When to remove a sitemap from Google Search Console
A site map file helps Google understand your website’s structure, but there are times when it becomes outdated or even counterproductive. Deleting an indexing file isn’t something you do often.
Here are key cases when you should remove a URL mapping file.
Launch Sitechecker’s GSC Dashboard to boost your Search Console reporting!
Expand GSC Data Limits
Bypass Google’s 1,000-row cap and unlock up to 36 months of Search Console history in a single dashboard.
1. The indexing file is outdated
If your sitemap contains outdated URLs, broken pages, or incorrect canonical tags, it can cause confusion for Google’s crawlers. An outdated sitemap can confuse Google, leading to indexing issues or lower rankings. Instead of keeping an inaccurate sitemap, remove it and upload an updated version.
2. A fresh index file has been uploaded
When you generate a new sitemap, you don’t want Google referencing the outdated one. If both versions exist in Search Console, Google may still scan incorrect pages if two indexing files are active, leading to indexing conflicts. To maintain efficient crawling, delete outdated URL directories.
3. Site redesign or migration
A major site update often leads to necessary indexing file updates. If your previous indexing file has dead links, or pages that no longer exist or have been redirected, keeping it active can cause unnecessary crawling and indexing errors. In such cases, removing the old indexing document and submitting a fresh one that reflects the new site structure is essential for a clean transition.
4. The sitemap contains private or sensitive pages
Sometimes, webmasters accidentally include pages in a sitemap that were never meant to be indexed — such as staging URLs, internal dashboards, or other private sections. If you notice sensitive pages in your indexing document, removing it from Search Console is a crucial first step. However, you should also block these pages using robots.txt or add noindex tags to prevent them from being indexed in the future.
5. You no longer want to index certain content
If you’ve removed a section of your website and don’t want it to be crawled anymore, simply deleting the pages isn’t enough. An old sitemap might still signal to Google that those pages exist. In this scenario, removing the sitemap ensures search engines stop looking for content that no longer needs to be indexed.
Is Your Sitemap Hurting SEO? Check Now!
Outdated sitemaps can confuse Google. Scan your site now and remove incorrect sitemaps instantly.
How to remove a sitemap from Google Search Console
If your indexing file no longer serves a purpose, deleting it is the right choice, removing it from Search Console is a simple but important step. While deleting a indexing document won’t immediately stop Google from crawling your site, it helps ensure that search engines are working with the most accurate and updated version of your content. Here’s how to properly remove a sitemap from Search Console.
Step 1: Log in to Google Search Console
1. Go to Google Search Console.
2. Sign in with your Google account that has access to your website’s property.
3. Select the correct website from the property list if you manage multiple sites.
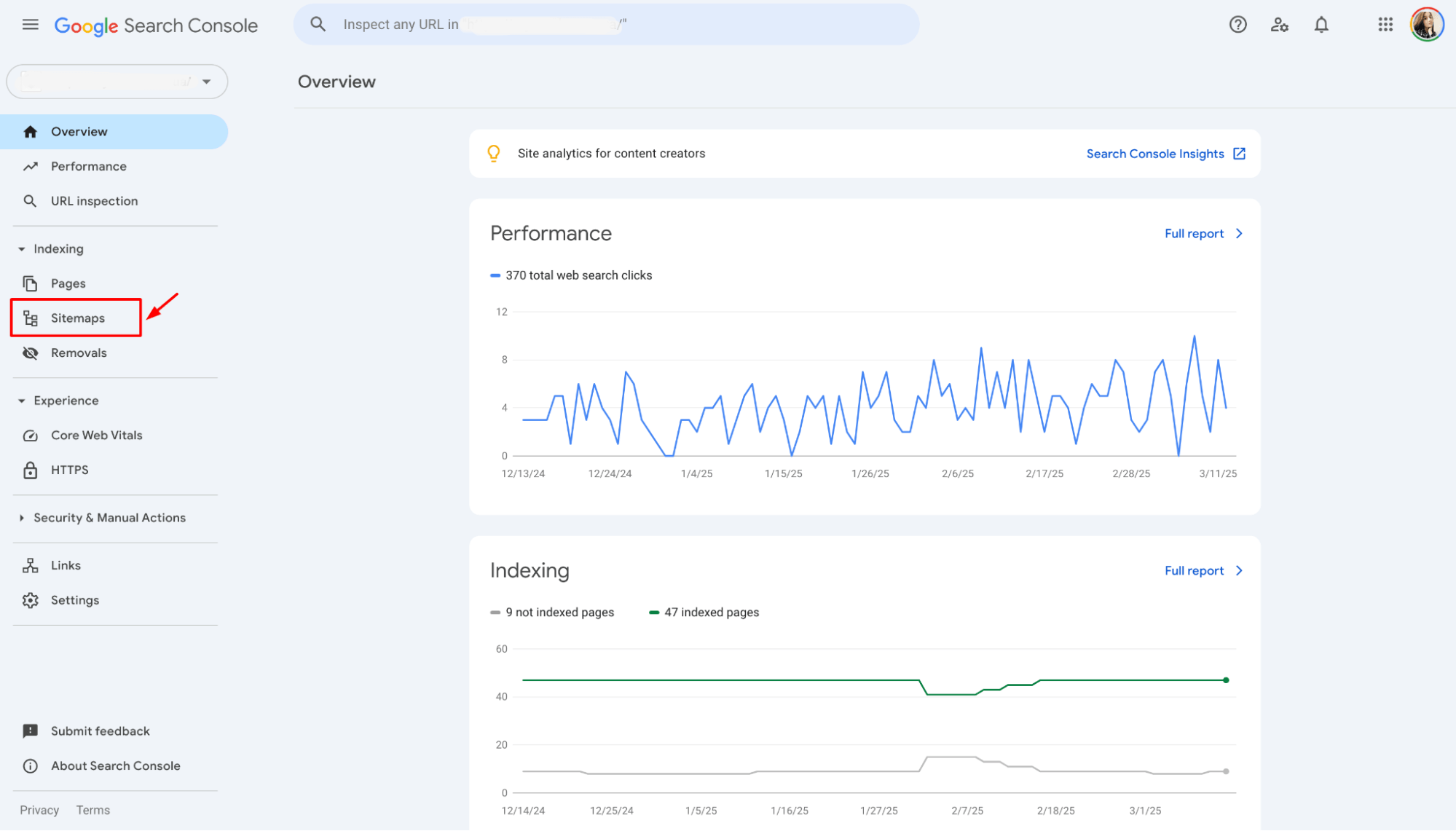
Step 2: Navigate to the sitemaps report
1. In the left-hand menu, click on “Sitemaps” under the Indexing section.
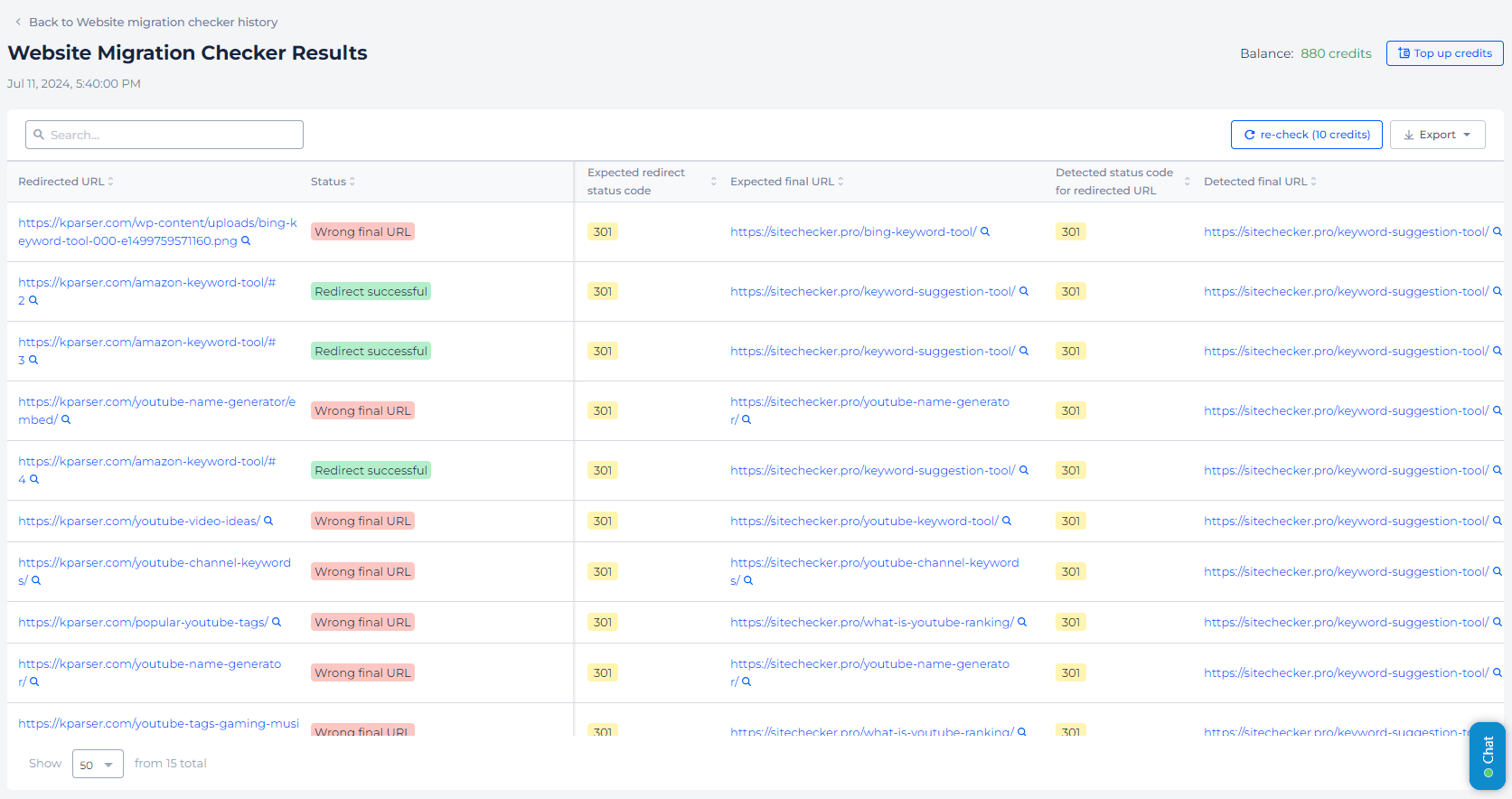
2. Here, you will see a list of all the sitemaps that have been submitted for your site.
Step 3: Find the indexing document you need to delete
1. Find the sitemap you want to remove.
2. Click on the sitemap URL to open its details.
3. Click the “Remove” or “Delete” option (if available).
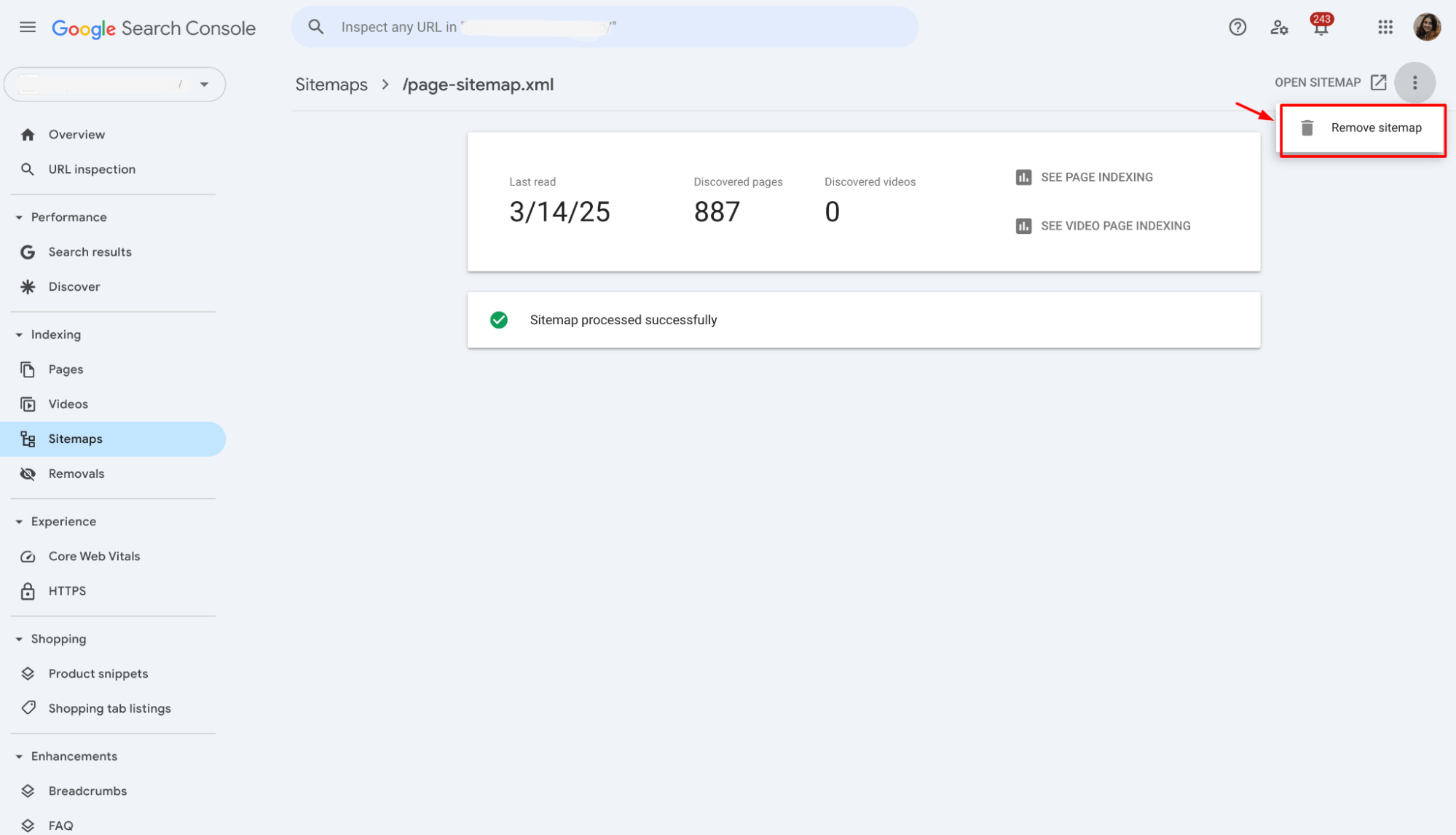
Step 4: Prevent Google from crawling the sitemap again
Simply removing a sitemap from Google Search Console doesn’t prevent Google from continuing to crawl it. To ensure it’s completely ignored, follow these steps:
1. Delete the XML File – If the indexing document is no longer needed, remove it from your server.
Use robots.txt to Block the Sitemap – Add the following rule to your robots.txt file:
Disallow: /sitemap.xml2. Return a 410 Gone Status Code – If users or crawlers attempt to access the old sitemap URL, configuring your server to return a 410 Gone status tells search engines that the file is permanently removed.
Step 5: Upload an updated site index if required
If you’re replacing an outdated sitemap, upload a fresh version:
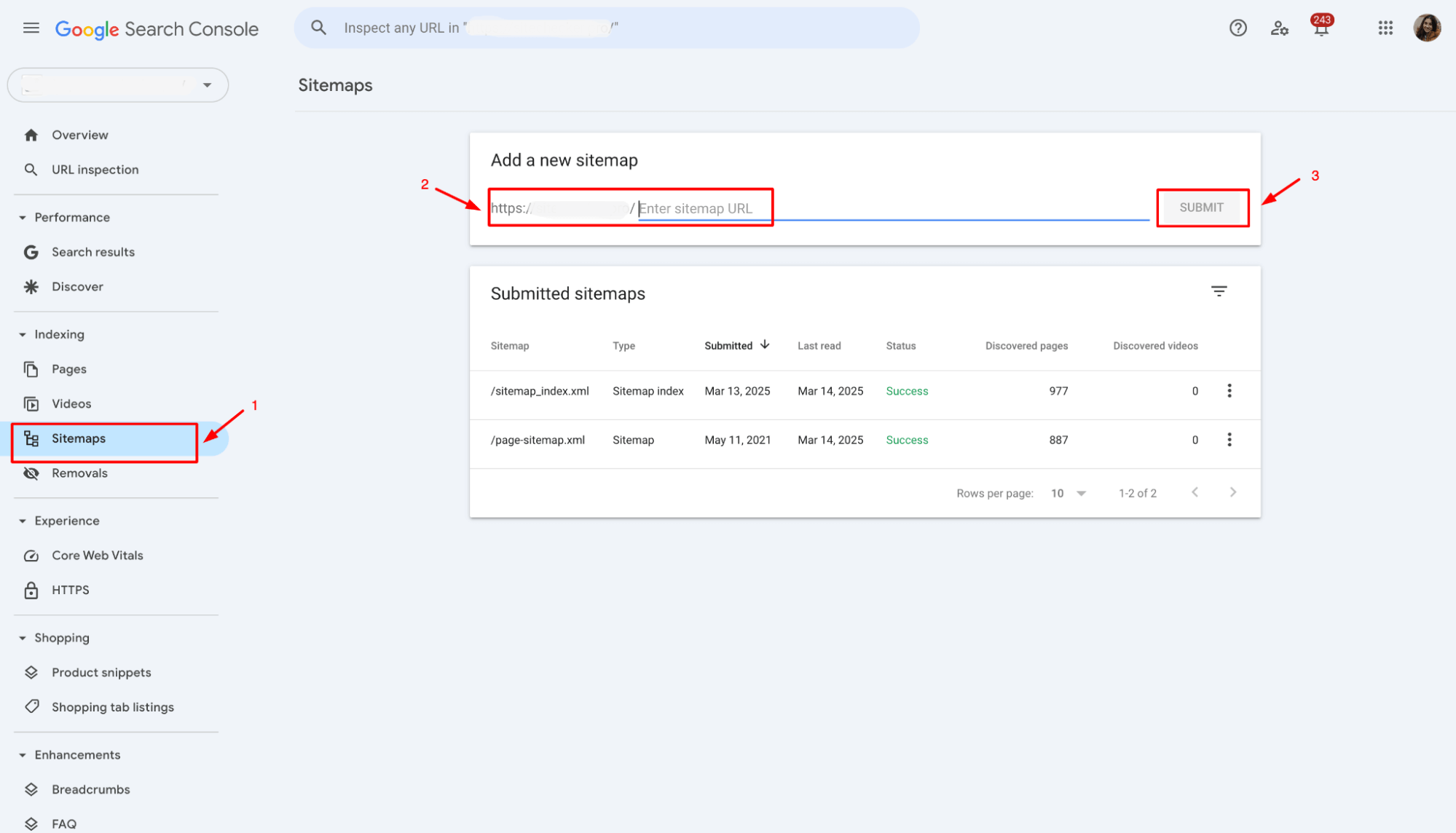
1. Go back to the Sitemaps section in Google Search Console.
2. Enter the new sitemap URL in the “Add a new sitemap” field.
3. Click Submit and allow Google time to process the updated file.
Final thoughts
Removing an XML file from GSC is an important step when making major changes to your website. Whether you’re replacing an old sitemap, cleaning up outdated data, or preventing Google from indexing certain pages, following this process ensures that search engines are working with the most accurate version of your site.