What is a Search Query?
A search query is the combination of words or phrases a user enters into a search engine’s search box. This is essentially the question or request they are posing to the search engine. The search engine then scans its database to find the most relevant web pages that answer or relate to this query. Search queries are crucial because they represent the user’s intent, and understanding this intent is key for optimizing content for search engines.
Types of Search Queries
There are various types of search queries, primarily categorized based on the user’s intent and relevant search results. Understanding these types is fundamental for SEO professionals and content creators to ensure that their content aligns with what users are looking for.
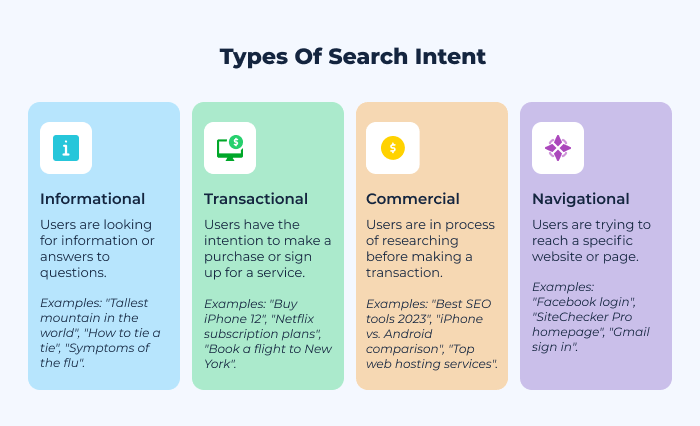
Navigational search queries
Navigational queries are made when a user is trying to locate a specific website or web page they already have in mind. For example, entering “YouTube” or “OpenAI website” into a search engine indicates the user intends to visit these specific sites. They might not know the exact URL, so they use the search engine as a navigation tool.
How to Optimize for Navigational Queries?
- Branding: Ensure your brand name is consistent across all platforms and digital assets.
- URL Structure: Make sure your URL is clean, concise, and relevant.
- Meta Titles and Descriptions: These should clearly identify your site or brand.
- Claim and Optimize Business Listings: For businesses, platforms like Google My Business can help improve visibility for navigational queries.
Informational search queries
Informational queries are made by users looking for information on a topic. Examples include “how to tie a tie” or “symptoms of the common cold.” These queries often start with “how,” “what,” “why,” or “where.”
Tips for Targeting Informational Queries
- Content Creation: Regularly produce high-quality, in-depth content that addresses common questions in your niche.
- Use of Headers: Break your content with relevant H1, H2, and H3 tags to make it scan-friendly.
- Internal Linking: Link to other related articles on your site to keep the user engaged and provide more information.
- Engage with Rich Snippets: Structured data can help your content appear in featured snippets, providing quick answers to user queries.
Transactional search queries
Transactional queries indicate the user’s intent to perform a transaction, like making a purchase. Examples of transactional query include “buy iPhone 13” or “best DSLR cameras for sale.”
Strategies for Transactional Search Queries
- Optimize Product Pages: Ensure product descriptions are clear, detailed, and contain relevant keywords.
- Mobile Optimization: Many transactions are performed on mobile devices. Ensure your site is mobile-friendly.
- Secure Checkout Process: Ensure your website’s checkout process is straightforward and secure to encourage conversions.
- Use of Reviews: Display product reviews prominently, as they can heavily influence purchasing decisions.
Is there a typo in the query? If so, one or multiple?
Search engines have become adept at identifying and autocorrecting typos in queries. But for content creators, understanding common misspellings of keywords can provide an edge. By incorporating these in meta tags or even content (without compromising quality), websites can cater to a wider audience.
Does the query match on the first letter? Does it match the whole word or only partially?
Partial word matches can indicate a user’s unfamiliarity with a topic or that they’re in the early stages of research. On the other hand, precise matches may indicate a user with a clear understanding or intent.
Does a word in the query match a synonym?
Synonyms in search queries suggest that users might use different terminologies to describe the same thing. For instance, someone might search for “sofa” while another might use “couch.”
Does the query match the title of a record or its description?
Users often search with precise terms they’ve encountered before, either from a previous search, a recommendation, or offline sources. Matching queries with titles or descriptions can indicate a higher intent.
Is one item more popular than another?
Search volume can hint at popularity. For e-commerce sites, if a particular product gets more queries, it might be trending or in-demand.
Google About the Search Queries
John Mueller, a Webmaster Trends Analyst at Google, has tweeted about search queries on several occasions. Here are some of his key takeaways:
Overall, Mueller’s tweets on search queries suggest that Google is focused on the quality of the content and the user experience. Google wants to make sure that users are able to find the information they need quickly and easily, regardless of how they search.
Crafting Content for Search Intent
Aligning content with search intent is fundamental in ensuring users find value in what you offer, leading to higher engagement rates, better conversion, and improved search rankings. This alignment requires strategic planning and a deep understanding of your target audience.
Choose relevant keywords
The foundation of search intent lies in keywords. These are the terms users input into search engines, seeking answers or solutions.
- Importance: Keywords serve as bridges connecting user queries with relevant content. If you select and target the right keywords, you’ll attract the right audience.
- Keyword Research: Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to identify high-volume and low-competition keywords relevant to your niche.
- Long-tail Keywords: While broad keywords have high search volume, long-tail keywords (longer and more specific keyword phrases) cater to more specific user intent and often have a higher conversion rate.
Create quality content to appear in more search queries
While keywords get users to your page, quality content keeps them engaged.
- Engaging and Relevant: Ensure your content directly answers the questions posed by the search query.
- Depth and Breadth: Cover topics in-depth and offer comprehensive insights to become an authoritative source.
- Freshness: Regularly update content to keep it current and relevant.
- Multimedia Elements: Incorporate images, infographics, and videos to enhance user experience and engagement.
Website Optimization for Better Search Performance
While great content attracts users, the technical aspects of your website determine how search engines perceive its value. Ensuring your website is optimized for performance can greatly influence your search rankings.
- Page Load Speed: Slow-loading pages can deter users and negatively impact rankings. Utilize tools like Google’s PageSpeed Insights to assess and improve load times.
- Mobile Optimization: With a significant number of users accessing content via mobile devices, having a mobile-responsive website is paramount.
- Secure and Accessible Website: Implementing HTTPS is not just about security but also about trust and search performance.
- Clear URL Structure: URLs should be concise, descriptive, and easy for search engines to crawl.
- Internal Linking: Strategically linking to related content on your site can enhance user experience and help search engines understand content context.
This video demonstrates how to utilize the Search Queries feature within Google Webmaster Tools to enhance your website.
Conclusion
Understanding and optimizing for search intent has become a cornerstone in the ever-evolving digital landscape. At its core, it’s about recognizing the needs and desires of online searchers and delivering content that directly addresses those needs. By closely aligning your content with search intent and ensuring your website performs at its best, you position yourself to not only attract but also retain and convert visitors. As the digital world continues to grow and shift, keeping a keen eye on user behavior and adapting accordingly will always remain a vital strategy for online success.