What is SEO Strategy?
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy is a comprehensive plan to enhance a website’s visibility and ranking on search engine results pages (SERPs). It encompasses a variety of tactics and best practices aimed at improving the website’s relevance and authority in the eyes of search engines like Google. A well-crafted SEO strategy involves keyword research to identify the terms and phrases potential customers are using, content creation that aligns with those keywords, and technical optimizations to ensure search engines can effectively crawl and index the site. Additionally, it includes building high-quality backlinks, optimizing for user experience, and regularly analyzing and adjusting the strategy based on performance metrics. The ultimate goal of an SEO strategy is to increase organic traffic to the site, leading to higher visibility, credibility, and, ultimately, conversions.
Why Your SEO Strategy Matters
In today’s digital age, having a strong online presence is crucial for businesses and individuals alike. An effective SEO strategy plays a pivotal role in achieving this presence. Search engines are the primary means through which people find information, products, and services online. By optimizing your site for search engines, you increase the likelihood of your site appearing in the top results for relevant queries. This visibility is vital as studies show that the majority of users do not go past the first page of search results.
Furthermore, users tend to trust search engines, so ranking highly can also enhance your site’s credibility. In addition to attracting more visitors, a well-executed SEO strategy ensures that the traffic is relevant, targeting users who are more likely to engage with your content or convert. This targeted approach not only drives more qualified traffic but also contributes to a better user experience, as visitors find the information or products they are seeking more efficiently. Ultimately, investing in SEO is investing in the long-term success and visibility of your online content, making it an essential component of any digital marketing strategy.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating an SEO Strategy
Creating an effective SEO strategy requires careful planning and execution. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you build a solid SEO foundation and enhance your online visibility.
Step #1: Create a List of Keywords
Begin by identifying the keywords and phrases that potential customers might use to find your products or services. Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to research and compile a list of relevant keywords. Focus on a mix of short-tail and long-tail keywords, and consider the search volume and competition for each. Don’t forget to include local keywords if your business serves a specific geographic area.
Step #2: Analyze Google’s First Page
Once you have your list of keywords, search for them on Google and analyze the first page of results. Look at the content types (blog posts, product pages, videos, etc.), the topics covered, and the user intent behind the top-ranking pages. This analysis will help you understand what Google deems relevant for these queries and what you need to do to compete.
Step #3: Create Something Different or Better
Based on your analysis, create content that is either different from or better than what is currently ranking. If the top results are all blog posts, perhaps you could create an informative video or infographic. If the existing content is outdated or lacks depth, create a more comprehensive and up-to-date piece.
Step #4: Add a Hook
Your content needs a hook—something that will attract links and shares. This could be original research, a unique perspective, or a helpful resource. Your hook should provide additional value to your audience and make your content stand out.
Step #5: Optimize For On-Page SEO
Ensure that your content is fully optimized for search engines. This includes using your target keyword in strategic locations like the title, headings, and body of the text. Additionally, optimize your images, use internal links to connect to other relevant content on your site, and ensure that your page loads quickly.
Step #6: Optimize For Search Intent
Make sure your content aligns with the search intent behind your target keywords. If people are searching for information, provide comprehensive and helpful content. If they are looking to make a purchase, ensure your product pages are clear and compelling.
Step #7: Focus On Content Design
The design of your content plays a crucial role in user engagement. Use clear headings, short paragraphs, and visuals to make your content more accessible and engaging. Additionally, ensure that your website is mobile-friendly, as a significant portion of searches are conducted on mobile devices.
Step #8: Build Links to Your Page
Backlinks from reputable websites can significantly boost your page’s authority and rankings. Focus on building high-quality backlinks through guest posting, outreach, or creating link-worthy content. Avoid shady link-building practices as these can result in penalties from Google.
Step #9: Improve and Update Your Content
SEO is an ongoing process. Regularly review your content and update it to ensure it remains relevant, accurate, and comprehensive. Additionally, stay abreast of any changes in SEO best practices and adjust your strategy accordingly.
By following these steps, you can create a robust SEO strategy that enhances your online visibility, attracts targeted traffic, and provides value to your audience.
Advanced SEO Topics
To further enhance your website’s visibility and performance, it’s essential to delve into advanced SEO topics. These areas require a more in-depth understanding of SEO principles and can significantly impact your site’s success in search engine rankings.
Technical SEO Strategy
Technical SEO involves optimizing the technical elements of your website to improve its visibility and usability. Focus on improving site speed, ensuring your site is mobile-friendly, and creating a clear site structure with a logical hierarchy. Implementing schema markup can also help search engines better understand your content and provide rich results. Regularly audit your website for crawl errors and fix any broken links or pages.
Mobile Search Strategy
With the increasing prevalence of mobile devices, having a mobile-optimized website is crucial. Ensure your website is responsive, meaning it adjusts to various screen sizes and devices. Pay attention to mobile usability, page speed, and local search optimization, as these factors significantly impact mobile search rankings. Implementing Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) can also enhance user experience and contribute to higher mobile rankings.
Video SEO Strategy
Video content is highly engaging and can drive significant traffic to your website. To optimize your video content for search engines, use descriptive titles and meta descriptions, and ensure your videos are accessible to search engine crawlers. Include a video transcript to make your content accessible and indexable. Additionally, host your videos on platforms like YouTube to increase their visibility and shareability.
Voice Search Strategy
Voice search is becoming increasingly popular, and optimizing your content for voice search is essential. Focus on natural language and conversational queries, as voice searches tend to be more informal and question-based. Ensure your website is optimized for local search, as many voice searches are location-based. Implementing structured data can also help your content stand out in voice search results.
Local SEO Strategy
Local SEO helps businesses promote their products and services to local customers. Optimize your Google My Business listing by ensuring your business information is accurate and up-to-date. Encourage satisfied customers to leave positive reviews, and respond to any negative reviews professionally. Focus on local keywords and include your business’s name, address, and phone number on your website.
International SEO Strategy
If your business operates in multiple countries or languages, international SEO is crucial. Use hreflang tags to indicate the language and regional targeting of your content. Ensure your website’s structure is optimized for international audiences, and consider using a country code top-level domain (ccTLD) or a subdomain/subdirectory for each country or language version of your site. Research and target region-specific keywords and cultural nuances in your content.
By mastering these advanced SEO topics, you can significantly improve your website’s search engine performance, reach a broader audience, and achieve your business objectives.
Practical Insights and Case Studies
Applying theoretical knowledge is crucial, but seeing real-world applications can provide invaluable insights. This section delves into practical examples and case studies, illustrating how SEO strategies have been successfully implemented and the impact they’ve had.
SEO Plan Case Studies
Explore detailed case studies of businesses from various industries that have successfully executed SEO strategies. Each case study should break down the challenges faced, the SEO strategies implemented, and the results achieved. Focus on diverse examples, showcasing different sizes of businesses and various market sectors. Highlight the steps taken, mistakes made, and lessons learned, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of the SEO journey from start to finish.
Value of Organic Search White Paper
This white paper should provide a deep dive into the significance of organic search traffic. Discuss the long-term benefits of investing in SEO, contrasting it with paid advertising and highlighting the cost-effectiveness and sustainability of organic search. Use data and statistics to back up claims, and include testimonials from industry experts and businesses that have thrived through a strong SEO foundation. This document should serve as a persuasive piece on why businesses should prioritize and invest in SEO, backed by empirical evidence and expert opinions.
By including these practical insights and case studies, readers can gain a more tangible understanding of SEO strategies in action, learning from real-world applications and appreciating the tangible impact of SEO on business success.
Integrating SEO with Marketing
In today’s digital age, SEO should not exist in a vacuum. Instead, it needs to be integrated seamlessly with broader marketing efforts to maximize impact. This section explores how SEO can be synergistically combined with overall marketing strategies, enhancing brand visibility, reputation, and customer engagement.
Branding, SEO and Reputation
Delve into the intricate relationship between branding, SEO, and corporate reputation. Discuss how a strong SEO strategy can enhance brand visibility and contribute to building a positive brand image. Provide strategies on managing online reputation through SEO practices, highlighting the importance of consistency in messaging across different channels. Explore how SEO can be used as a tool for reputation management, demonstrating how to address negative reviews and maintain a positive online presence.
SEO and Marketing Strategy Development
Explore the steps to integrate SEO into the overall marketing strategy of a business. Highlight the importance of aligning SEO objectives with marketing goals, ensuring that both efforts complement each other. Provide a roadmap for developing a cohesive strategy, emphasizing keyword alignment, content creation, and consistent messaging. Discuss the role of SEO in various stages of the marketing funnel, from awareness to conversion, and how it can be optimized for each stage to drive results.
Marketing Integration
Dive into practical ways to integrate SEO with other marketing channels like social media, email marketing, and paid advertising. Provide examples and case studies showcasing successful integration, and discuss the benefits of a holistic approach. Highlight the importance of data sharing between SEO and other marketing channels, demonstrating how insights from one area can inform and enhance strategies in another. Offer best practices for ensuring seamless integration, ensuring that all channels work together cohesively to drive business success.
By addressing these topics, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how SEO can be integrated with broader marketing efforts, enhancing overall business performance and driving more meaningful interactions with customers.
Monitor Technical Health of Your Website with Sitechecker
The SEO Checker & Audit Tool is an invaluable resource for anyone looking to enhance their website’s search engine optimization. With its user-friendly interface, this tool efficiently analyzes various elements of a website, including meta tags, headings, and keyword consistency. It quickly identifies SEO issues that could be hindering a site’s performance in search results, making it ideal for both beginners and seasoned webmasters. Whether you’re looking to improve your site’s visibility or diagnose current SEO challenges, this tool offers a comprehensive and accessible approach to SEO analysis.
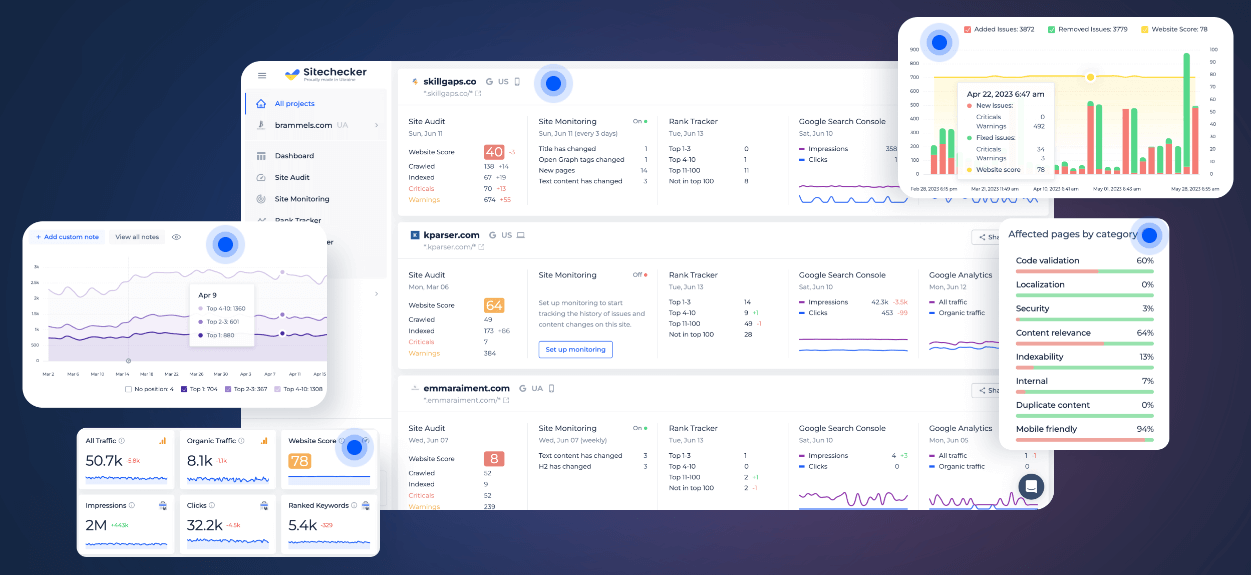
In addition to basic SEO evaluation, this tool offers advanced features that delve deeper into website optimization. It provides insights into backlink analysis, website speed, and mobile optimization, critical factors in today’s digital landscape. The tool also offers recommendations for improvements, helping users prioritize changes that will have the most significant impact on their site’s SEO performance. With regular updates and the ability to track progress over time, the SEO Checker & Audit Tool is a dynamic solution for maintaining and enhancing your website’s SEO strategy.
Boost Your Website's SEO Performance!
Optimize Your Website Like a Pro with Our SEO Checker & Audit Tool.
Conclusion
In wrapping up this comprehensive guide on SEO strategy, it’s crucial to emphasize the transformative power of SEO when effectively implemented and integrated with overall marketing efforts. SEO is not just a standalone tactic but a vital component of a holistic digital marketing strategy that can significantly boost online visibility, drive traffic, and enhance user experience.
The journey to SEO mastery requires continuous learning, adaptation, and the willingness to embrace new trends and technologies. By following the structured steps and considering the advanced topics and practical insights provided in this guide, businesses of all sizes can unlock the full potential of their online presence.
Remember, the digital landscape is ever-evolving, and staying ahead means being proactive, innovative, and committed to excellence in SEO practices. So, embark on this SEO journey with confidence, armed with the knowledge and strategies needed to succeed in the competitive world of online search.