What Does the “HTTPS Page Has Internal Links to HTTP” Mean?
The “HTTPS page has internal links to HTTP” error in a site audit indicates that there are links within your website that point to unsecured URLs instead of secured ones. This is problematic for several reasons:
Security Risks
HTTPS is a secure protocol that encrypts the data transmitted between the user’s browser and the server. HTTP, on the other hand, is not encrypted, which can expose the data to interception and tampering. Linking to unsecured URLs from an encrypted page can potentially expose users to security risks, such as man-in-the-middle attacks.
Mixed Content Warnings
When a secure page links to or includes HTTP resources (like images, scripts, or stylesheets), browsers may display mixed content warnings. This can undermine user trust and lead to a poor user experience.
SEO Impact
Search engines prefer secure sites and might penalize sites that have mixed content issues. This can negatively affect your site’s search engine rankings.
User Experience
Modern browsers may block or flag non-secure content on a secure page, which can cause parts of the page to not load correctly, leading to a disrupted user experience.
How to Check the Issue
Using any browser is enough to check the issue. Open the source code of the flawed page. To do this, click the right mouse button at any spot of the page and choose “browse the code” option, or apply an online tool https://codebeautify.org/source-code-viewer.
Find a tag <a href=”http://site.com”>. The presence of the http protocol in a href attribute specifies that there is an issue.
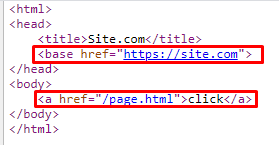
If there is an issue notification, and your site applies a relative URL, find a <base> tag in the website’s code and check its value in the href attribute. The presence of the http protocol in a href attribute specifies that there is an issue. Here is an example:
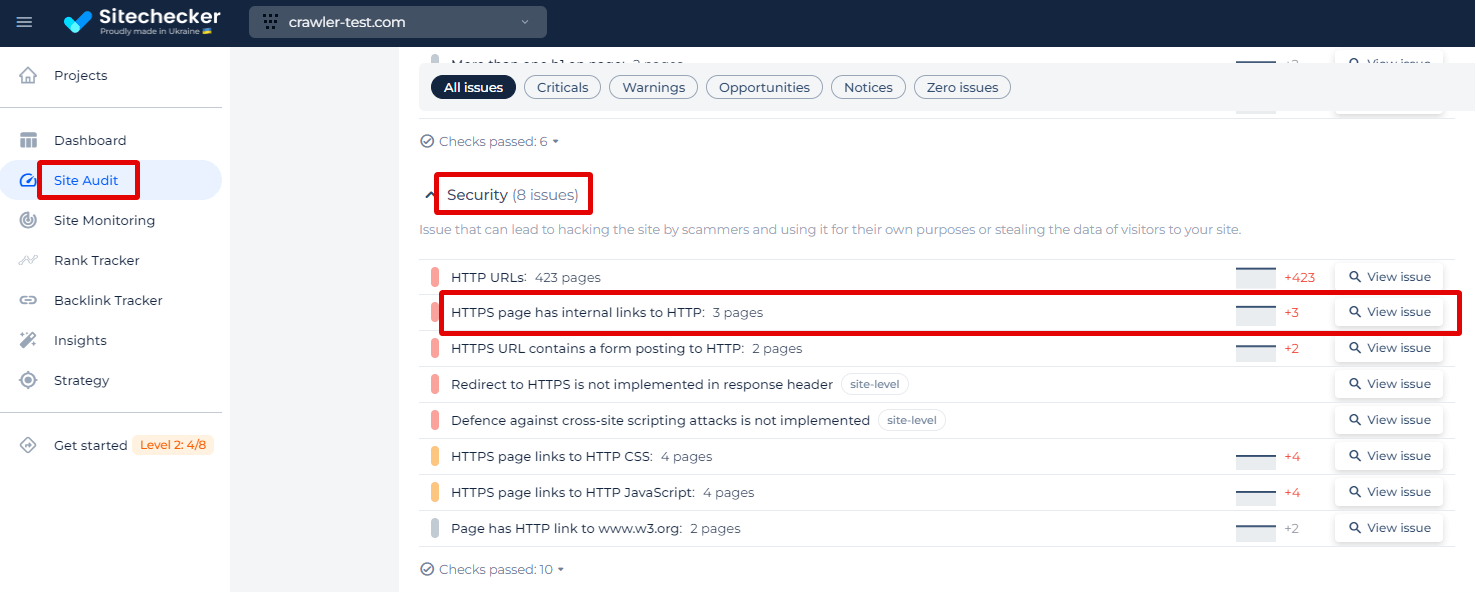
Here is a screenshot instruction on how to check this issue with Sitechecker. It focuses on the “Security” category of site issues, particularly identifying the problem where an “HTTPS page has internal links to HTTP page.”
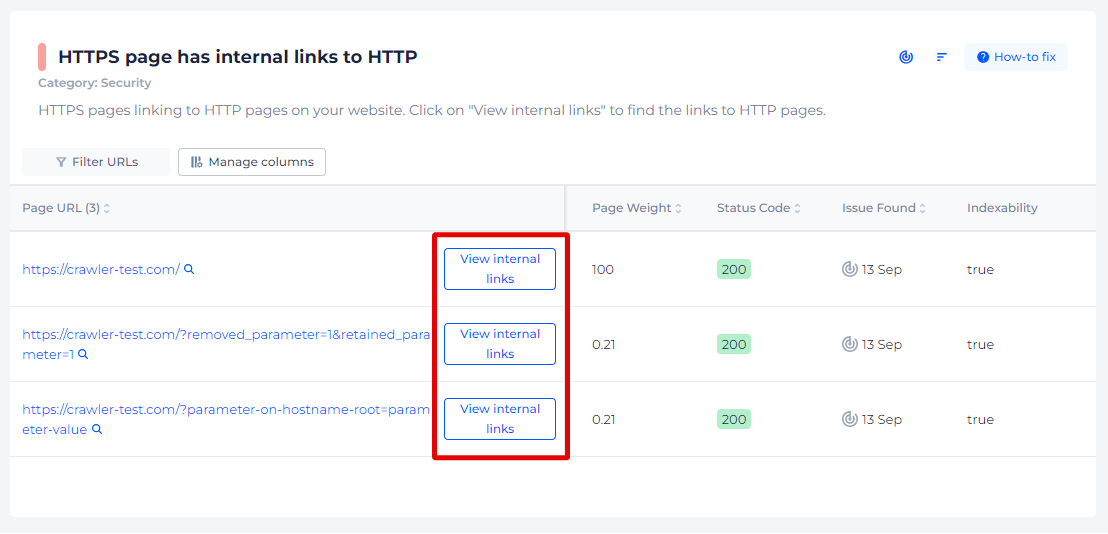
By simply clicking on “View issue,” the tool provides a straightforward list of all the HTTPS pages on your site that contain internal links leading to HTTP pages. Additionally. you will have capability to view all internal links on every page from the list.
Upgrade to Full HTTPS Security!
Discover all HTTP links on your HTTPS pages and fortify your site's defenses with Sitechecker.
How to Fix This Issue
Fixing the “HTTPS page has internal links to HTTP” issue involves several steps to ensure that all internal links on your website point to encrypted URLs. Here’s a detailed guide on how to do this:
1. Update Internal Links in HTML Code
Go through your HTML files and manually change all internal links from HTTP to HTTPS. Use a text editor with a search and replace function to find all instances of http:// and replace them with https://.
2. Check and Update CMS Settings
In your Content Management System (CMS), ensure that the site URL is set to secure protocol. If your CMS generates links automatically, check the settings to make sure it is configured to use HTTPS.
3. Database Update
If your website content is stored in a database (common with CMS platforms like WordPress), you can use a plugin or a script to search and replace unsecured URLs with encrypted protocols in the database. Always backup your database before performing any search and replace operations.
4. Update Configurations and Scripts
Update any configuration files that contain URLs, such as .htaccess, nginx.conf, or configuration files for frameworks.
Ensure that all URLs in your JavaScript and CSS files are using HTTPS.
5. Set Up Redirects
Configure your server to redirect HTTP requests to HTTPS. This can be done via .htaccess for Apache, nginx.conf for Nginx, or other server configurations.
Apache Example:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} off
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://%{HTTP_HOST}%{REQUEST_URI} [L,R=301]
Nginx Example:
server {
listen 80;
server_name yourdomain.com;
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
6. Use Protocol-Relative URLs
In some cases, you can use protocol-relative URLs (starting with //) so that the browser will use the same protocol as the current page. However, using absolute HTTPS URLs is generally better for clarity and security.
7. Check Third-Party Content
Ensure that any third-party resources (like images, scripts, and stylesheets) you include are available over secure protocol and update their URLs accordingly.
8. Run a Site Audit
Use Sitechecker to scan your website and identify any remaining HTTP links. Review the audit report and fix any remaining issues.
9. Regular Maintenance
Perform regular checks to ensure that new content or updates do not introduce HTTP links. The tool can be scheduled to run periodically to catch these issues early.