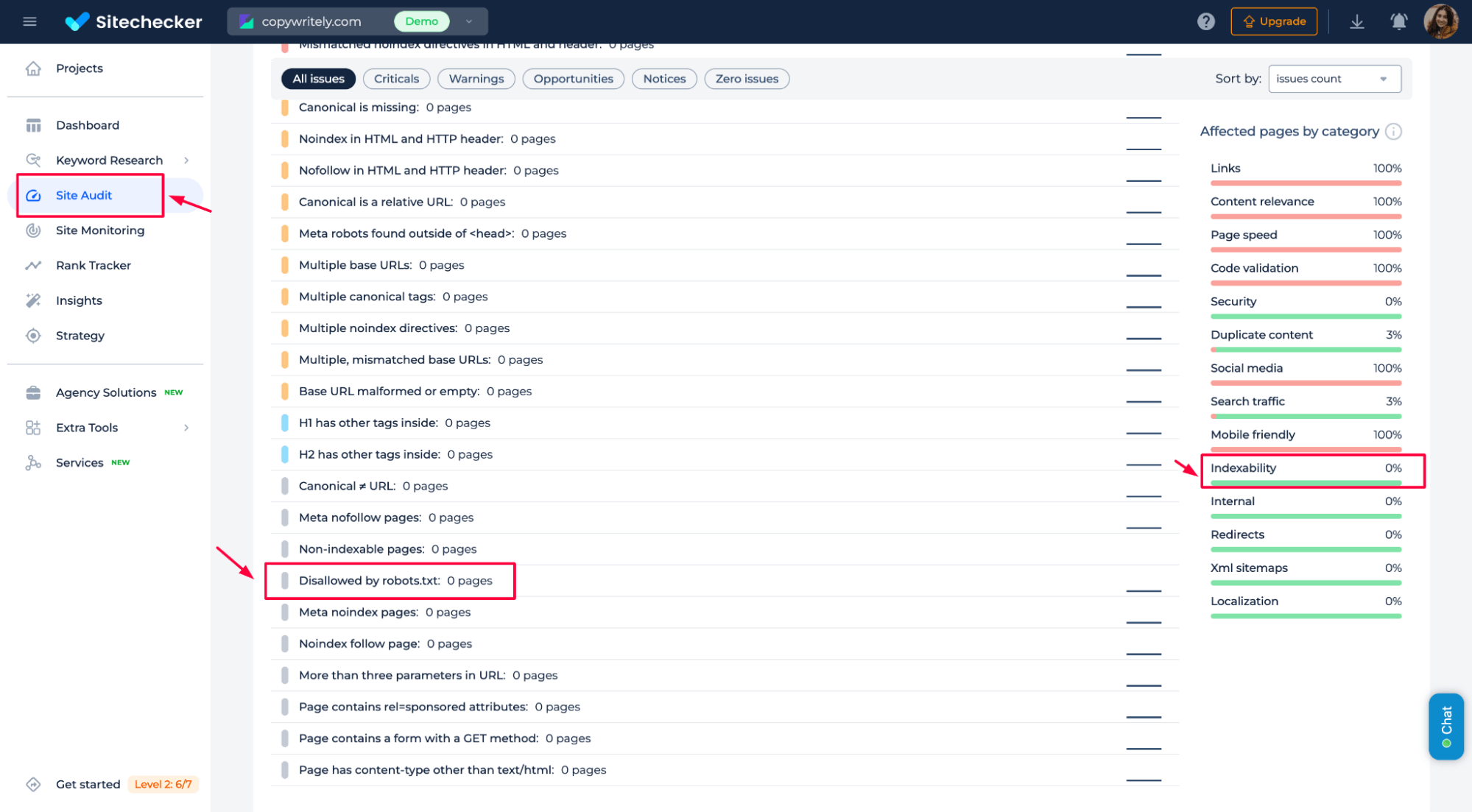
– It isn’t disallowed in robots.txt
Using Robots.txt Tester, you can quickly check which pages are blocked by robots.txt. It highlights disallowed URLs and helps you fix crawl restrictions in seconds.
– Doesn’t have a meta noindex tag
Request Indexing Not Working?
Use our tool to instantly check for crawl blocks, noindex tags, and robots.txt issues.
If you’re still stuck, this guide on fixing “Submitted URL marked ‘noindex’” breaks it down step-by-step.
How long does it take for Google to recrawl?
There’s no guaranteed timeframe. Sometimes, Google crawls your page within a few hours, especially after a manual request. Other times, it can take days or weeks, depending on factors like your site’s authority, crawl budget, update frequency, and server health.
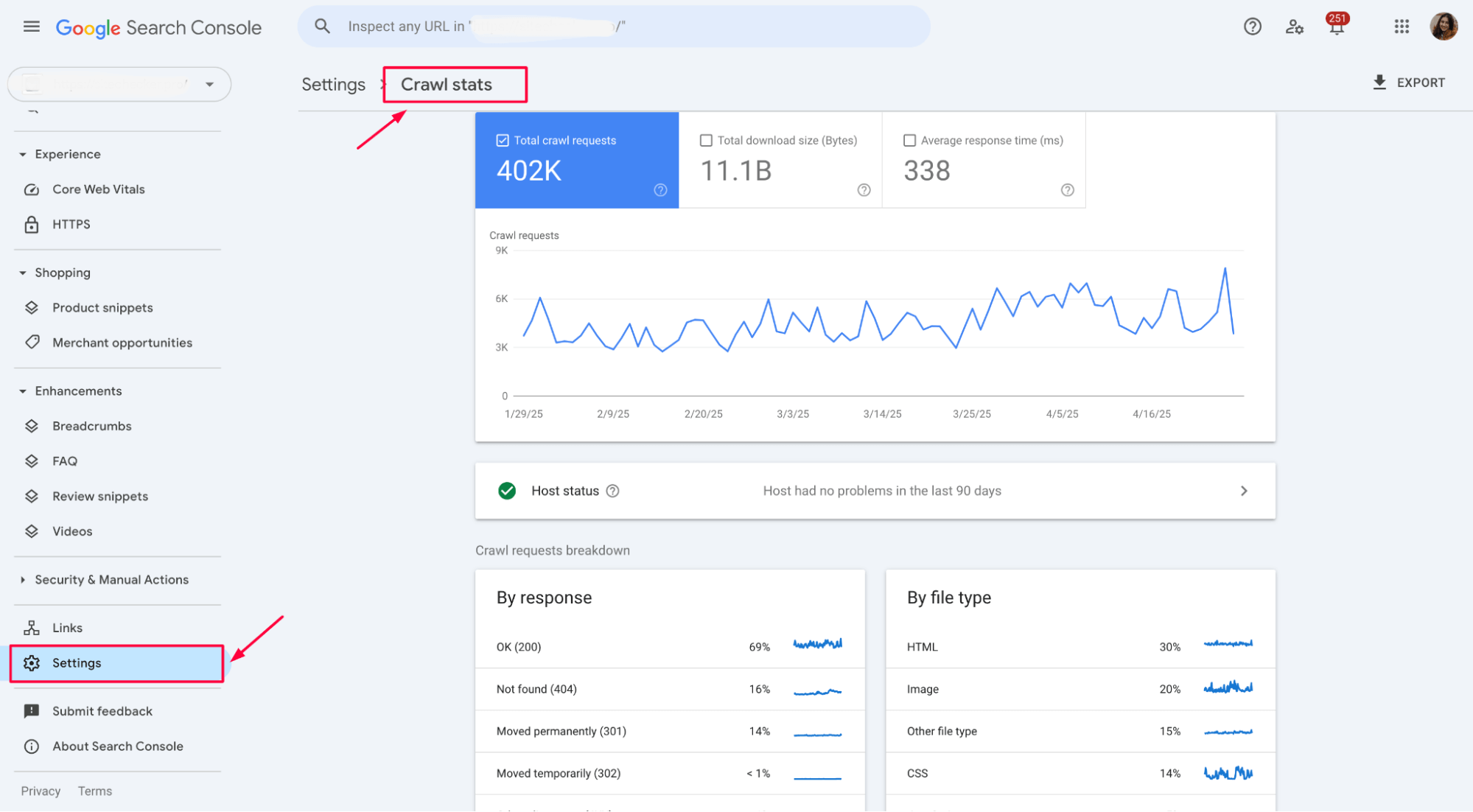
You can check your site’s crawl stats in GSC under Settings > Crawl stats. This helps you monitor how often Googlebot visits your site and spot any crawling issues that might slow reindexing.
High-authority or frequently updated sites usually get recrawled faster. New or low-traffic sites might wait longer unless you nudge Google with tools like Search Console, updated sitemaps, or strong internal links.
Final idea
Submitting a URL to Google for indexing is simple using the URL Inspection Tool in Search Console, but it’s not always instant. Use this feature strategically after major updates. If manual requests aren’t available, boost visibility through updated sitemaps, internal links, backlinks, and traffic signals. Watch for errors like blocked pages or low-quality content, and monitor crawl activity in Search Console.
While you can’t force Google to recrawl instantly, improving your site’s structure and authority increases your chances of faster indexing.