What is the Text to HTML Ratio?
The text to HTML ratio refers to the amount of actual readable text present in a web page compared to the amount of HTML code on the same page. Expressed as a percentage, this ratio can be calculated using the following formula:
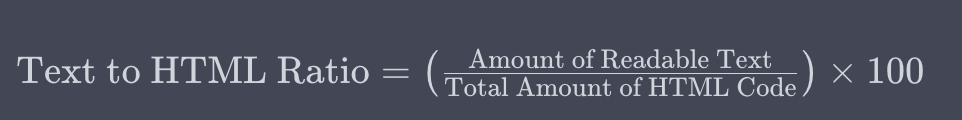
For example, if a web page contains 500 characters of readable text and 1000 characters of HTML code, the text to HTML ratio would be 50%.
It’s essential to understand that this ratio doesn’t exclusively image tags that represent the visible content like paragraphs or headings. Instead, it includes all the readable text within the HTML code, such as content within the meta tags, alt attributes for images, and even scripts.
But why is this ratio important? In the realm of web development and search engine optimization (SEO), the text to HTML ratio is considered by some as a factor that can influence a website’s quality and relevance. Websites with a higher text to HTML ratio are often seen as containing more valuable, content-centric material as opposed to those dominated by excessive HTML code itself, which may be heavy with design elements, scripts, or unnecessary divs.
However, while the text to HTML ratio can provide insights about the structure and content quality of a website in search results, it’s essential to view it in conjunction with other metrics and not in isolation. It’s just one of many factors that contribute to the overall user experience and search engine performance of a site.
In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into the ideal text to HTML ratios, how they may affect SEO, and how to optimize them for the best outcomes.
Remember, the exact relevance and importance of the amount of text to HTML ratio can vary based on evolving SEO best practices, so it’s always good to stay updated with the latest trends and recommendations.
What is the Best Text to HTML Ratio?
Determining the “best” text to HTML ratio is a subject that has been a topic of debate among web developers and SEO experts. The ideal code to text ratio isn’t set in stone, and it can vary based on the nature of the website, its audience, and its content. However, there are some general guidelines and considerations to keep in mind:
| General Benchmark | While there isn’t a universally accepted “perfect” ratio, many SEO professionals recommend aiming for a text to HTML ratio between 25% to 70%. This range suggests that the website has a balanced amount of content compared to its HTML structure. |
| Content-Heavy Sites | For websites that are content-centric, like blogs or news platforms, a higher text to HTML ratio might be desirable. This means that there’s a substantial amount of readable content relative to the HTML code, emphasizing the content’s value and relevance. |
| Design-Heavy Sites | Websites with extensive design elements, interactive features, or multimedia content might naturally have a lower text to HTML ratio. It’s essential to ensure that these design elements enhance user experience rather than impede it. |
| Mobile Optimization | With the increasing importance of mobile browsing, having excessive HTML can slow down page load times on mobile devices. A higher text to HTML ratio can be beneficial for mobile optimization, ensuring faster loading times and better performance. |
| Avoid Fluff Content | While having more text relative to HTML might seem beneficial, it’s crucial that the content adds value. Simply adding fluff or filler content to increase the ratio can be counterproductive, as search engines prioritize high-quality, relevant content. |
| SEO Considerations | Search engines don’t explicitly use the text to HTML ratio as a ranking factor. However, pages heavy with unnecessary HTML, scripts, or non-content elements might be viewed as less relevant or user-friendly. |
| Tools and Analysis | There are numerous online tools available that can help webmasters analyze their website’s text to HTML ratio. Regularly checking and optimizing this metric can offer insights into potential areas of improvement. |
In conclusion, while the text to HTML ratio can provide a snapshot of a site’s structure and content depth, it’s not an end-all metric. The focus should always be on delivering high-quality, relevant content in a user-friendly format. Rather than obsessing over achieving a specific ratio, webmasters should aim to strike a balance that best serves their audience’s needs and ensures optimal website performance.h2 How does text to HTML ratio affect SEO?
What are the Most Prominent Benefits of High Text to HTML Ratio?
A high text to HTML ratio signifies that a webpage contains a significant proportion of actual content relative to its HTML markup. This ratio can be indicative of the content’s quality and the efficiency of the webpage’s structure. While it’s crucial not to view this amount to code ratio as the sole benchmark for a website’s quality or efficiency, there are undeniable advantages associated with maintaining a relatively high text to HTML ratio:
- Boosted Page Performance: Pages with a higher text to HTML ratio generally have less superfluous code. This streamlined code can result in faster page loading times, which is beneficial for both user experience and search engine rankings.
- Enhanced User Experience: A webpage that emphasizes content over excessive design elements or unnecessary markup often offers a clearer, more direct user experience. Readers can focus on the content without being distracted by redundant elements.
- SEO Benefits: While the text to HTML ratio isn’t a direct ranking factor for search engines, a clean codebase can have indirect SEO advantages. Efficient coding can lead to quicker page load times, a factor that search engines consider. Additionally, a content-rich page might be deemed more valuable, thereby earning higher organic rankings.
- Mobile Optimization: In today’s mobile-centric browsing environment, ensuring web pages load efficiently on mobile devices is paramount. Pages with a higher text to HTML ratio are often more mobile-friendly, leading to better mobile user experiences and potentially lower bounce rates.
- Greater Accessibility: Simplified page structures, often evident in pages with high text to HTML ratios, tend to be more accessible. Such pages are better suited for screen readers and other assistive technologies, fostering inclusivity for users with disabilities.
- Content Emphasis: A high ratio often signals a focus on delivering substantial and valuable content. This can enhance the website’s credibility, positioning it as a reliable resource or authority in its domain.
- Reduced Server Load: Excessive or redundant code can strain server resources, especially during high traffic periods. Efficiently coded pages, indicated by a high text to HTML ratio, can be less taxing on servers, ensuring smoother performance.
- Economical Bandwidth Usage: For both website owners and users, especially those with limited bandwidth or data plans, efficiently structured pages can consume less data, leading to cost savings.
- Future-Proofing: A clean and efficient codebase can make future updates or redesigns easier. Web developers can navigate and modify the structure without wading through redundant or outdated code.
In a nutshell, a high text to HTML ratio, while not the definitive measure of quality, can offer several advantages ranging from improved user experience to potential SEO gains. It’s essential, however, to prioritize genuine content quality and user-centric design over merely chasing a specific text ratio.
How to Optimize Text to HTML Ratio for Better SEO?
Optimizing Text to HTML Ratio
Achieving an optimal text to HTML ratio isn’t just about improving a numerical value; it’s about ensuring your webpage is efficiently structured and content-centric. Here are some strategies to optimize this ratio:
| Minimize Unnecessary HTML | This might seem obvious, but many sites have redundant divs, spans, and other elements. Streamlining your code by removing these can improve your ratio. |
| Compress Inline CSS and JavaScript | Rather than having extended CSS or JS directly in your HTML, utilize external files. If it’s essential to keep them inline, ensure they’re compressed and as concise as possible. |
| Utilize Content Effectively | Instead of overloading your site with heavy media or unnecessary design elements, focus on delivering quality content. Remember, the text in this ratio refers to valuable, readable content, not just any text. |
| Opt for CSS Image Sprites | If you’re using multiple images or icons, consider using CSS image sprites. This can reduce the amount of code needed to display each image individually. |
| Regularly Audit Your Code | Tools like the W3C’s Markup Validation Service can help identify and eliminate unnecessary or redundant code. |
| Avoid Inline Styling | Inline styles can add a significant amount of code to your pages. Where possible, move styling to external CSS files. |
| Use Semantic HTML | This means using HTML elements for their intended purpose, which can result in cleaner and more efficient code. |
| Minify HTML, CSS, and JavaScript | Minification removes all unnecessary characters from code without changing its functionality, leading to a leaner codebase. |
By optimizing your text to HTML ratio, you’re not just chasing a metric but ensuring that your site is effectively structured, content-focused, and user-friendly, leading to better user experience and potentially improved SEO.
Website Directory Scanner to Discover Site Directory Structure
The Text to HTML Code Ratio Checker tool from SiteChecker is an insightful utility for web developers and SEO experts aiming to optimize their web pages. A balanced text-to-HTML ratio can contribute to better user experiences and potentially affect search engine rankings. This tool analyzes the content of a webpage and provides a quick measurement of the visible text volume compared to the underlying HTML code — a metric often used as an indicator of a page’s cleanliness and efficiency.
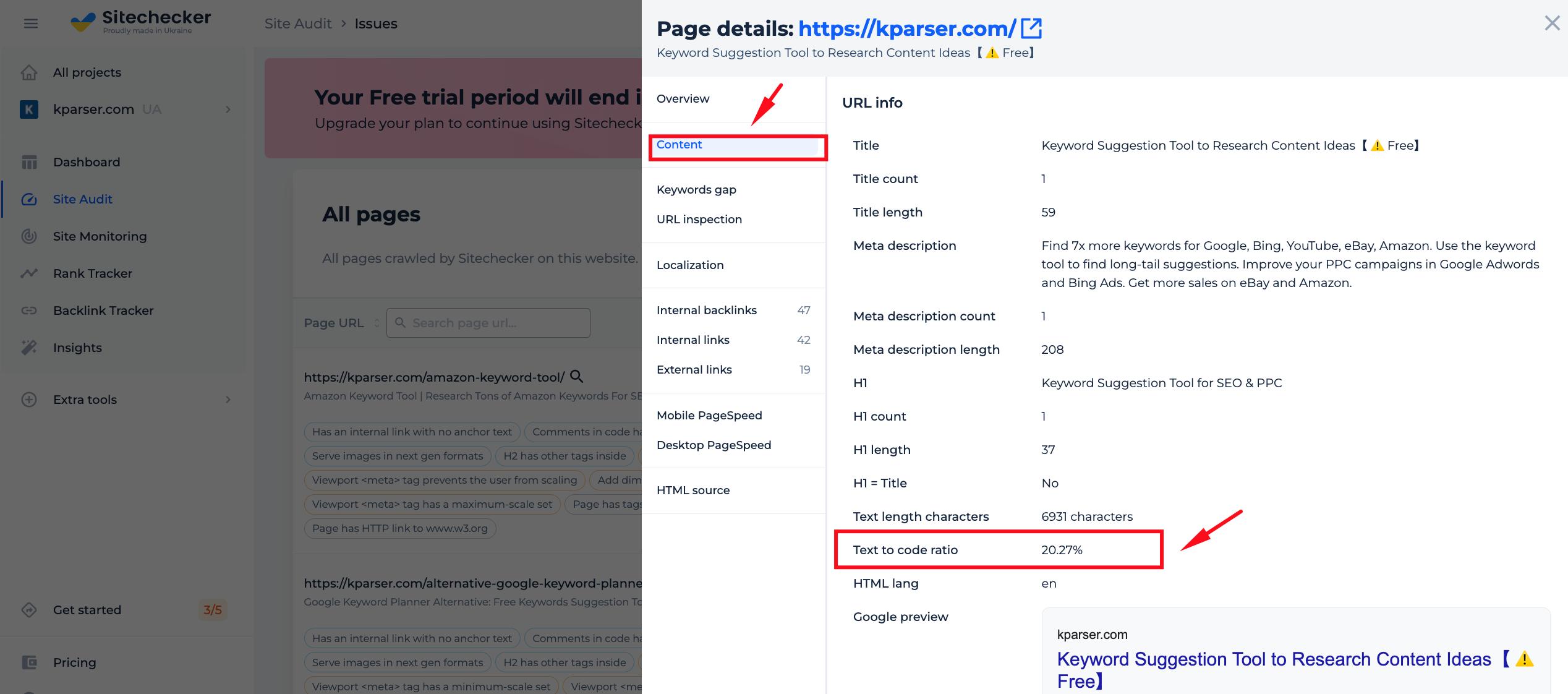
Beyond the basic ratio calculation, this tool offers a deeper examination of the elements constituting the webpage. It identifies excessive code or HTML bloat that may be slowing down your site and recommends areas for optimization. By providing a detailed breakdown of the text and code elements, the Text to HTML Code Ratio Checker is invaluable for those looking to refine their website’s performance, ensure faster load times, and improve overall site health in the eyes of both search engines and visitors.
Analyze Your Text to Code Ratio Today!
Discover the optimal text to HTML ratio for better performance and SEO with our tool.
Conclusion
The text to HTML ratio, while a useful metric, is just one aspect of creating a high-quality, user-friendly website. It offers insights into the structure and content balance of a webpage, with higher ratios often indicating a content-centric approach. However, it’s essential to consider this in tandem with other critical factors, such as the Google Web Core Vitals, which provide a more holistic view of user experience. In optimizing websites, the ultimate goal should always be to deliver value to users, whether through streamlined coding, engaging content, or fast, responsive design. Balancing these elements effectively will ensure both optimal user satisfaction and search engine performance.