What are Orphan Pages?
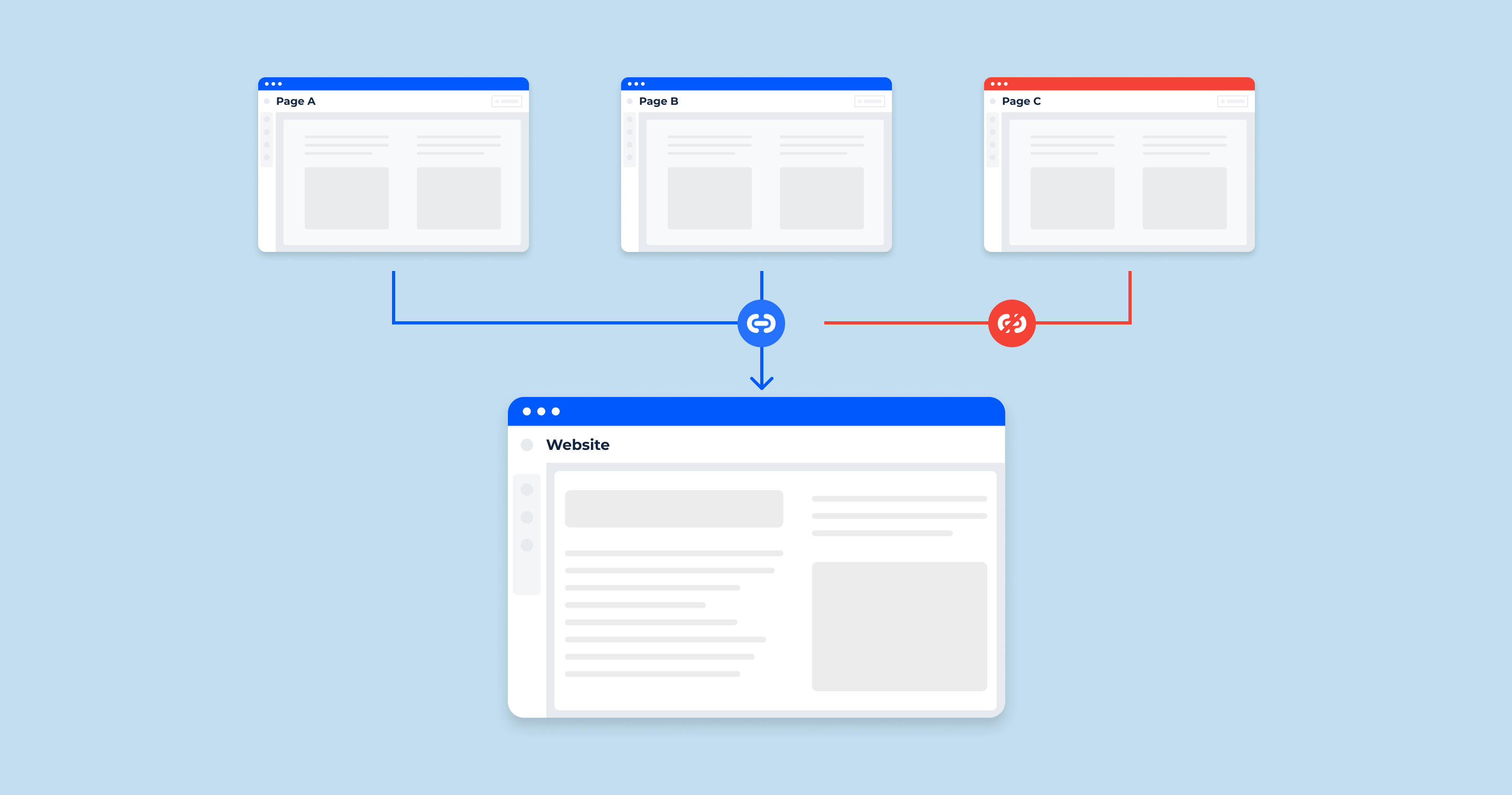
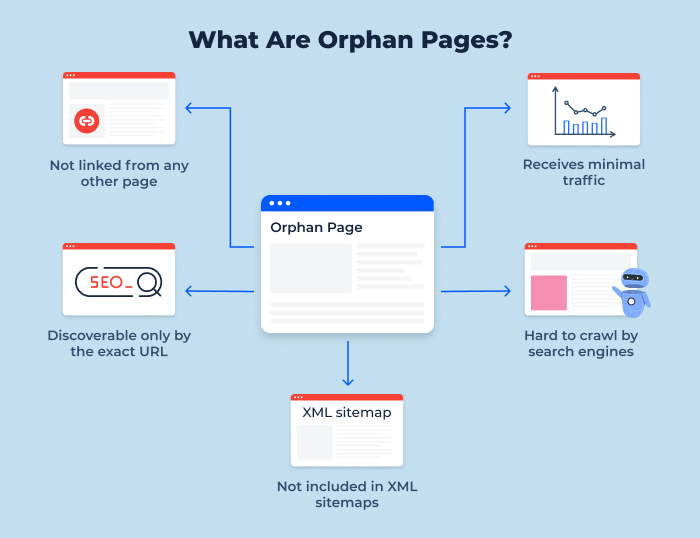
Orphan pages, in the context of website management and search engine optimization (SEO), refer to web pages that exist on a website but are not linked to from any other page within the same website. In other words, these pages are isolated, disconnected, and do not form part of the website’s navigational structure.
Orphan pages are a common issue that can have significant implications for your website’s SEO performance. When search engines like Google crawl your site, they rely on links to discover and index pages. If a page has no internal links pointing to it, it becomes challenging for search engines to find and index that page. This can result in the page not appearing in search engine results pages (SERPs) or receiving very little organic traffic.
To illustrate, think of your website as a network of interconnected roads, and each web page as a destination along those roads. Internal links act as the road signs and directions that guide both users and search engines to these destinations. Orphan pages are like hidden gems in this network, without any road signs pointing to them. As a result, they often remain undiscovered.
Orphan pages can take various forms. They might be:
- Outdated Content: Pages that were once relevant but have become outdated and are no longer linked from the main website.
- Test Pages: Pages created for testing purposes that were never integrated into the site’s structure.
- Unlinked Blog Posts: Blog posts that were published but were not linked from other related content.
- Product Pages: Product pages that were added but not integrated into the site’s product catalog or category pages.
- Legacy Pages: Older pages that were once part of the site’s structure but were removed or deprecated without updating internal links.
In summary, orphan pages are a hidden aspect of your website that can negatively impact SEO efforts. Identifying and addressing these pages is crucial for ensuring that your entire website is accessible to search engines and users, ultimately helping to improve your site’s visibility in search results and the overall user experience.
In the following sections, we will explore why orphan pages are a concern for SEO, how to identify them, and most importantly, how to fix and prevent them effectively.
Orphan vs. Dead End Pages
When discussing issues related to website structure and SEO, it’s essential to differentiate between orphan pages and dead-end pages, as they are related but not the same.
Orphan Pages:
- Orphan pages, as mentioned earlier, are pages that are not linked to from any other page within the same website. They exist in isolation within your site’s structure.
- Search engines may have difficulty discovering and indexing orphan pages because they lack internal links that act as pathways for crawling.
- Orphan pages can be overlooked during routine site maintenance and content updates, potentially resulting in missed SEO opportunities.
Dead-End Pages:
- Dead-end pages, on the other hand, are pages that do not provide a clear path for users or search engine crawlers to navigate further into your website.
- While dead-end pages may not necessarily be orphaned (they could still be linked from other pages), they often lack calls-to-action, internal links, or navigation elements that guide users to other parts of the site.
- Dead-end pages can lead to poor user experiences and high bounce rates, as visitors may leave the site after viewing these pages, finding nowhere else to go.
Key Differences:
- Orphan pages are primarily a concern for search engine indexing and may not directly impact user experience.
- Dead-end pages impact user experience, potentially leading to a loss of engagement and conversions.
- Addressing orphan pages is crucial for SEO, while dealing with dead-end pages is essential for improving user engagement and reducing bounce rates.
In summary, both orphan pages and dead-end pages should be addressed in your website management strategy. Orphan pages impact SEO by hindering search engine discovery, while dead-end pages affect the user experience by discouraging further exploration of your site. By understanding the differences between these issues, you can effectively address them to enhance your website’s overall performance and SEO rankings.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into strategies for identifying and resolving both orphan pages and dead-end pages to ensure a well-optimized and user-friendly website.
What Causes Orphan Pages?
Orphan pages can be the result of various factors and issues within your website’s structure and content management. Understanding these causes is crucial for both identifying and preventing orphan pages. Let’s explore some common causes:
Common Causes of Orphan Pages and How to Resolve Them
Non-Canonical https/http or www/non-www
One common cause of orphan pages is related to the canonicalization of URLs. Canonicalization refers to the process of selecting the preferred version of a URL when multiple variations exist. This issue typically arises in the following scenarios:
- HTTP vs. HTTPS: If your website serves content through both HTTP and HTTPS, search engines may see these as separate versions of the same page. This can lead to one version being indexed while the other remains orphaned.
- www vs. non-www: Similarly, if your site is accessible via both www and non-www URLs (e.g., “www.example.com” and “example.com”), it can create confusion for search engines. They might index one version and not the other.
Resolving Non-Canonical Issues:
- Choose a Preferred Version: Decide whether you want to use HTTP or HTTPS and whether you prefer www or non-www URLs. This should be based on your site’s security and your branding preferences.
- Implement 301 Redirects: Once you’ve decided on your preferred version, set up 301 redirects to ensure that all variations of your URLs (including non-preferred ones) redirect to the canonical version. This helps consolidate link equity and prevents orphan pages.
Trailing Slashes
Trailing slashes refer to the forward slash (/) that sometimes appears at the end of a URL. Inconsistent use of trailing slashes can lead to orphan pages because search engines may treat URLs with and without trailing slashes as distinct pages.
For example, “example.com/page” and “example.com/page/” can be seen as separate URLs, resulting in one version being indexed while the other remains orphaned.
Resolving Trailing Slash Issues:
- Choose a Consistent Format: Decide whether you want URLs to end with a trailing slash or without it. This should be based on your site’s structure and preference.
- Implement Redirects: Set up redirects to ensure that URLs consistently follow your chosen format. If a user or search engine accesses a URL in the non-preferred format, they should be automatically redirected to the preferred version.
By addressing these common causes of orphan pages, you can significantly improve your website’s SEO performance and ensure that all of your valuable content is accessible and indexable by search engines.
In the following sections, we will explore additional strategies for identifying and resolving orphan pages and maintaining a well-structured website.
Why are Orphan Pages Bad for SEO?
Orphan pages can be detrimental to your website’s search engine optimization (SEO) efforts. While they might seem harmless at first glance, they can have several negative impacts on your site’s overall performance in search engine rankings. Here are key reasons why orphan pages are bad for SEO:
| Poor Indexation | Orphan pages often go unnoticed by search engine crawlers because they lack internal links. As a result, these pages may not get indexed in search engine databases. If a page isn’t indexed, it won’t appear in search engine results, effectively making it invisible to potential visitors. |
| Reduced Visibility | When your web pages don’t appear in search results, you miss out on valuable organic traffic. This can result in fewer visitors to your site and, consequently, reduced opportunities for engagement, conversions, and revenue generation. |
| Weakened Authority | Search engines assess the authority and relevance of web pages based on various factors, including the number and quality of internal and external links pointing to them. Orphan pages miss out on internal linking, which means they may not accumulate the authority that linked pages do. This can impact their ability to rank for relevant keywords. |
| Inefficient Crawl Budget Allocation | Search engines allocate a limited amount of time, known as the crawl budget, to crawl and index your website. Orphan pages consume a portion of this crawl budget without contributing to your site’s visibility. This inefficient allocation can affect the indexing of important pages and new content. |
| User Experience Issues | While orphan pages primarily affect SEO, they can indirectly harm the user experience. When users land on an orphan page, they may feel lost and frustrated if they can’t easily navigate to other relevant content on your site. This can result in high bounce rates and a negative perception of your website. |
| Missed Conversion Opportunities | Orphan pages may contain valuable content or offers that could convert visitors into customers or leads. When these pages remain isolated, your site misses out on potential conversion opportunities, impacting your business goals. |
| Content Silos and Lack of Context | Orphan pages disrupt the natural flow and organization of your website’s content. A well-structured website should guide users through a logical sequence of content. Orphan pages disrupt this flow and hinder users from finding related information. |
Orphan pages represent an SEO challenge that can limit the visibility, authority, and overall performance of your website. To mitigate these issues, it’s crucial to identify and address orphan pages as part of your website maintenance and SEO strategy. In the following sections, we will explore how to find and fix orphan pages, ensuring that your website is fully optimized for search engines and user engagement.
How to Find Orphan Pages
Identifying orphan pages on your website is a crucial step in optimizing your site’s SEO performance. By finding these isolated pages, you can take action to ensure they are properly integrated into your website’s structure and benefit from improved search engine visibility. Here are four steps to help you find orphan pages:
1. Find crawlable URLs
The first step in identifying orphan pages is to determine all the crawlable URLs on your website. This involves creating a comprehensive list of all the pages that search engine crawlers can potentially access. You can do this by using website crawling tools or by examining your website’s sitemap if one is available.
Here’s how to find crawlable URLs:
- Use SEO crawling tools like Orphan Page Checker to crawl your website and generate a list of all accessible URLs.
- Alternatively, you can manually inspect your website’s sitemap or use the “site:” operator in Google (e.g., “site:yourwebsite.com”) to see the pages that Google has indexed.
2. Find URLs with hits (Including Google Analytics)
Once you have a list of crawlable URLs, the next step is to identify which of these pages have received traffic or hits. This information is crucial because orphan pages might still receive organic traffic even if they are not linked internally. Here’s how to find URLs with hits:
- Utilize web analytics tools like Google Analytics to track the performance of individual pages on your website. Look for pages that have received traffic over a specific time period.
- Identify pages with sessions, pageviews, or other engagement metrics. These pages are likely not orphaned but may still need proper internal linking.
3. Cross-reference the two URL sources
Now that you have a list of crawlable URLs and pages with hits, it’s time to cross-reference these two sources. This step will help you pinpoint which pages are both crawlable and have received traffic. These pages are not orphaned and are likely part of your website’s existing structure.
- Compare the list of crawlable URLs with the list of pages with hits. Pages that appear on both lists are not orphaned and can be considered part of your site’s structure.
- Focus your attention on the pages that are in the list of crawlable URLs but do not appear in the list of pages with hits. These are potential orphan pages.
4. Other Places to Look for Orphan URLs
In addition to the above steps, consider checking other areas of your website where orphan pages might exist:
- Robots.txt File: Review your website’s robots.txt file to ensure that it is not inadvertently blocking search engine crawlers from accessing certain pages.
- XML Sitemap: Examine your XML sitemap to see if it includes all important pages. An up-to-date sitemap can help search engines discover your content more efficiently.
- Internal Search Queries: Analyze internal search queries on your website to see if users are searching for pages that are not easily accessible through navigation. These pages may need better internal linking.
By following these steps and thoroughly examining your website, you can identify orphan pages and take the necessary actions to integrate them into your site’s structure for improved SEO and user experience.
How to Fix Orphan Pages
Once you’ve identified orphan pages on your website, it’s essential to take action to address these issues. Fixing orphan pages not only enhances your website’s SEO but also improves the overall user experience. Here are several strategies to consider for fixing orphan pages:
Internally link
One of the most effective ways to address orphan pages is by creating internal links to them from other relevant pages within your website. Internal linking connects the isolated pages to the broader site structure, allowing search engines to discover and index them more easily.
Here’s how to use internal linking to fix orphan pages:
- Identify Relevant Anchor Text: Choose anchor text that accurately describes the content of the orphan page. This text should be relevant to both the source page and the target orphan page.
- Contextual Links: Integrate internal links naturally within the content of your pages. These contextual links provide valuable information to users and search engines.
- Navigation Menus: Include links to orphan pages in your website’s navigation menus or footer, ensuring that users can access them easily.
- Sitemaps: Update your website’s XML sitemap to include the orphan pages. Submit the updated sitemap to search engines to help them discover the pages more efficiently.
Noindex
In some cases, you may decide that certain orphan pages should not be indexed by search engines. This can be a valid strategy if the content on these pages is redundant, low-quality, or not relevant to your site’s overall goals. Adding a “noindex” tag to these pages informs search engines not to include them in search results.
Here’s how to use the “noindex” tag to address orphan pages:
- Meta Robots Tag: Add a meta robots tag with the “noindex” directive to the HTML header of the orphan page. This tells search engines not to index that specific page while allowing them to crawl it.
- Robots.txt: Alternatively, you can use the robots.txt file to disallow indexing of the orphan page. However, keep in mind that using robots.txt prevents search engines from crawling the page altogether.
Merge/consolidate
If you have multiple orphan pages with similar or overlapping content, consider merging or consolidating them into a single, comprehensive page. This can improve the overall quality of your content and reduce the number of orphaned pages.
Here’s how to merge or consolidate orphan pages:
- Content Audit: Review the content of all orphan pages and identify common themes or topics.
- Choose a Primary Page: Select one page to serve as the primary source for that topic. This page should be the most comprehensive and well-optimized.
- Redirects: Set up 301 redirects from the other orphan pages to the primary page. This ensures that users and search engines are directed to the consolidated content.
Delete
In cases where orphan pages are outdated, irrelevant, or no longer serve a purpose, consider deleting them from your website. Removing unnecessary pages can streamline your site’s structure and improve user experience.
Here’s how to safely delete orphan pages:
- Backup: Before deleting any pages, ensure that you have a backup of the content in case it needs to be restored in the future.
- 301 Redirects: If the deleted page had any external backlinks or received traffic, implement 301 redirects to relevant, existing pages to preserve link equity and prevent 404 errors.
- Remove from Sitemap: Update your XML sitemap to exclude the deleted pages and submit the updated sitemap to search engines.
By following these strategies, you can effectively fix orphan pages on your website, improving both SEO and user experience. Be sure to monitor the impact of your actions on search engine rankings and user engagement to ensure positive results.
How to Prevent Orphan Pages
Preventing orphan pages is essential for maintaining a well-organized and SEO-friendly website. By implementing proactive strategies, you can reduce the likelihood of orphaned content appearing in the first place. Here are some effective methods for preventing orphan pages:
Have a plan for site migrations
Site migrations, which can involve changes in domain names, CMS platforms, or structural overhauls, are common triggers for orphan pages. Having a well-thought-out plan for site migrations can help minimize the risk of creating orphaned content during the process.
Here’s how to prevent orphan pages during site migrations:
- Inventory and Mapping: Before the migration, create a comprehensive inventory of all existing URLs on the old site. Map each old URL to its corresponding new URL on the new site. This ensures that every page has a clear destination.
- 301 Redirects: Implement 301 redirects from old URLs to their new counterparts. This not only preserves SEO value but also prevents pages from becoming orphans during the migration.
- Crawl and Test: Use crawling tools to verify that all old URLs redirect correctly to the new site. Test the redirects to ensure they are functioning as intended.
Set up your site structure for success
A well-structured website from the beginning is the foundation for preventing orphan pages. Design your site structure with a logical hierarchy and user-friendly navigation to minimize the chances of content isolation.
Here’s how to set up your site structure to prevent orphan pages:
- Clear Hierarchy: Organize your website content into clear categories and subcategories. Ensure that each page has a place within this hierarchy, making it easy for users and search engines to navigate.
- Internal Linking: Establish a system of internal linking that connects related pages. Ensure that every page has links to other relevant content, guiding users and search engine crawlers through your site.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular content audits to identify outdated or redundant pages. Remove or update these pages as needed to maintain a streamlined structure.
By implementing these prevention strategies, you can maintain a well-structured website that minimizes the risk of orphan pages appearing in the first place. Preventing orphan pages not only improves SEO but also enhances the user experience, making your website more user-friendly and efficient.
Check Your Website for Orphan Pages with Orphan Page Checker
The Orphan Page Checker tool is an invaluable asset for website owners and digital marketers seeking to optimize their online presence. An orphan page, being a page that isn’t linked to from any other page on the same website, often remains unnoticed and receives minimal traffic. By identifying these overlooked pages, the tool helps to unveil potential areas of content that can be optimized or linked to, enhancing site navigation and SEO.
Beyond its primary function, the Orphan Page Checker offers an array of additional features tailored to enhance user experience. It not only pinpoints the orphaned pages but also provides insights on how to effectively integrate them into your site’s structure. By leveraging this tool, users can ensure a cohesive internal linking strategy, improving page authority, user experience, and ultimately boosting organic traffic. Don’t let valuable content go to waste; utilize this tool to maximize your site’s potential!
Discover all the Orphan Pages!
Use our Orphan Page Checker to uncover, link, and boost them to the forefront.
Conclusion
Orphan pages can be a hidden hindrance to your website’s SEO and user experience. These isolated pages often go unnoticed, leading to missed opportunities for engagement and conversions. However, with a systematic approach, you can not only identify and fix orphan pages but also prevent them from occurring in the first place.
Remember, internal linking, strategic planning for site migrations, and a well-structured website hierarchy are your allies in the fight against orphan pages. Regular maintenance and content audits are key to keeping your website in top shape.
By taking proactive measures to address and prevent orphan pages, you can ensure that your website is not only visible to search engines but also provides a seamless and user-friendly experience, ultimately boosting your online presence and achieving your SEO goals.