What does “Videos to appear outside the viewport” mean?
“Videos to Appear Outside the Viewport” refers to situations where a video element on a webpage is positioned so that it’s not visible within the user’s initial view when they load the page.
In other words, the media file may be off-screen, hidden, or positioned beyond the browser window’s visible area (the “viewport”).
What causes videos to appear outside the viewport?
❌Improper CSS Handling – if the video container has fixed dimensions or wrong width and height properties, the media file can overflow beyond the visible area of the page.
❌Incorrect Use of object-fit – the object-fit property helps control how the video scales. If not used properly, the video can stretch or be misaligned, causing it to appear outside the viewport.
❌Lack of Responsiveness in Layout – without proper responsive design, Videos may not adjust for different screen sizes. This is particularly an issue when mobile device media queries aren’t well configured.
❌Issues with Embed Codes – videos embedded from platforms like YouTube or Vimeo may not automatically scale to fit smaller screens, causing them to overflow if their embed code isn’t set up for responsiveness.
When videos appear outside the viewport, it’s usually due to a few key factors related to how they are embedded or styled.
Common solutions to fix video outside the viewport
To fix the issue of visual content appearing outside the viewport, you can try the following solutions:
✔️Resize Video Embed – adjust the video width and height to fit within the page’s borders.
✔️CSS Styling – set the iframe width to 100% and height to auto for responsive scaling.
✔️Server-Side Solution – create multiple visual content versions at different resolutions and serve the one that matches the device or screen size.
✔️Intersection Observer API – load the media file only when it comes into view.
Ensuring media files are responsive using max-width, height, and allowfullscreen:
Adjusting meta tags and viewport settings for mobile-first design:
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">Request re-indexing
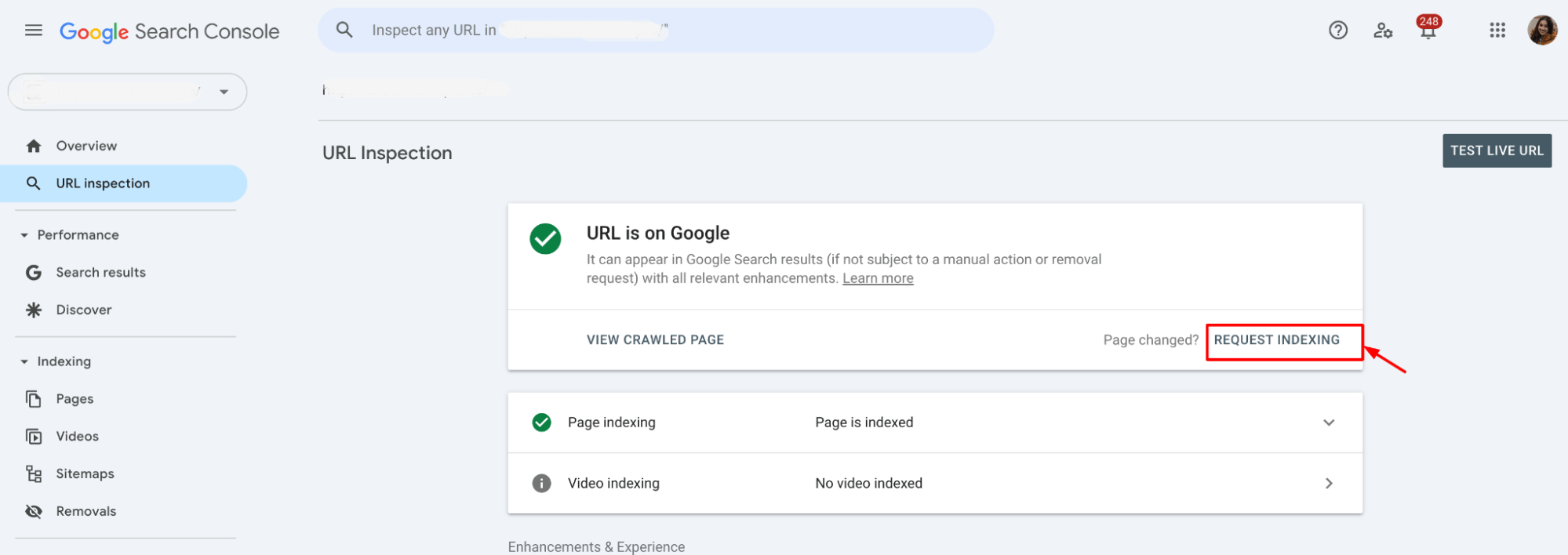
After you’ve fixed any issues, return to the URL Inspection Tool and request re-indexing for the affected pages. This will prompt Google to re-crawl your updated content and reflect the changes in search results.
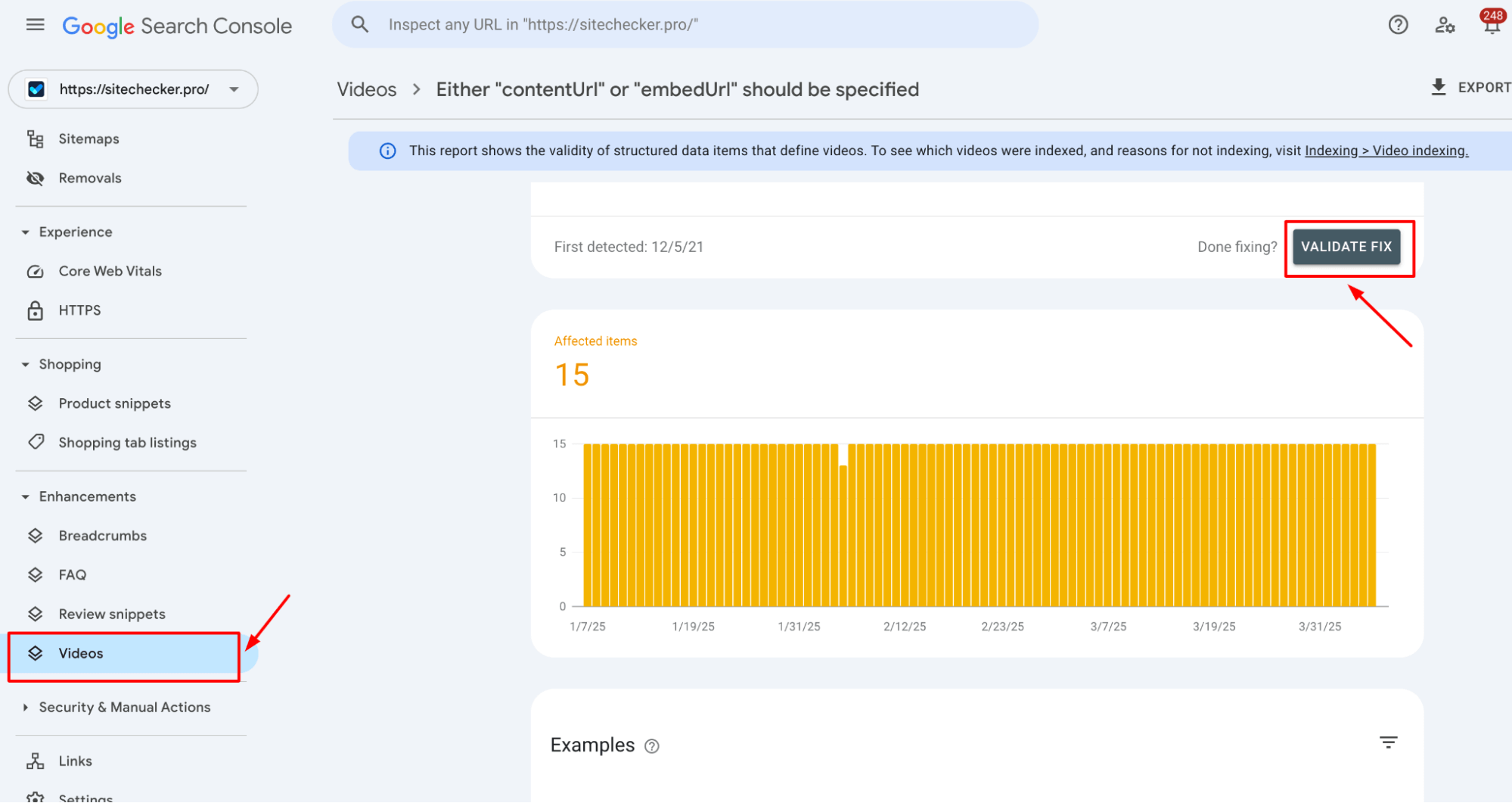
Validate and fix
Once all issues are fixed, return to the Videos section in Google Search Console. If the error is resolved, click “Validate Fix” to confirm the changes and clear the error. This will prompt Google to recheck your media files and update the status.
Check out this video for best practices to optimize your videos for Google Search & Discover:
Launch Sitechecker’s GSC Dashboard to boost your Search Console reporting!
Expand GSC Data Limits
Bypass Google’s 1,000-row cap and unlock up to 36 months of Search Console history in a single dashboard.
SEO implications of video outside the viewport
It’s easy to overlook the SEO impact of a video that’s stuck outside the viewport, but it’s something that can hurt your search rankings.
When your media file aren’t correctly visible, both users and search engines are affected in several ways:
| SEO Implication | Description | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Google might miss it | Googlebot may not crawl videos hidden outside the viewport, leading to indexing issues. | Ensure media files are obvious within the viewport upon page load to facilitate proper indexing. |
| Bad user experience = bad SEO | Hidden or inaccessible media files can increase bounce rates, negatively impacting SEO. | Position media files prominently and ensure they load correctly to enhance user engagement. |
| Less visibility in search results | Videos not properly indexed may not appear in search results, reducing visibility. | Place videos above the fold and ensure they are appropriately sized for better indexing. |
| Mobile users are affected too | Improperly displayed videos on mobile can harm mobile usability scores and rankings. | Use responsive design techniques to ensure media files display correctly across all devices. |
How to identify video outside the viewport issues
Identifying “video outside the viewport” issues is essential to ensure that videos are visible and indexed adequately by users and search engines.
Here are some ways you can identify and fix these issues:
1. Check using Google Search Console
Google Search Console might flag videos that are not accessible or properly indexed. If Google can’t see the video because it’s outside the viewport, it might show up as an error:
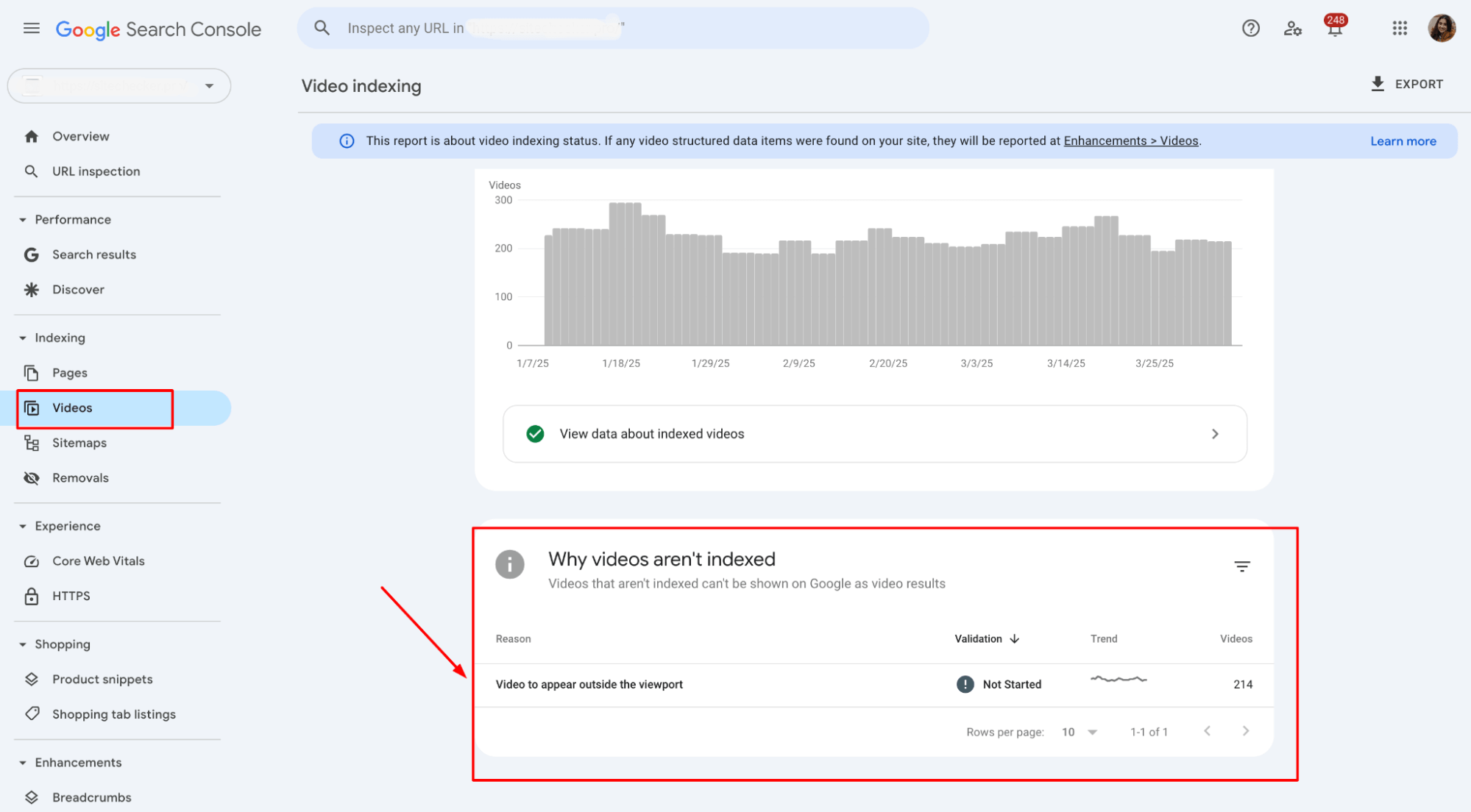
Google might flag errors indicating that the media file is inaccessible, hidden, or improperly formatted, which can lead to indexing issues.
Below the graph in the “Videos” section of Google Search Console, there is a part explaining why videos aren’t indexed. If there are issues with the video visibility or viewport positioning, it could be listed here as a reason (e.g., “Video outside the viewport” or “Video isn’t a watch page”).
1. Visit the enhancements section
In the Enhancements tab, you’ll find specific issues related to video indexing. If a visual content is improperly indexed due to viewport issues, it might show up here with an alert about visibility or positioning problems.
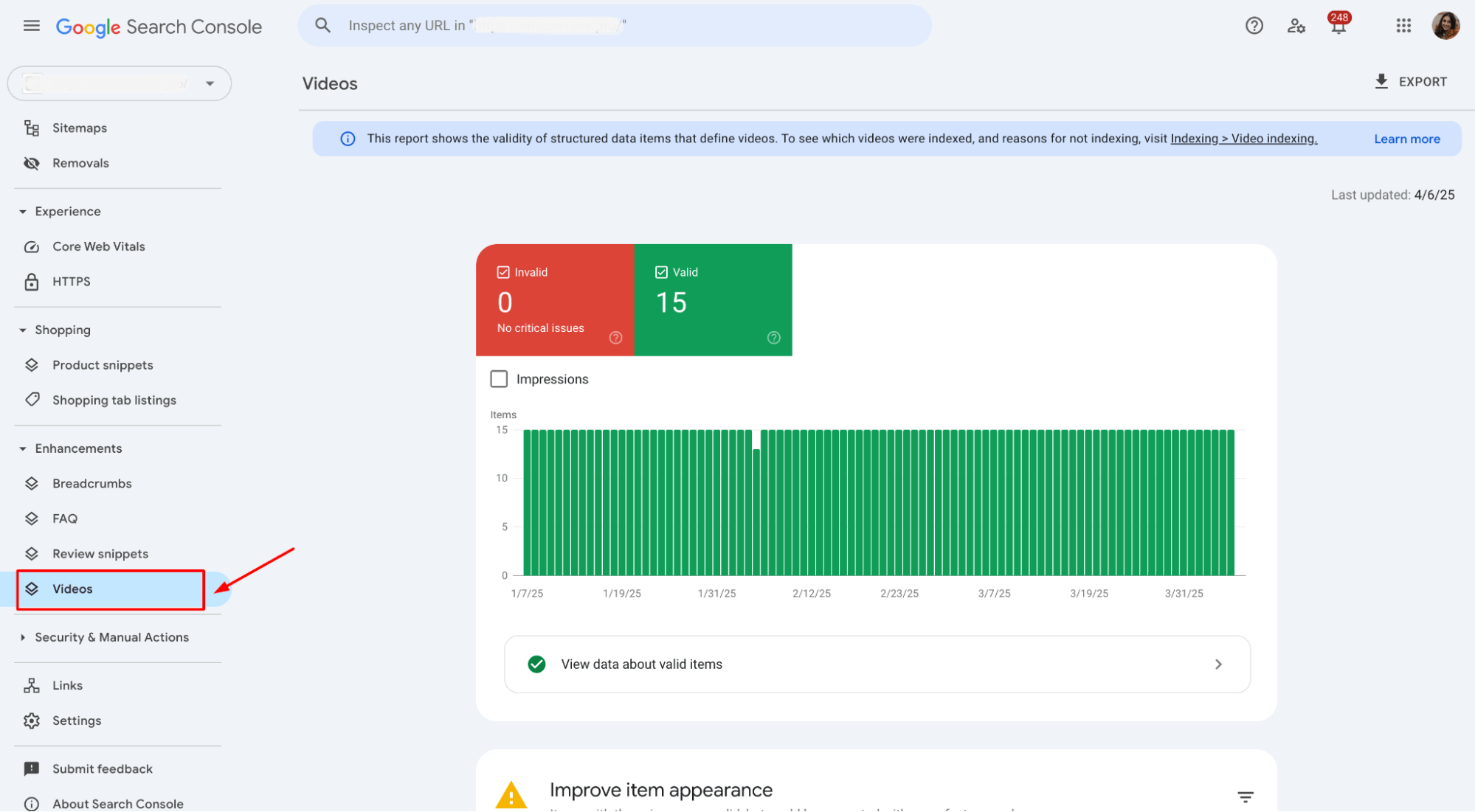
2. Use the URL Inspection tool
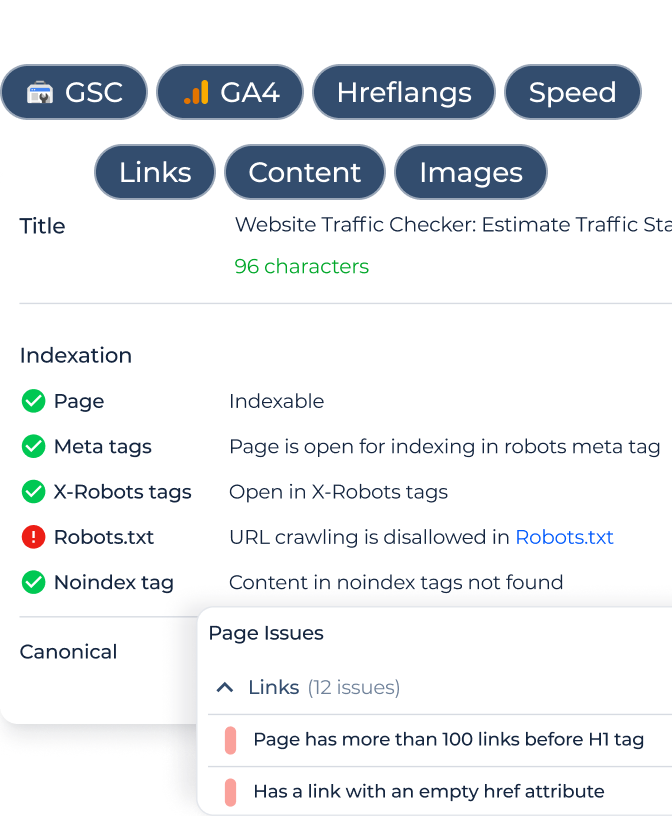
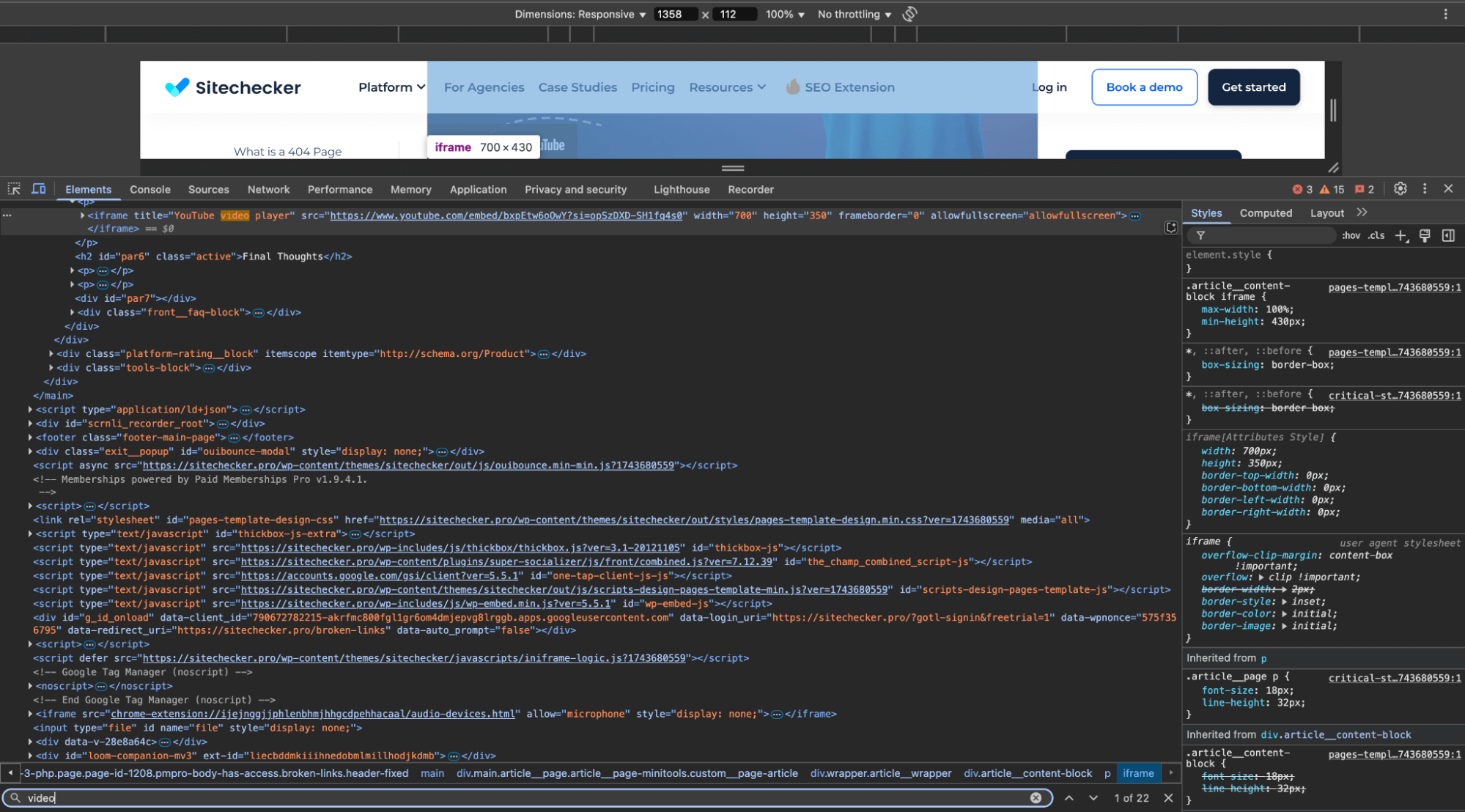
The Sitechecker Inspection Tool helps you see exactly how Googlebot views your page. By checking pages with media files, you can confirm if the media file is outside the viewport, which can prevent proper indexing or crawling.
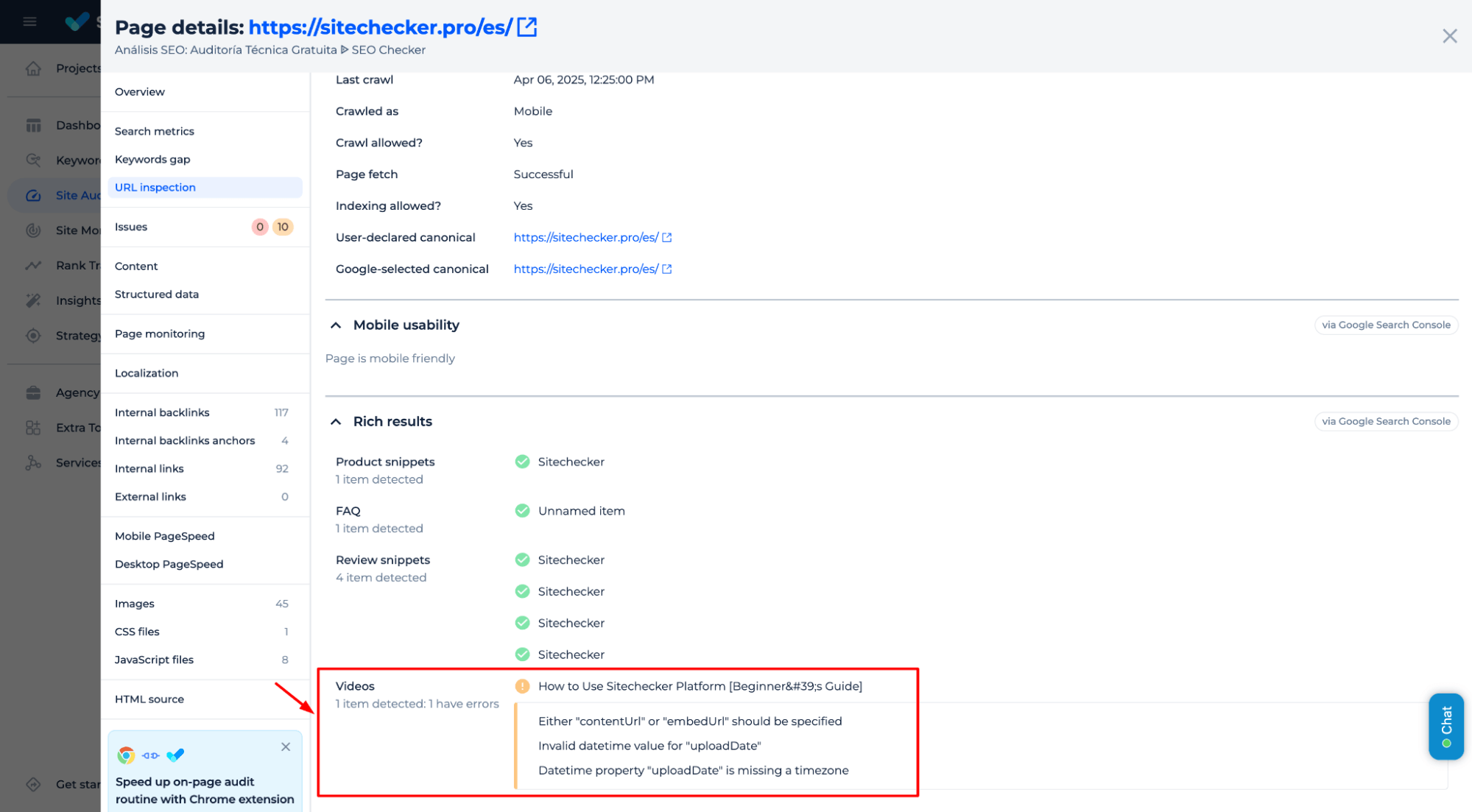
Check If Your Videos Are Outside the Viewport!
Ensure videos are correctly visible and indexed for better SEO.
2. Use browser developer tools
Open your website in a browser (like Chrome) and inspect the page using the developer tools.
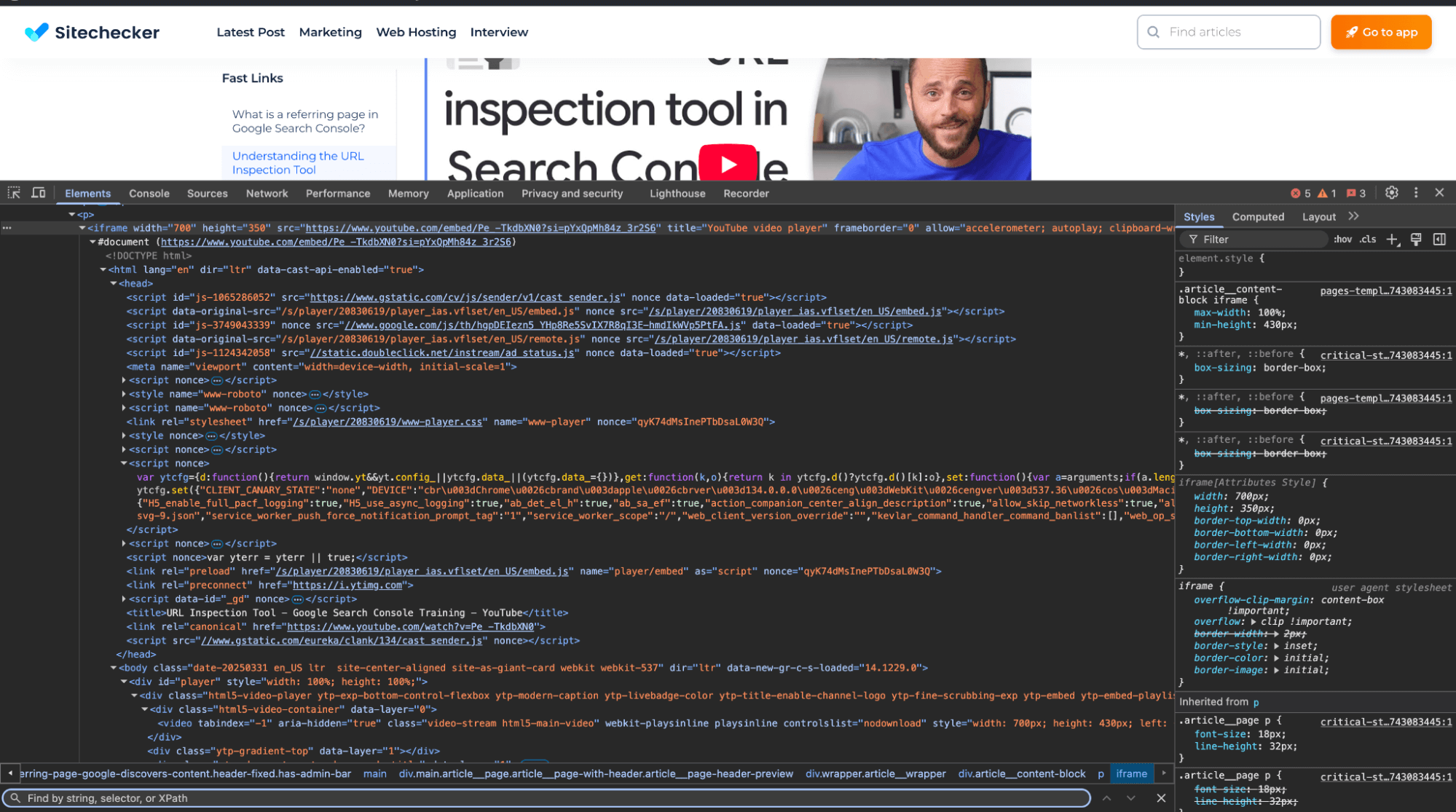
Right-click on the page and select “Inspect” or “Inspect Element. ” Then, check the video’s positioning. Ensure it’s within the visible area of the browser window (i.e., not off-screen).
You can use the “Elements” tab to see if the video’s CSS properties (like position, top, left, width, height) are causing it to appear outside the viewport.
3. Viewport testing
Resize your browser window to simulate different screen sizes, or use a mobile device emulator in the browser.
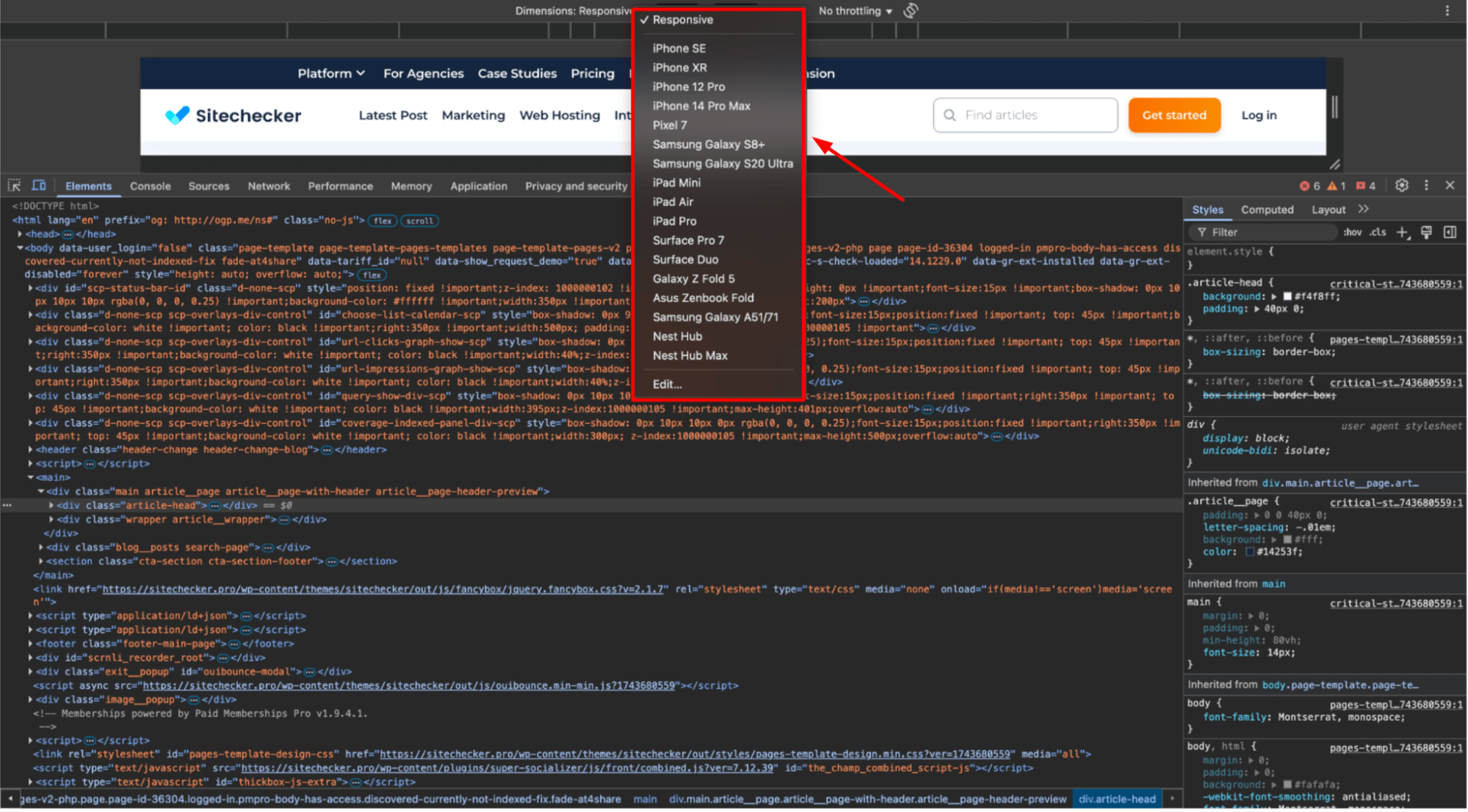
Ensure the media file scales correctly and remains within the visible area on different screen sizes. Check whether it’s appropriately responsive and adjusts when switching between desktop, tablet, and mobile views.
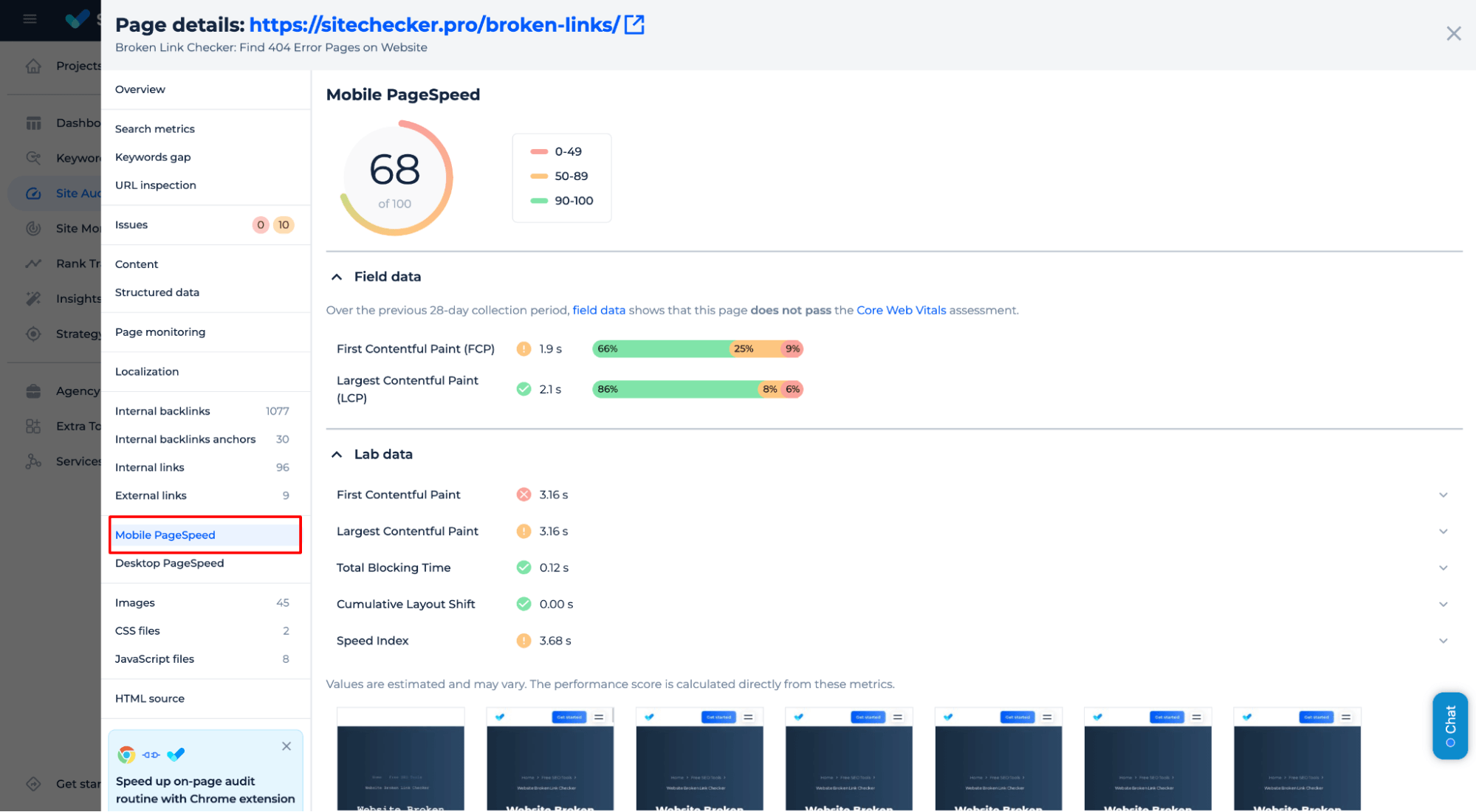
4. Use responsive design tools
Meta Tag Viewport Checker identifies and fixes any real-time issues related to your viewport settings. Sitechecker shows you how the page behaves on different screen sizes and detects errors as you adjust, ensuring your visual content is always visible and optimized for SEO.
Tools like BrowserStack, Responsinator, or Chrome DevTools’ built-in responsive mode can help you test how your page (and media file) looks on different devices and screen sizes.
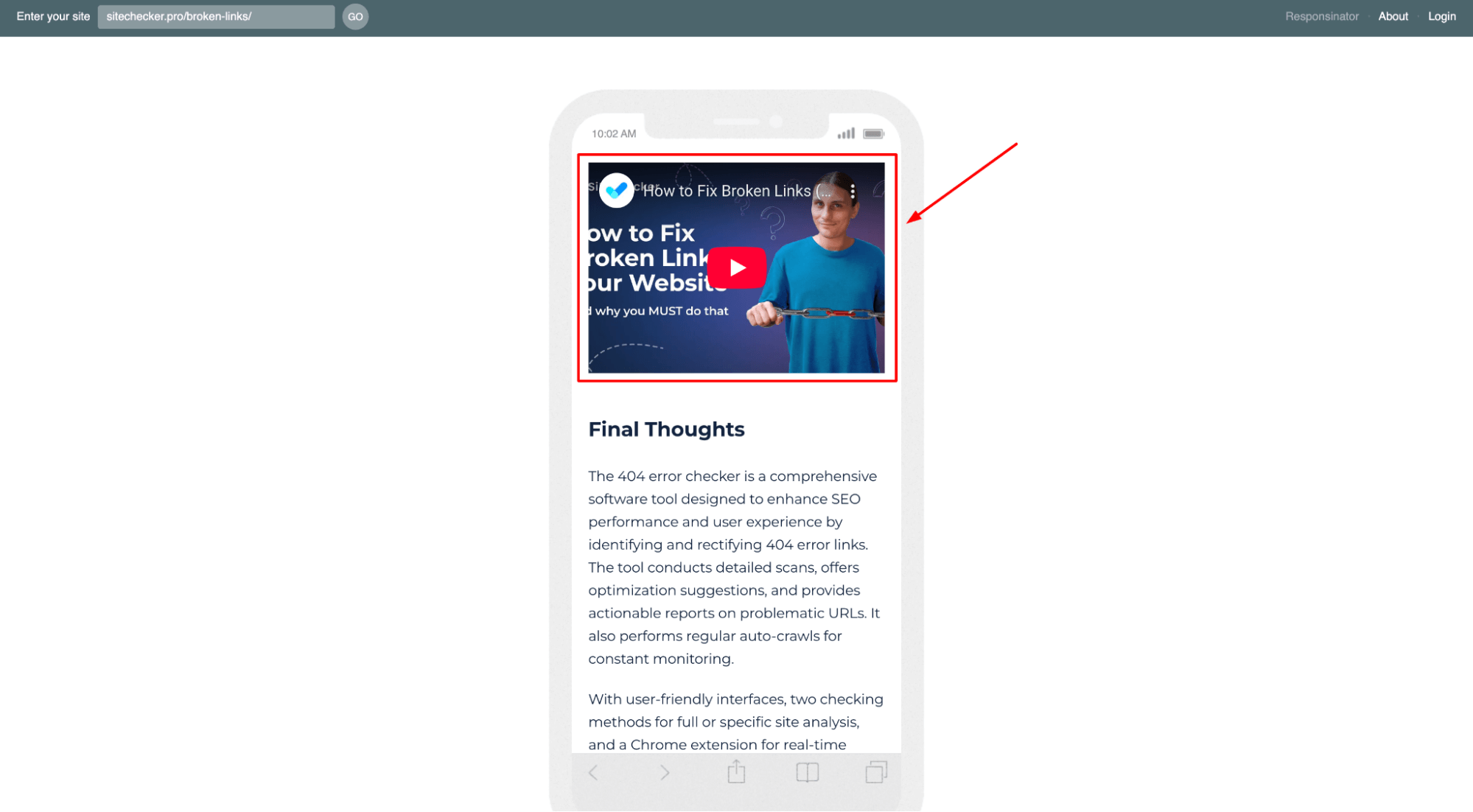
These tools allow you to simulate various devices and check if the video remains visible and properly sized within the viewport.
5. Perform manual checks
Scroll through your page on different devices and observe whether the visual content is positioned outside the viewport or hidden.

If the video does not appear correctly, check your CSS and HTML to ensure it is styled and fully visible on all screen sizes and devices.
Final idea
To resolve the “Video Outside the Viewport” issue, ensure videos are correctly positioned within the viewport for both users and search engines. Factors such as improper CSS, incorrect object-fit, lack of responsiveness, and embed code issues can cause hidden or improperly displayed media files. Use tools like Google Search Console, Chrome DevTools, and BrowserStack to identify, test, and fix these issues. After making the necessary adjustments, validate the fixes by requesting re-indexing in GSC. Follow best practices for video SEO and use Sitechecker to detect viewport-related problems in real-time for optimal results.